Shape definition for kids
Shapes – Definition with Examples
What are Shapes?
In geometry, a shape can be defined as the form of an object or its outline, outer boundary or outer surface.
Everything we see in the world around us has a shape. We can find different basic shapes such as the two-dimensional square, rectangle, and oval or the three-dimensional rectangular prism, cylinder, and sphere in the objects we see around us. These geometric shapes appear in objects we see as credit cards, bills and coins, finger rings, photo frames, dart boards, huts, windows, magician’s wands, tall buildings, flower pots, toy trains, and balloons.
Different Types of Shapes
Shapes can be classified into open and closed shapes.
| In geometry, an open shape can be defined as a shape or figure whose line segments and/or curves do not meet. They do not start and end at the same point. | In geometry, a closed shape can be defined as an enclosed shape or figure whose line segments and/or curves are connected or meet. |
Closed geometric shapes can further be put into two broad categories, namely two-dimensional and three-dimensional shapes.
| The 2-Dimensional shape is flat. | A 3-Dimensional Shape is a solid shape. |
| It has two dimensions, that is, length and width. | It has two dimensions, that is, length, width, and depth. |
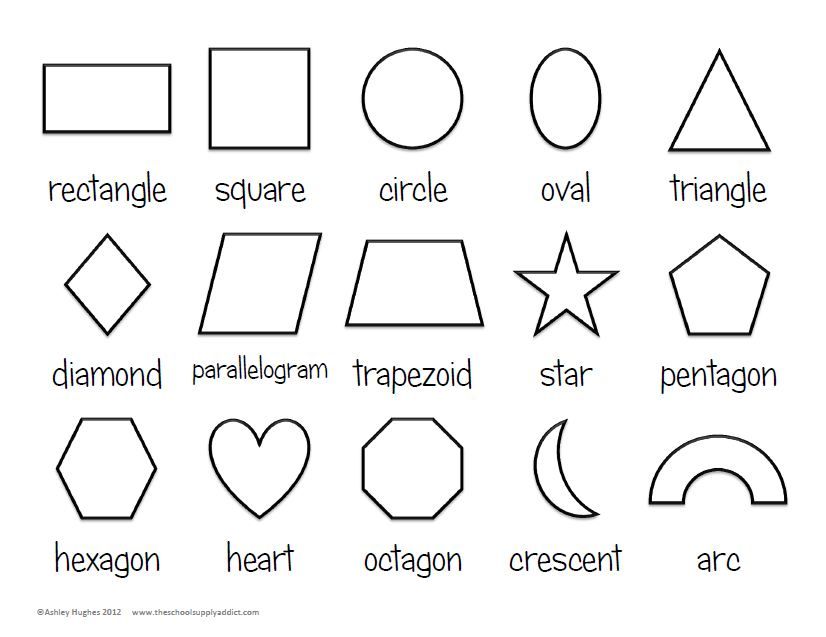
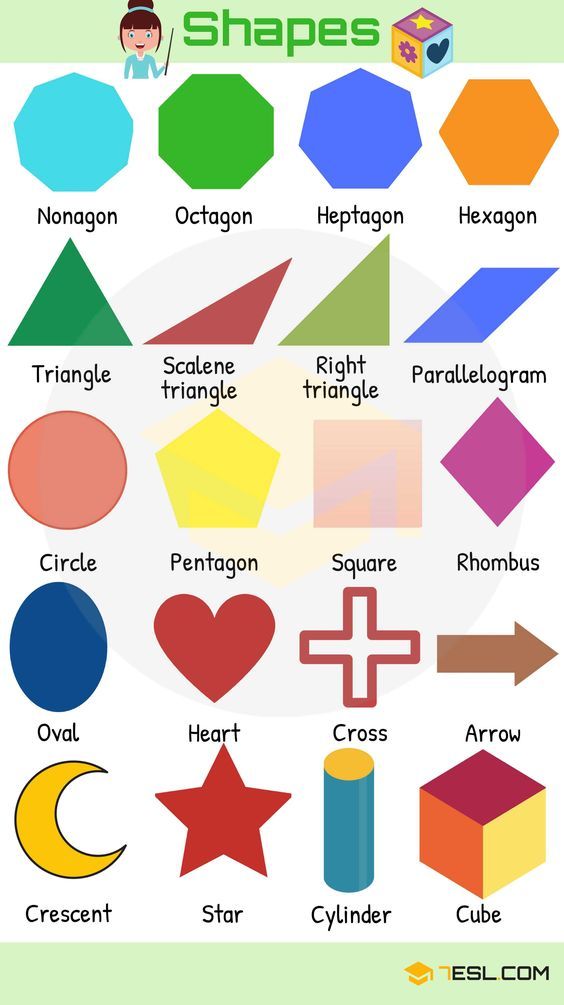
Here’s a list of 2-D or two-dimensional shapes with their names and pictures:
| Two-Dimensional Geometric Shapes |
Here’s a list of 3-D or three-dimensional shapes with their names and pictures:
| Three-Dimensional Geometric Shapes |
The color, overall size, and orientation called the non-defining attributes of a two-dimensional or three-dimensional shape do not define or affect the shape in any way. These attributes can change without any effect on the shape.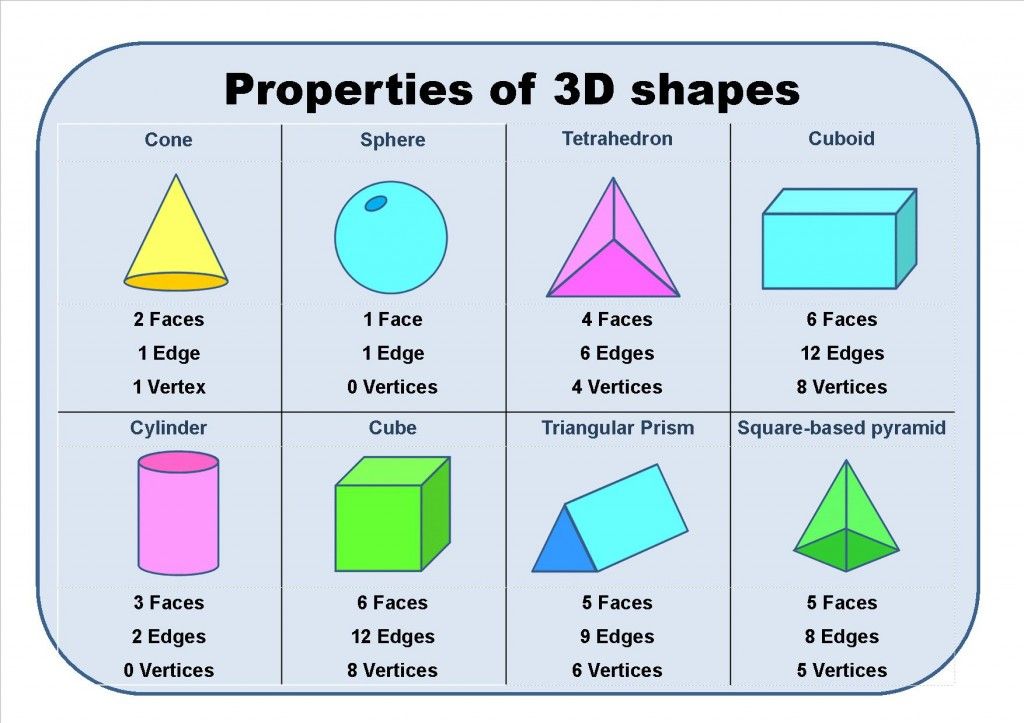
On the other hand, defining attributes such as the number of sides (parallel or non-parallel, straight or curved), vertices, edges, and faces of a shape, whether the shape is open or closed, and the angle measures determine the shape of a two-dimensional or three-dimensional object. Any change in these defining attributes will change the shape.
Solved Examples on Shapes
Example 1: Name the shapes.
- A polygon with 6 sides.
- Outline of a door.
- When you fold square corner to corner.
- A square and a triangle on top of it.
Solution:
- Hexagon
- Rectangle or quadrilateral
- Triangle
- Pentagon
Example 2: Classify the given letters as open shape or closed shape.
C, D, L, M, O, S, U, V, Z
Solution:
Open shape: C, L, M, S, U, V, Z
Closed shape: D, O
Example 3: Identify the solid shape of given objects.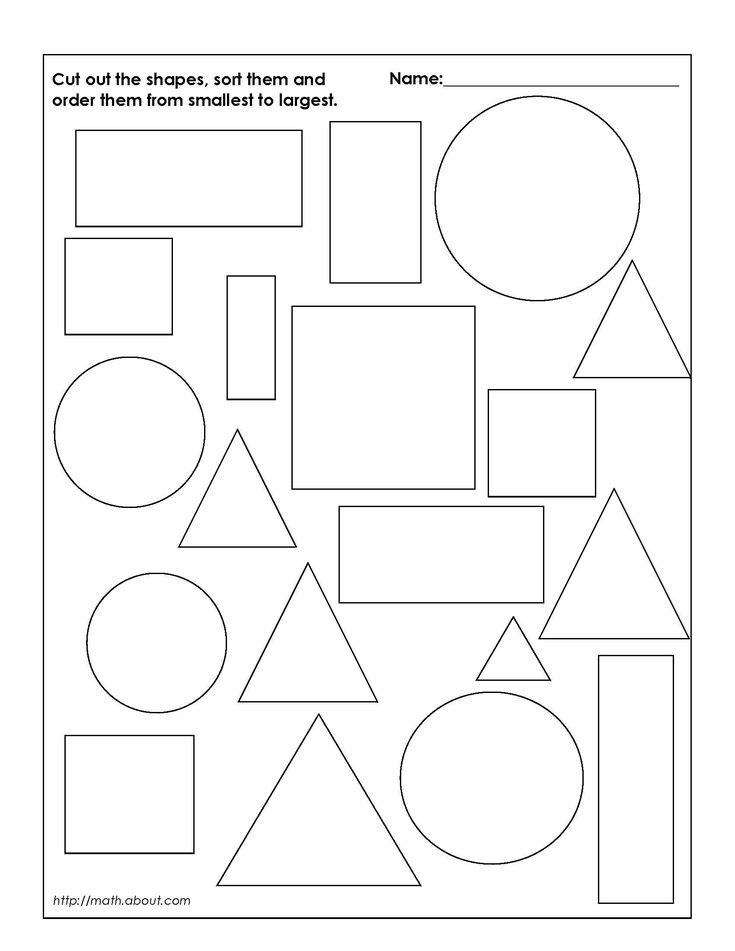
- Globe
- Book
- Cold drink can
- Dice
Solution:
- Sphere
- Cuboid
- Cylinder
- Cube
Example 4: Why is the crescent-shaped moon not a polygon?
Solution:
Crescent shape moon is not a polygon as it has curved lines.
Practice Problems
1
What is 8-sided polygon known as?
hexagon
heptagon
octagon
quadrilateral
Correct answer is: octagon
A polygon with 8 sides is known as octagon.
2
How many dimensions does a solid shape have?
1
2
3
depends on the shape
Correct answer is: 3
All solid shapes are 3-dimensional shapes.
3
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
closed shapes can have only straight sides.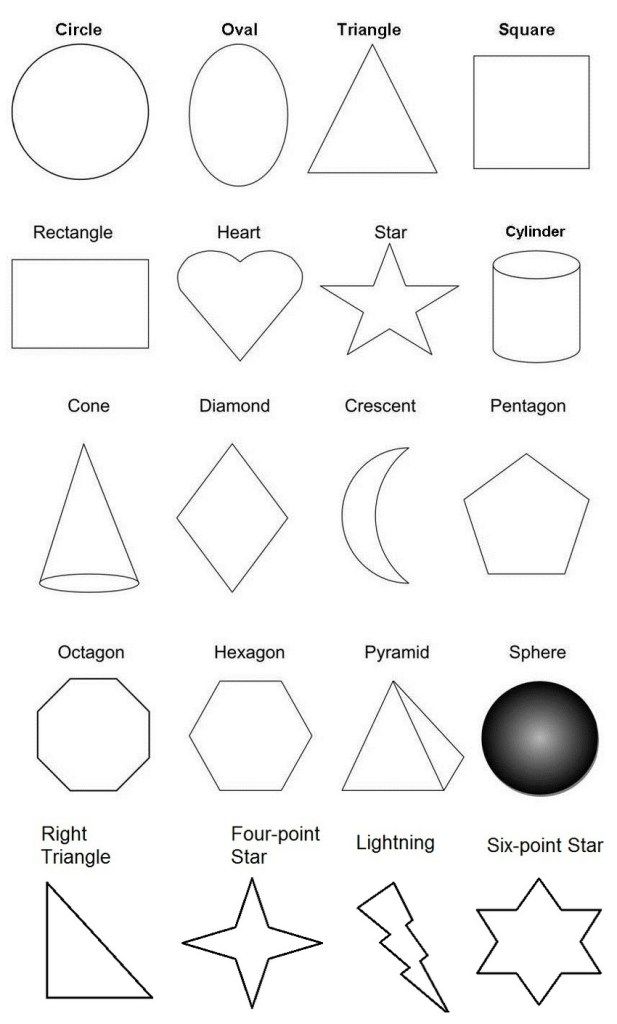
closed shapes have definite area.
start and end point of a closed shape are the same.
start and end point of a open shape are the different.
Correct answer is: closed shapes can have only straight sides.
Closed shapes are shapes whose start and end points are the same. It is not necessary that it is formed by only straight sides.
Geometric shapes for Kids with Definition, Cute Illustrations!
Are you trying to teach geometric shapes for your kids? But you are not sure about what are the 16 basic shapes in mathematics? and How do you help your kids to identify geometric shapes easily?
Here you will find our list of different Geometric Shapes in Math Printable Worksheet with really cute characters, definitions, and suggested activities for your kids, or students to learn it with excitement.
There is an image of each shape, as well as the attributes of that shape.
Using these sheets will help your children, students:
- Know the properties of different shapes;
- Know the inner angles of an equilateral polygon;
- Identify list of 2d geometric shapes, including triangles, quadrilaterals and polygons
List of Geometric Shapes – Triangles for Students
- Equilateral Triangle – Irregular Triangle
- Square – Irregular Quadrilateral
- Pentagon – Irregular Pentagon
- Equilateral Triangle
- Angle: 60°
- Interior angles add up to 180°
Square
- Angle: 90°
- Interior angles add up to 360°
Pentagon
- Angle: 108°
- Interior angles add up to 540°
| >>> Try Geometric Shapes Learning Games for Kids
Equilateral Triangle
- Angle: 60°
- Interior angles add up to 180°
Square
- Angle: 90°
- Interior angles add up to 360°
Pentagon
- Angle: 108°
- Interior angles add up to 540°
| >>> Try for free: Shapes Matching Puzzles games for Toddlers
Hexagon
- Angle: 120°
- Interior angles add up to 720°
Heptagon
- Angle: 128.
 6°
6° - Interior angles add up to 900°
Octagon
- Angle: 135°
- Interior angles add up to 1080°
| >>> Try our Cool Math Games for Kids
List of Geometric Shapes – Quadrilaterals
List of Geometric Shapes – Quadrilaterals in Mathematics for students to learn. A quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides. A quadrilateral is sometimes referred to as a quadrilateral or a quadrilateral. There are quite a few members of the quadrilateral family.
There are also some members that are subset of other family members! See below if this confuses you!
Squares have 4 equal sides and 4 right angles.
They have 4 lines of symmetry. All squares belong to the rectangle family. All squares belong to the rhombus family. All squares are also parallelograms.
Rectangles have 4 sides and 4 right angles.
They all have 2 lines of symmetry (4 lines if they are also a square!) All rectangles belong to the parallelogram family.
Rhombuses (rhombii) have 4 equal sides.
Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. They all have 2 lines of symmetry (4 lines if they are a square!). All rhombuses belong to the parallelogram family.
Parallelograms have 2 pairs of parallel sides.
Some parallelograms have lines of symmetry (depending on whether they are also squares, rectangles or rhombuses), but most do not.
Trapezoids US (Trapeziums UK) have one pair of parallel sides.
Some trapezoids have a line of symmetry. Please note the differences between the definitions for US and UK.
Kites have 2 pairs of equal sides which are adjacent to each other.
Convex and Concave Polygons – geometric shapes for kids
Polygons can be concave or convex in their shape.
Convex shapes have all angles less than 180°. Concave shapes have at least one reflex angle greater than 180°
Triangles are always convex.
we learn flat and three-dimensional geometric shapes
Masaru Ibuka in his book “After three it's too late” claims that in the first three years of life a child has the highest potential for learning and development, so inaction is akin to a crime.
Of course, we may feel that the child is too small. And what can he learn if he cannot even speak? But the brain of a child, like a sponge, absorbs all the information around it. And it depends on the parents what the child will learn at this age.
Is it worth it to start learning geometric shapes at such an early age? Undoubtedly. The child lives in an environment of geometric shapes. The knowledge you give should not be divorced from your daily life. Mom is the guide of the baby in this world, and it is absolutely not necessary for her to have a degree in order to tell the child how the world works.
Why should a child learn geometric shapes?
The first three years of a child's life is a period of development of brain cells, when a solid foundation for new achievements is formed. Already at 3-4 months, the baby is able to distinguish forms. This does not mean that the time has come to memorize the names of geometric shapes, but when talking with a baby, a mother may try to use the phrases: “Here is our favorite round saucer”, “Let's see what's in a square box” and the like.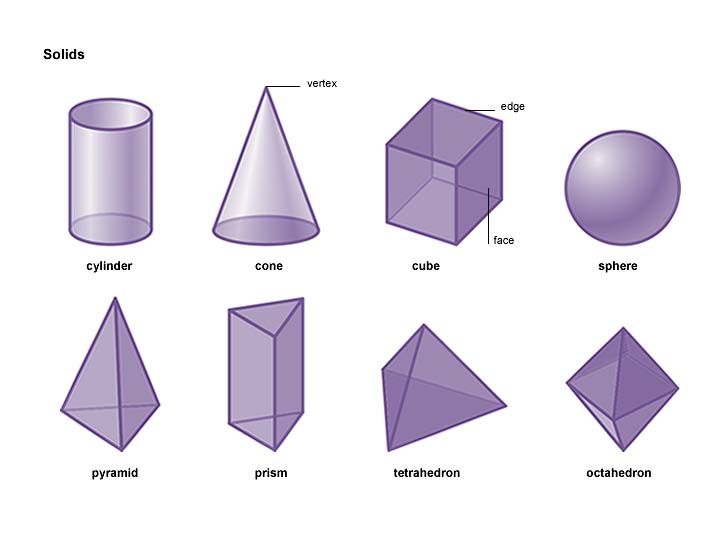
Knowledge of geometric shapes helps:
- develop spatial thinking, orientation in space;
- broaden one's horizons;
- develop the ability to compare, analyze, summarize and highlight the main thing, classify;
- to replenish vocabulary.
And, of course, the knowledge acquired by a preschooler will serve him as an excellent help in studying mathematics at school.
How to teach geometric shapes with a preschooler?
- Education for preschoolers should be built in the form of an exciting game.
- No need to scold the child if he did not remember the names of the figures from 1 time, even if from 31 - it's not worth it.
- Do not forget to organically weave geometric knowledge into life: “give a square box”, “take an apple from a round plate”.
- On the way to the garden, look for rectangular or round objects, compete to find and name the most.
- In the game arsenal you should have toys of the correct geometric shape - balls, cubes, designer parts.
- Usually kids like to help their mother in the kitchen. Get round, square, rectangular molds and bake edible geometric shapes.
- It is important to use tactile memory when studying figures. It will be much more interesting for a child not only to see, but also to feel, stroke, and maybe even lick the object of study.
- Load the child's brain in doses, gradually supplementing with information. For example, when studying shapes, repeat colors as well: “Look, what a blue oval it turned out to be.”
Basic Shape Memorization Techniques
There are many techniques and techniques that will make memorizing shapes interesting for children. The choice of methods will depend on the age and knowledge of the child.
- Before reaching the age of 1.5, we pronounce the surrounding objects aloud, supplying our story with information about the shape (let's take a round apple).
- At the age of 1.5 - 2 years, we use pictures, color the figures, use sorters to study the figures.
 We start with the simplest - the circle. We will connect the rest of the figures only after the child has learned the concept of "circle".
We start with the simplest - the circle. We will connect the rest of the figures only after the child has learned the concept of "circle". - From the age of 2 until reaching school age, we can apply all existing methods, following from simple to complex.
When studying geometric figures, it is important to proceed in stages. You should start with light shapes: circle, square, triangle, rhombus, rectangle, oval. Knowledge of these figures is available for children 2-3 years old.
Older children, 4-5 years old, include in their vocabulary and use the idea of a trapezoid, parallelogram, pentagon, hexagon, octagon, decagon and other polygons. They already know how to analyze, so they can easily compare and find differences between figures.
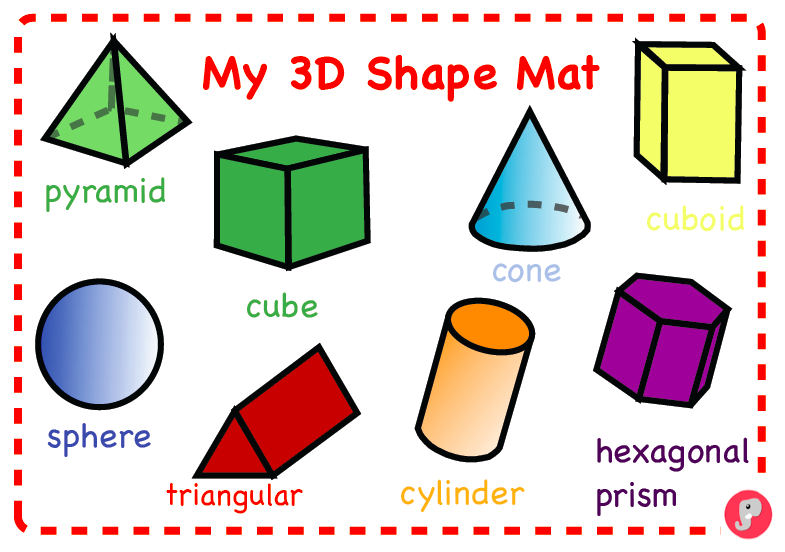
Senior preschool children get acquainted with three-dimensional figures: cylinder, pyramid, cube, ball, cone, prism.
Let's analyze some variants of techniques for studying geometric shapes:
1. Sorter - looking for a "house" for each shape. The child will not only remember the figures, but will also develop fine motor skills, coupled with thinking.
Sorter - looking for a "house" for each shape. The child will not only remember the figures, but will also develop fine motor skills, coupled with thinking.
2. Modeling . Sculpt geometric shapes with your baby - you simply can’t imagine a better activity for developing fine motor skills of hands and perseverance.
3. Three-dimensional stickers and magnets depicting geometric shapes can also help the child fix the names of the shapes in memory.
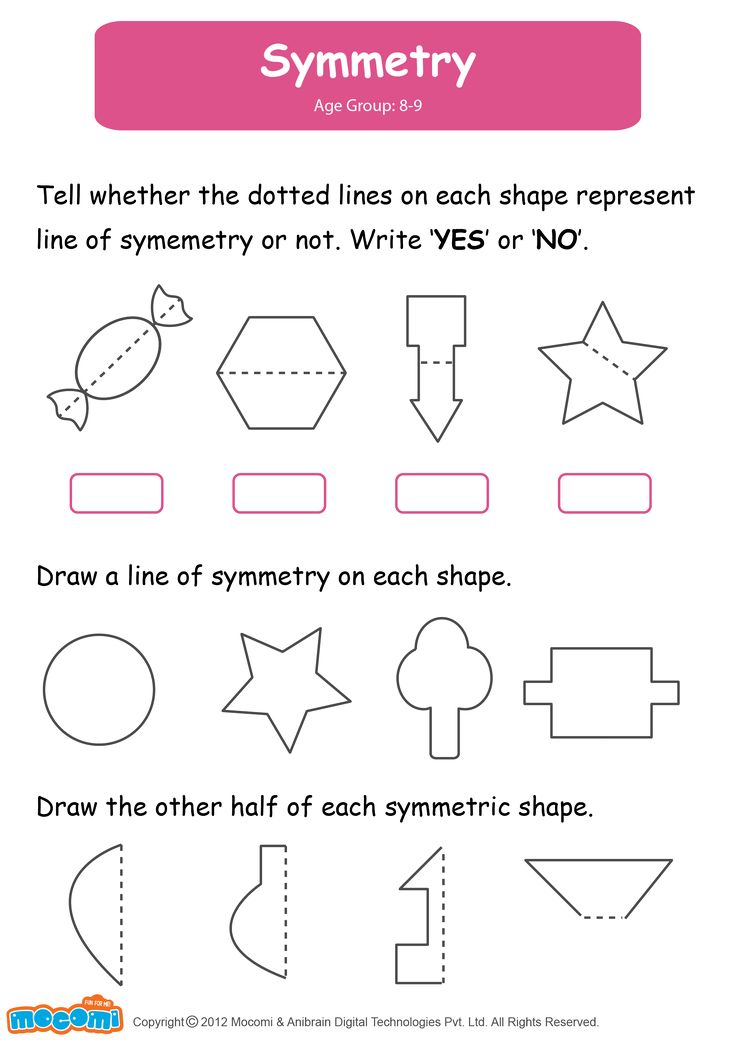
4. Looking for halves of . Cut the geometric shapes into two parts, mix and invite the baby to find the other half.
5. Applications . You can also make a geometric application from cut out figures. For example, a house (square + triangle), Christmas tree, car.
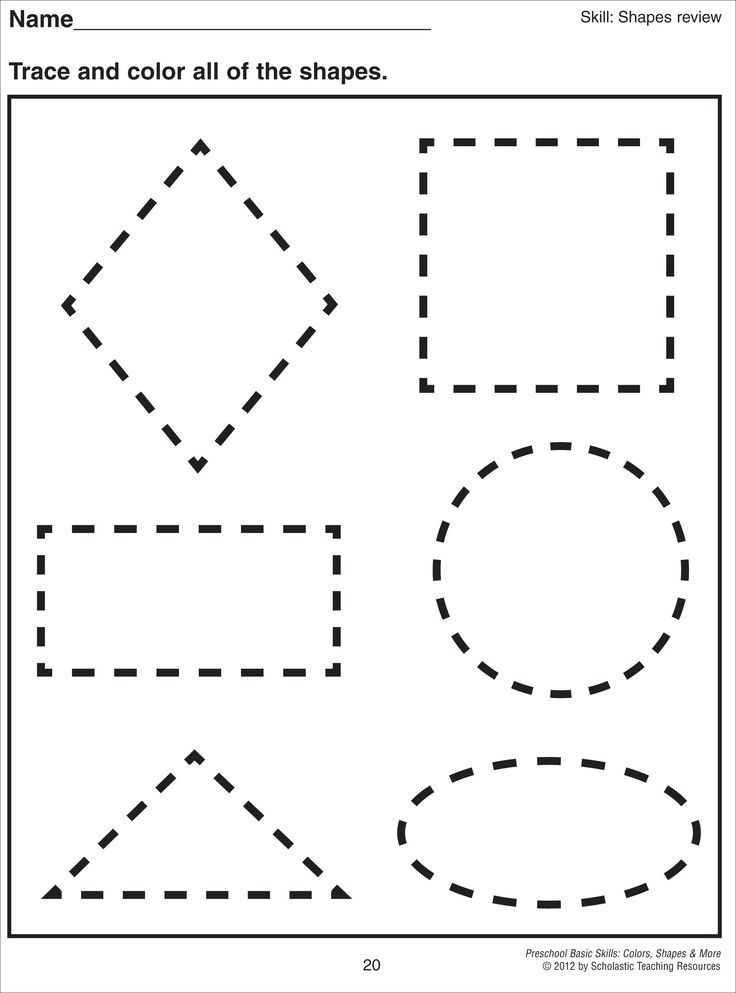
6. Outline dashed geometric shapes .
7. Color or shade the geometric shapes you suggested .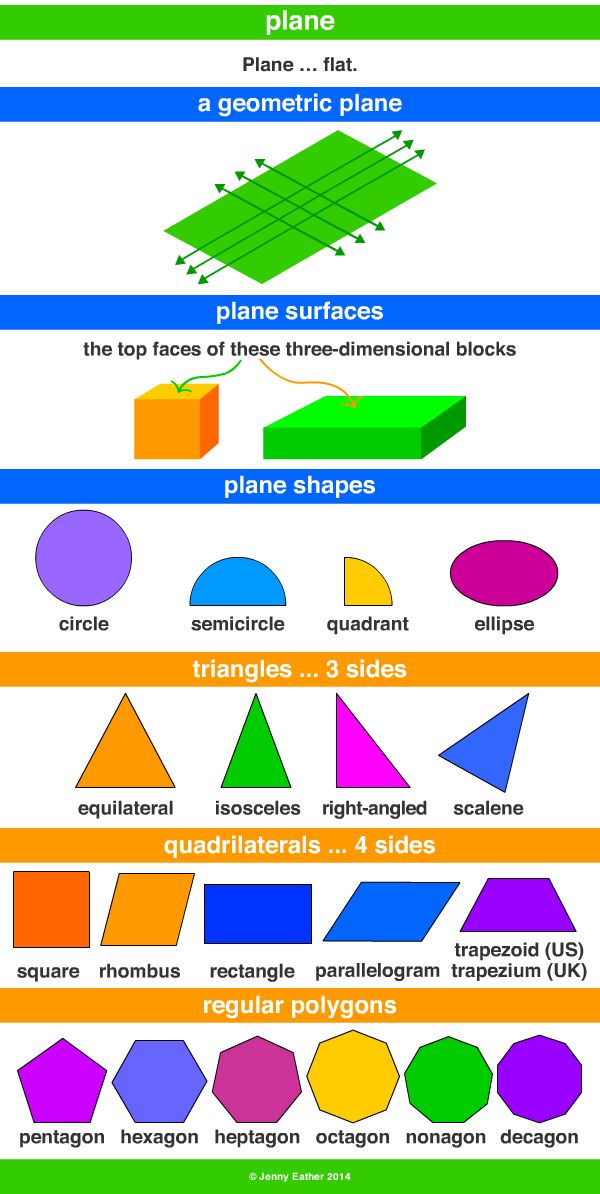
7. Finish the figure according to the sample.
8. Draw figures using stencils.
9. Listen to a fairy tale where the main characters are geometric figures, and then draw what you hear.
10. Put figures of different shapes into an opaque bag and suggest guessing the shape of the object by touch.
11. An excellent game for the development of memory and attentiveness. An adult prepares cut out figures of different colors and sizes and lays them out in front of the baby. They discuss colors, name the figures, and then the adult hides the figure. The task of the child is to find and name which figure is not.
12. Laying out geometric figures with counting sticks or matches. When the child masters this skill, you can move on to a more difficult level - solve puzzles. For example, remove one match to make a triangle.
13. Associations . Invite the child to name objects that a circle or rectangle looks like.
14. Laces and various insert frames , for example, Nikitin squares, where you need to recreate a square from several objects, or Segen boards, where you need to insert the missing part.
Laces and various insert frames , for example, Nikitin squares, where you need to recreate a square from several objects, or Segen boards, where you need to insert the missing part.
15. Outdoor games . For example, an oval, a triangle, a square, a rectangle are drawn on the asphalt. At the command of an adult, the child must find the named figure and stand in it.
16. Videos . There are a large number of cartoons and educational materials about geometric shapes. Watch the video with the baby and be sure to discuss what you see.
17. Find on the Internet and print out pictures that artists draw with geometric shapes, and invite your child to count how many circles, rectangles, etc. are there. objects (for example, ball = ball). And, of course, to involve the study of the subject through games:
- Finding a three-dimensional figure from a flat pattern is an excellent exercise for developing spatial thinking.
- "Sleuth". Children are given an “orientation” - a flat drawing of the desired figure from all sides. Children need to match the pictures and find the right shape.
- Create a 3D model yourself. An adult can print stencils from the Internet. It remains for the child to bend along the lines and glue to make a figure.
- Models, origami - you can try with your child to create your own voluminous paper toy.
- Constructor. Build a tower or a castle for the princess with the help of details. This game will contribute to the development of fine motor skills, imagination, understanding the properties of three-dimensional figures.
The study of geometric figures should not become torture for a child and an adult. Choose the method that's right for you. Show patience and ingenuity, and then the result will not be long in coming. Most importantly, do not forget to encourage the child for his new discoveries and repeat the knowledge gained from time to time.
Mathematics and logic for children 7-13 years old
We develop logical thinking through solving plot mathematical problems in an interactive game format
learn more
Determining the child's place of residence examination \ Acts, samples, forms, contracts \ ConsultantPlus
- Home
- Legal resources
- Collections
- Determination of the place of residence of the child examination
Compilation of the most important documents on request Determination of the place of residence of the child examination (legal acts, forms, articles, expert advice and much more).
- Family:
- Act on the survey of housing conditions
- Act of housing conditions
- Grandmother Law representative
- Grandmother is a member of the family
- Bankruptcy responsibility of minors
- Act on the survey of housing conditions
- Act of examination of housing conditions
- Alimony for minor children
- Grandmother UPROY
- more .
 ..
.. - 8 Judicial practice : determination trial access to the ConsultantPlus system free on 2 days
Open a document in your ConsultantPlus system:
Selection of court decisions for 2019: Article 65 "Exercise of parental rights" of the RF IC
(R.B. Kasenov) determining the place of residence of children. Resolving the stated requirements for determining the place of residence of children, the court, guided by the provisions of Article. 65 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, art. 6 of the UN Convention "On the Rights of the Child", took into account the conclusions of the guardianship authorities, the conclusions of the conclusions of the psychological and psychiatric examination, reasonably took into account the desire of the children to live with the plaintiff - the mother and considered it appropriate and in the interests of minors to determine their place of residence with their mother.
Articles, comments, answers to questions : determining the place of residence some aspects of the court determining the place of residence of the child when the parents live apart
(Rudman D. S.)
S.)
("Family and Housing Law", 2019, N 4) From the point of view of developmental psychology and pedagogy, if in the first years of his life the boy needs mainly mother, then from the age of seven "the polarization of the sexes passes." During this period, the boy begins to turn into a man, and in order to become one in the future, he "must know himself in the world of men." Of course, the presence of a father nearby and his positive example at this age is very important for the formation and development of the boy's qualities that will be useful to him in adulthood. So, in the case of determining the place of residence of a child (boy), a psychological and pedagogical examination was carried out. From the expert's conclusion, it followed that the age-related features of the child's development require an example of male behavior for the further development of the personality. Based on this and other circumstances established in the case, the court decided to determine the place of residence of the minor with his father. On the contrary, girls between the ages of seven and twelve "discuss fashion, housekeeping, get closer to their mother."
On the contrary, girls between the ages of seven and twelve "discuss fashion, housekeeping, get closer to their mother." Register and get trial access to the ConsultantPlus system for free on 2 days
Open a document in your ConsultantPlus system:
Article: Parental rights to determine the place of residence of the child and the order of communication with him 9:02 (Zykov S.V.)
("Actual Problems of Russian Law", 2022, N 3) An unsolvable problem for our law enforcement is the alienated parent syndrome (PAS). So, in one of the cases in which the guardianship authorities revealed only a negative attitude towards the father (“because the father scandalizes, does not work, does not take care of them”), an independent examination found “psychological induction” as the reason for such an attitude on the part of one of the children from other family members. The court, agreeing with the examination, nevertheless substantiated the determination of the place of residence of children with their mother not only by the above age criterion and the absence of exceptional circumstances for separation from her, but also by the "desire" of the children themselves.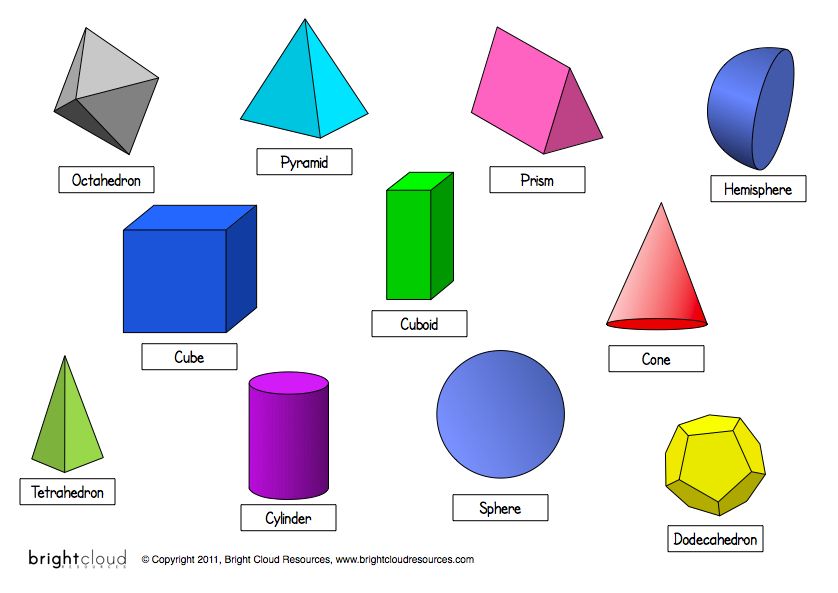
Regulations : Determining the place of residence of a child examination"Review of the practice of interstate bodies for the protection of human rights and fundamental freedoms N 8 (2021)"
(prepared by the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation) As seen from the decision, the authorities also referred to the opinion of a psychologist L. However, the Court noted, the domestic courts did not rely on this conclusion in their decisions. In any case, this opinion was prepared on the basis of a single consultation held before the separation of the parents. This consultation dealt more with problems in the marital relationship between the first applicant and M., rather than with their relationship with X. The Court was not convinced that it could replace an expert examination on the specific issue of the child’s place of residence and, therefore, on determining the degree of X.'s attachment to each of the parents and their parental competence (paragraph 110 of the resolution).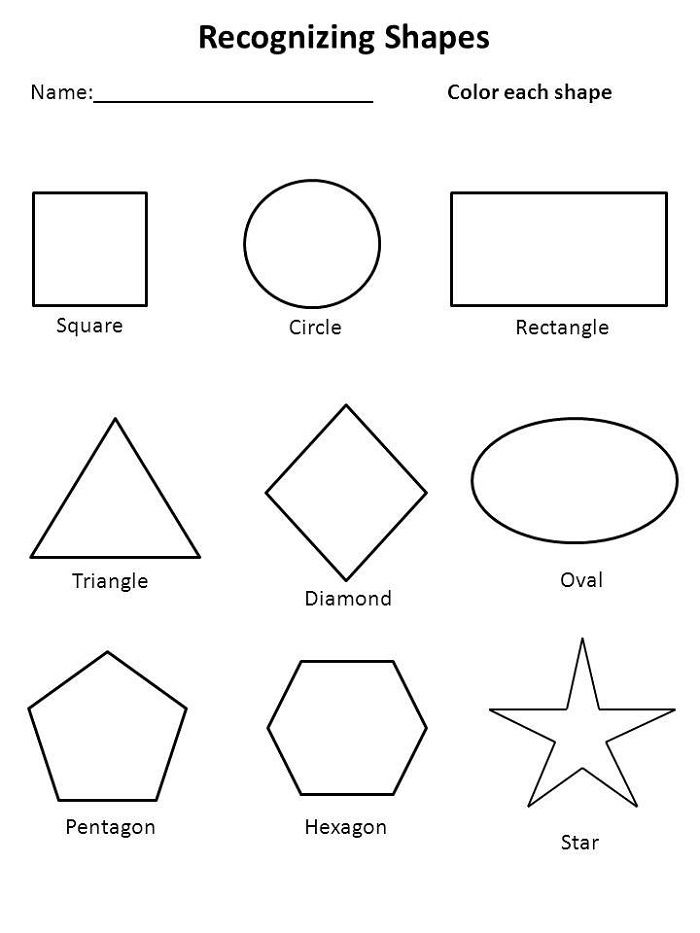
Learn more