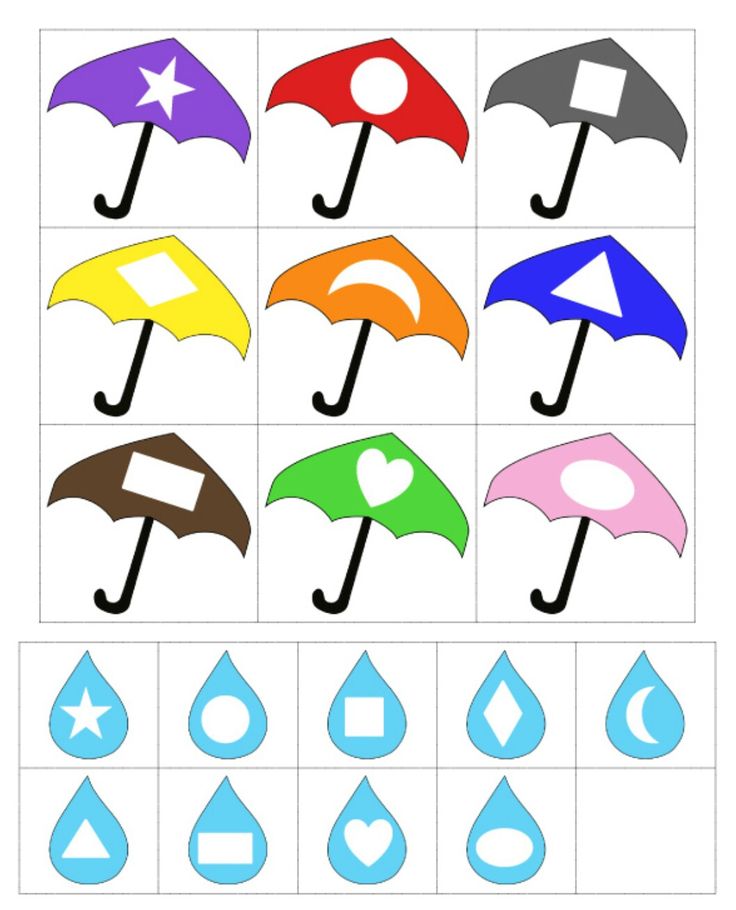
Shape theme preschool
40 Easy And Fun Hands-On Shape Activities For Preschoolers
One of the first math concepts that preschoolers learn is identifying shapes. They begin to distinguish among the different shapes and categorize items according to shape. They learn the names of shapes and their characteristics. They find shapes in everyday items. This collection of shape activities for preschoolers can lead preschoolers to explore shapes in all kinds of ways.
Shapes Activities for Preschoolers
These activities will help your preschoolers learn their shapes. These shape activities for toddlers, will work in your preschool classroom and your kindergarten classroom.
1. Road Shapes with Cars (Pre-K Pages) – 22 printable road shape mats to help your litte learners identify shapes.
2. Making Shapes with Play Dough (Pre-K Pages) – A fun, hands-on playful learning experience that uses play dough to teach shapes!
3. Pattern Block Shapes (Pre-K Pages) – Pattern blocks can actually help your little learners build a strong foundation for learning geometry later.
4. Making Shapes with Geoboards (Pre-K Pages) – If you haven’t tried geoboard activities in your classroom yet, your kids are going to love them!
5. Create a Shapes Photo Book (Pre-K Pages) – To introduce shape concepts to my son, I grabbed the book So Many Circles, So Many Squares from our library as the anchor to our learning ship. Using this book, we went on a shape scavenger hunt and made a fun shape keepsake.
6. Perfect Square Shapes Art (Pre-K Pages) – This Perfect Square art activity is so easy to set up and totally open-ended. It goes perfectly with the book and would be an excellent addition to a shapes unit.
7. Building Shapes with Craft Sticks (Pre-K Pages) – Pair this activity with the book Shapes, Shapes, Shapes by Tana Hoban and you’ve got the perfect low-prep shapes lesson!
8. Teaching 3D Shapes (Pre-K Pages) – Here are some of my favorite ideas for teaching 3D shapes to young children in pre-k or kindergarten. I also wrote some very simple 3D shape songs for you that incorporate hands on learning; keep reading to download the 3D shapes printable song charts.
I also wrote some very simple 3D shape songs for you that incorporate hands on learning; keep reading to download the 3D shapes printable song charts.
9. Nature Shape Scavenger Hunt (Pre-K Pages) – A Star in My Orange is a great way to reinforce shape recognition with your preschoolers. They will also immediately want to run outside for their very own shapes scavenger hunt in nature!
10. The Shape of Things Chalk Drawings (Pre-K Pages) – Shapes are found, identified, and drawn in all preschool classrooms! Discovering just how often circles, squares, and triangles occur in our everyday life make them relevant to children.
11. Shape Wands (Pre-K Pages) – Make some shape wands and turn your home or classroom into the perfect place for kids to learn and identify shapes.
12. Shape Exploration (Pre-K Pages) – After reading the wonderful book Mouse Shapes by Ellen Walsh, I thought it would be fun to make a mouse that could be used in a shape game. The mice in the book explore shapes so, why shouldn’t we?
The mice in the book explore shapes so, why shouldn’t we?
13. Make a Tortilla Shape Snack (Pre-K Pages) – We have the perfect recipe for exploring a math concept. Read aloud one great children’s book. Make a healthy and yummy treat. Combine the two together and you have a lesson on shapes.
14. Shapes Word Chart (Pre-K Pages) – This word chart focused on shapes but you can make a word chart for any topic.
15. “I Have Who Has” Shapes Game (Prekinders) – You may have seen the “I Have, Who Has” card games circulating the internet a lot lately, so this is a fun twist for Pre-K to teach shapes.
16. Games and Activities for Teaching Shapes (Prekinders) – Here are a fun few ways to teaching shapes, like shape bingo and a memory game.
17. Tracing Shapes on the Flannel Board (Teach Preschool) – A wonderful way to introduce letters and shapes while building pre-writing skills!
18. Hunting for Shapes (Teach Preschool) -Explore shapes with a fun and interactive game!
19. Exploring Shapes with Blocks on a Table Top (Teach Preschool) – A simple and engaging exploration of shapes and colors!
Exploring Shapes with Blocks on a Table Top (Teach Preschool) – A simple and engaging exploration of shapes and colors!
20. Learning Shapes by Rolling a Ball (Hands On As We Grow) – Try a fun hands on activity for toddlers for a creative twist to learn shapes!
21. Finding Shapes at the Playground (Buggy and Buddy)- Just print out the free shape hunt printable and go searching for shapes at the playground with this fun geometry activity for children!
22. Geometric Shapes Math Activity (Little Bins for Little Hands) – This simple geometric shapes activity for kids is easy to do at home or as a math center in school. It also makes a terrific STEAM project including a bit of art and design too.
23. Gruffalo Themed Shape Animals (Educators’ Spin on It) – Exploring shapes with young children can be such fun when you involve a few animal friends from The Gruffalo.
Shapes Activities for Preschoolers
24. Feed the Shape Monster Game (Imagination Tree) – Make a fun activity for preschoolers and school aged kids with this feed the hungry shape monsters sorting game!
25. Sticky Shape Bugs Activity (Mom Inspired Life) – This was a great way to develop fine motor skills and critical thinking skills while learning about shapes.
Sticky Shape Bugs Activity (Mom Inspired Life) – This was a great way to develop fine motor skills and critical thinking skills while learning about shapes.
26. Learning Shapes with Spaghetti Noodles (Teaching Mama) – Looking for a fun way to teach shapes? Well here’s a very fun way using spaghetti noodles! This hands-on activity also is a great sensory activity.
27. Matching Shapes to Outlines (Busy Toddler) – Create this fun easy DIY shape mat to practice shapes with your preschoolers.
28. Chalk Shapes Jumping Game (Craftulate) – All you need for this shape activity is some sidewalk chalk!
29. Open and Closed Polygons Game (JDaniel4’s Mom) Grab some LEGOs and have fun with these polygon games, like hockey!
30. Shape Sensory Squish Bag (Still Playing School) – Create this sensory squish bag with triangles, circles, and squares. It’s irresistible to touch and talk about in the window or on the table. It’s super easy to make, too!
31. DIY Shape Puzzles (Munchkins and Moms) – If you have some Jenga blocks and markers, then this easy DIY shape puzzle will be a fun engaging activity for your preschoolers.
32. Stamping Shapes in Kinetic Sand (Still Playing School) – Stamping shapes into kinetic sand is a great opportunity to work on shape identification, count the sides and corners, and compare and contrast the shapes.
33. Making Trucks from Shapes (Powerful Mothering) – Using your wooden blocks to draw and create trucks!
34. DIY Waldorf Square (Rhythms of Play) – An easy DIY toy for kids made with wooden blocks and liquid watercolor paints.
35. Magazine Shape Hunt and Sort (Mom Inspired Life) – This magazine shape hunt is jam-packed with learning! Kids will learn shapes while they practice cutting, gluing and sorting. It’s also an awesome way to work on critical thinking and observation skills.
36. Building Rockets with Shapes (Stir the Wonder) – Building rockets with shapes is a fun way to review shapes and colors with toddlers and preschoolers!
37. Build on Shape Outlines (Brick by Brick) – Use wooden blocks in a new fun way and work on shapes at the same time!
38. Shapes in Our Neighborhood Book (Munchkins and Moms) – Go for a walk and look for shapes in the neighborhood and then create a photo book after!
Shapes in Our Neighborhood Book (Munchkins and Moms) – Go for a walk and look for shapes in the neighborhood and then create a photo book after!
39. Sorting Shapes in the Sensory Bin (Learning 4 Kids) – Your preschoolers will practice their shapes and fine motor skills while having fun with this shape sensory bin.
40. I Spy Shape Hunt (Munchkins and Moms) – Create these fun easy spy glasses and go on a shape hunt!
Follow my Shapes Pinterest Board for more great ideas!
2D Shape Activities for Preschool, Pre-K, and Kindergarten
Learning about 2D shapes is a must for every early childhood classroom. I’m here to share with you my favorite, go-to 2D shapes activities! Some teachers may do a shapes theme or unit (like me), some may do a shape of the week, and some sprinkle in shape activities all year long. These activities will work for all types of classrooms and teaching styles! Grab your lesson plan binder, and let’s get started! Want all shape printables now? You can find them in my Shapes Unit on TPT HERE.
This post contains affiliate links.
Shape Manipulatives
When setting up a shape activity, the first thing I do is go into my supply closet and pull out all my shape games, manipulatives, and puzzles. Pattern blocks, shape cookies, and shape magnet blocks are distributed into various classroom centers. Students need to be playing, manipulating and creating with shapes all over the classroom, not just in the math center!
I love this 2D & 3D shape building set! It’s a ton of fun and comes with shape cards.
Toothpick Shapes
Toothpick Shapes are a fun and interactive way to learn shapes! Students can make shapes with toothpicks and play dough or marshmallows. When teaching your little learners about shapes, it’s important to teach about the sides and vertices too. Use those big vocabulary words! Feel, touch and count the number of sides and vertices a shape has. Don’t forget that a circle doesn’t have any sides or vertices!
In the Discovery Center: Learning about math and science
In the discovery center, I set up a shapes exploration table. The wall has shape posters with real photographs, the back of the table is lined with shape building cards and manipulatives and translucent shapes. There is a sorting board with shape flashcards on top. It’s just a poster board I made with tape. Super simple! The basket is filled with real objects and shape cards students can sort. This exploration table gives students the opportunity to talk about, touch, feel, build, and manipulate shapes with a peer or independently.
The wall has shape posters with real photographs, the back of the table is lined with shape building cards and manipulatives and translucent shapes. There is a sorting board with shape flashcards on top. It’s just a poster board I made with tape. Super simple! The basket is filled with real objects and shape cards students can sort. This exploration table gives students the opportunity to talk about, touch, feel, build, and manipulate shapes with a peer or independently.
Shape Building Blocks Cards! This is a close up of the building block shape cards. Students use the blocks to create the shape on the card. After the shape theme is over, put the shape building cards in with your manipulatives or STEM drawers!
Geoboard shape cards! I put these shape geoboard cards in my geoboard basket. Students can make the shapes with loom bands on the geoboard. To introduce this activity, I put it out for table time as an arrival activity. It’s also great to build those little fine motor muscles too!
Shape cover up! Cover up is a fun game to practice matching shape! Students spin the spinner and cover the matching shape. I love these translucent spinners for my math games. This game is in my Shapes pack. It comes in four different levels.
I love these translucent spinners for my math games. This game is in my Shapes pack. It comes in four different levels.
Shapes graph it! This is another fun shapes game that my students love. It’s also a great opportunity to talk about more, less and equal to. Try using magnet bingo chips to cover the graph then using a magnet wand at the end to make the game even more exciting.
In the Sensory Table
This shape sensory table is filled with shaped manipulatives and a few cupcake pans for sorting. It has foam shape beads, shape chains and translucent shapes. Perfect for sorting, lacing, and linking together. And you guessed it, it’s great for their fine motor, too!
Transition Activity
Shape sort! Transition activities are the perfect time to do a quick assessment or learning check. We have snack after music and movement time. I always plan a transition activity for that time for several reasons. The first is so the whole class isn’t lined up at the same time to wash their hands, which is just asking for crazy behaviors to occur. The second is because it’s another time I can squeeze in more learning! What I do is call on a student and give them a card to sort. It’s a quick and easy way for me to check and see if they know or don’t know a shape.
The second is because it’s another time I can squeeze in more learning! What I do is call on a student and give them a card to sort. It’s a quick and easy way for me to check and see if they know or don’t know a shape.
In the Library Center
Sand writing trays with shape flashcards! Students can write and draw shapes in the sand. This tray is from a lacing set but you can use any small tray you have. I know some teachers use foil pie plates or kid plastic divided dinner plates for writing trays.
Shape mini books! After we make a shape mini books together during small group or table time, I put them in the center. They LOVE making them! Staplers scare me a bit with my little learners so I put in this stapleless stapler! It’s amazing!
Shapes emergent reader! For a small group activity, students create their own shape emergent reader. After they are complete and we have read them a few times together, they are put in the library center for students to read.
In the Art Center
My students LOVE play dough trays so I try to make one for each theme we do. In this activity, they create play dough shape monsters. Students use the shape cookie cutters to create the body. Then add arms, legs, eyes and hair using cut up pipe cleaners, small popsicle sticks, toothpicks, and googly eyes. The tray is from the Dollar Tree.
Play dough shape mats! Students can create play dough shapes on these shape mats. They can make the shape by rolling play dough snakes or by molding the dough.
Shape Prints! It’s great fine motor and makes beautiful pieces of art for your classroom. We cut up paper towel tubes for this circle printing project.
We printed with wooden shape blocks too!
Shape collages! It’s important to provide activities for students to create new items using shapes. In fact, it’s a learning objective/standard in many states. Students need to be able to manipulate shapes to create new shapes, objects or pictures. Shape collages are the perfect activity to address this learning objective.
Shape collages are the perfect activity to address this learning objective.
Single shape collages! You can also have students create shape collages using just one kind of shape. One year my students were struggling with triangles so we created triangle shape collages. Students were finding triangle shapes, talking about triangles (how they are alike and different), and making pictures with triangles!
Dramatic Play
You can change the dramatic play center to so many different things for a shape theme but my favorite thing to do is a Pizza Restaurant. There are shapes all over a pizza restaurant. The pizzas can be different shapes and the slices too! Then the toppings are so many different shapes too. You should totally try it!
Make learning about shapes FUN by providing your students with hands-on learning experiences and play! Want all the 2D Shape printables in this post? Click HERE to grab my 2D Shapes unit from my TPT store. It’s packed with over 200 pages of shape building cards (legos, geoboards, popsicle sticks, toothpicks, play dough), posters, sorting mats, worksheets, games & MORE.
Learning about shapes is a fun theme and concept to do with little learners and you can check more fun shape activities by clicking on the image below!
Love these shape activities? Pin this image!
Variable forms of preschool education
Tsapenko M.M.
Candidate of Pedagogical Sciences, Deputy Head of the Department for the Development of the Content of General, Preschool and Special Education Department of Education of Moscow Candidate of Pedagogical Sciences, Moscow Department of Education, Southwestern District Department of Education
Chervova A.S. teacher - psychologist, Kindergarten No. 768 Moscow, Russia
VARIATIVE FORMS OF PRESCHOOL EDUCATION
Annotation: Along with state preschool educational institutions, there are various forms of preschool education called variable. As a rule, they exist on the basis of the preschool educational institution as its structural divisions. However, they may exist as an alternative. Thus, the main principle of the educational policy of Russia in the field of preschool education is that all children have the right to equal starting conditions before starting school.
Thus, the main principle of the educational policy of Russia in the field of preschool education is that all children have the right to equal starting conditions before starting school.
The main principle of Russia's educational policy in the field of preschool education is that all children have the right to equal starting conditions before starting school.
The system of kindergartens is designed both for the initial socialization of children, teaching them communication skills with peers, and for a mass, public solution to the problem of their parents' employment (for which the kindergarten's working hours in most cases coincide with the typical work schedule of most professions: from 7 up to 19hours five days a week). The kindergarten system also provides a minimum preparation of children for schooling - at the level of primary reading, writing and numeracy.
The following types of preschool educational institutions are traditionally typical for the Russian Federation:
1. Kindergarten of a general developmental type with a priority direction, for example: physical, intellectual, artistic and aesthetic education.
Kindergarten of a general developmental type with a priority direction, for example: physical, intellectual, artistic and aesthetic education.
2. Child development center - kindergarten.
3. Kindergarten of a combined type - along with the usual groups, there are groups for children with some form of developmental disabilities. As a rule, these are speech therapy groups (speech correction).
4. Kindergarten of compensatory type - specialized and sanatorium. In such kindergartens, some chronic diseases are corrected. In specialized kindergartens, unlike sanatoriums, children with chronic diseases can go to the same groups as healthy children.
In public preschools, depending on the type of kindergarten, the curriculum, the number of children in the group, the quality of food and toys, and even, to a large extent, the psychological atmosphere will vary.
One of the main tasks of the development of preschool education is to strengthen the institution of the family, in connection with which a whole system of public preschool education has been created, focused on a child brought up in a family environment. So, along with state preschool educational institutions, there are various forms of preschool education, called variable. As a rule, they exist on the basis of the preschool educational institution as its structural divisions. However, they may exist as an alternative.
So, along with state preschool educational institutions, there are various forms of preschool education, called variable. As a rule, they exist on the basis of the preschool educational institution as its structural divisions. However, they may exist as an alternative.
The first category includes:
1. Advisory centers
2. Early intervention services
3. Child play support centers in preschools
4. Lekothekas
5. Family kindergartens
(60023) stay (7.) Bilingual groupIn the second category we can distinguish:
1. Private kindergartens
2. Home kindergartens
3. Leisure centers
4. Schools
(5.) Bilingual kindergartens
Let's take a quick look at what we have conventionally called the "first category".
Advisory centers ensure the unity and continuity of family and social education, provide psychological and pedagogical support to parents, promote the comprehensive development of the personality of children who do not attend preschool educational institutions.
Early intervention services provide medico-social and psychological-pedagogical assistance to infants and young children with identified developmental disabilities (at risk of impairment) and their families in crisis situations, and also determine the educational route of a problem child.
Children's play support centers carry out pedagogical activities aimed at the comprehensive development of a child aged 6 months to 3 years.
Lekothekas are open to children from 2 months to 7 years old who do not attend state educational institutions for health reasons or due to developmental problems and who need psychological, pedagogical and medical and social assistance.
Family kindergartens are created by large families with three or more children aged 2 months to 7 years, with one of the parents acting as a teacher for children.
Short-stay groups are focused on visiting preschool children 3 times a week for 3 hours. As a rule, groups are of different ages and solve two main tasks: adapting children to kindergarten and preparing them for a longer stay there in the future.
Bilingual groups means that in the kindergarten group the pedagogical process is conducted in several languages.
An alternative to state preschools is a number of educational institutions that are either in the full sense of the word preschools, but exist on a private basis, or preschool education is only one of the components of their educational activities, the list of services they provide is much wider.
Private kindergartens - a duly registered preschool educational institution that operates in accordance with the Russian Federation Law "On Education", has a state license and premises that meet the requirements for a preschool educational institution (as a rule, its own or rented separately standing
low-rise building with an adjacent enclosed area). In the city, private kindergartens, as a rule, occupy the premises of former state or departmental kindergartens, and outside the city they are small cottages built in accordance with the requirements of the law and the characteristics of children's residence.
Home kindergartens are, to some extent, a kind of private kindergarten, differing in that they are organized in large (three- or four-room) apartments, where some of the rooms are reserved for children. Theoretically, it is impossible to obtain a license for educational activities for a kindergarten organized in an apartment. However, according to the Regulation on Licensing Educational Activities, developmental activities (classes in circles, sections, studios), educational activities, leisure activities, seminars, trainings, lectures, consultations, etc., are not subject to licensing, that is, any activity that is not accompanied by final certification and issuance of documents on education and (or) qualifications. In this case, the owner of the home kindergarten registers as an individual entrepreneur (IP), buys a cash register, keeps accounts and calls the Soviet children's institution a development center.
Leisure centers - as a rule, they are municipal and represent to some extent an analogue of the same development center that we talked about in relation to home kindergarten, with some exceptions, however: the list of additional education services they provide is much wider, t . e. pre-school education may be only a small part of it.
e. pre-school education may be only a small part of it.
Schools - many schools are now taking on the function of preparing children aged 6-7 for admission to grade 1 by organizing appropriate preparatory courses. It is worth touching on the topic of creating educational clusters. It is assumed that the merger of capital schools with kindergartens will allow: firstly, to solve the problem of continuity between preschool educational institutions and schools; secondly, to expand the number of development profiles offered by schools to future students.
Bilingual kindergartens differ from ordinary kindergartens only in that educational activities are carried out in several languages (there may be several different age groups, respectively, in this case, the kindergarten may offer the possibility of choosing a language).
In conclusion, it should be noted that the "first category" of institutions is characterized by the fact that educational services are provided free of charge, while the "second category"
implies payment. In general, with the transition of our education system to self-sufficiency, it is possible to predict the expansion of the list of paid educational services provided by state preschool educational institutions.
In general, with the transition of our education system to self-sufficiency, it is possible to predict the expansion of the list of paid educational services provided by state preschool educational institutions.
Pedagogical sciences
Interactive forms of interaction between a preschool educational organization and family in preschool children
Azaryan A. A.,
Student of SBEI HE SSPI, branch in Zheleznovodsk Karamova K.I. Student of SBEI HE SSPI, branch in Zheleznovodsk Khutieva O.A. Candidate of Philosophical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Primary and Preschool Education. 91.2020.2.62.348
ABSTRACT
The article deals with interactive forms of interaction between a preschool educational organization and a family in the upbringing of preschool children.
ANNOTATION
The article deals with interactive forms of interaction between a preschool educational organization and a family in the upbringing of preschool children.
Key words: interactive forms, cooperation, education. Key words: interactive forms, cooperation, education.
At present, cooperation with the parents of students occupies a valuable place in many priority areas
of the educational process in preschools. Most teachers are well aware of the primacy of family education and the need for psychological and pedagogical assistance to parents.
The family is a unique primary society that gives the child a sense of psychological security and emotional "support". The family not only lives with the child, but is also a source of social experience. It is in the family that the child finds role models, this is the beginning of social birth.
Currently, unfortunately, there is a fact of some "deviation" of parents from the upbringing and education of children, parents are becoming more in the position of "executors of material duties", creators of material benefits for their children. And only in the process of close interaction, which is created by kindergarten teachers, parents begin to understand that the main responsibility for the upbringing of children lies with the parents, and teachers are called upon to support and supplement their educational activities.
And only in the process of close interaction, which is created by kindergarten teachers, parents begin to understand that the main responsibility for the upbringing of children lies with the parents, and teachers are called upon to support and supplement their educational activities.
Cooperation between teachers and parents requires equality of partners, respect for the parties that interact with each other, taking into account their individual capabilities and abilities. The most important way to implement cooperation between teachers and parents is their interaction, when parents are not passive observers, but active participants in the educational process, so we can conclude that a single field of activity should be formed between parents and teachers - cooperation in resolving issues related to education, training and development of children.
A modern preschool organization uses various interactive forms of interaction with parents, allowing them to participate in the educational process of their child.
The word "interactive" came to us from the English language, from the word "interact", where "Inter" is mutual and "Act" is to act. "Interactive" means to interact or be in the mode of conversation, dialogue with something [1, p.27].
Main goals of interactive communication:
1. exchange of experience;
2. skills development;
3. creating conditions for dialogue;
4. group cohesion;
5. change in the psychological atmosphere [4, p. 510].
The variety of interactive forms of interaction with parents allows teachers to significantly improve relationships with families, improve the pedagogical culture of parents and expand children's understanding of various areas of education.
Domestic pedagogical science has accumulated considerable experience in the interaction between the kindergarten and the family. K. D. Ushinsky, N. K. Krupskaya, A. S. Makarenko, V. A. Sukhomlinsky, P. F. Lesgaft made a great contribution to the context of modern teacher education; relevant are their scientific generalizations and conclusions that the family is the beginning of all undertakings, that the family is the first educational institution that laid the foundation for a fully developed personality. Researchers believe that if we want to bring up a morally healthy generation, we must solve this problem "with the whole world": kindergarten, family, society [3, p.416c]. Modern researchers also emphasize the importance of interaction between teachers and parents in the upbringing and development of preschoolers.
Researchers believe that if we want to bring up a morally healthy generation, we must solve this problem "with the whole world": kindergarten, family, society [3, p.416c]. Modern researchers also emphasize the importance of interaction between teachers and parents in the upbringing and development of preschoolers.
In their works, researchers offer various forms and methods of fruitful cooperation between the kindergarten and the family: the so-called. Dronova, T. A. Markova, E. P. Arnautova - reveal the need for self-development of teachers and parents. Markova N. F. Vinogradov G. N., Godin L. V., Zugich - pay attention to the content of work with the family. Scientists put forward the basic principles in the content of work with the family:
1. unity in the work of preschool organizations and the family in the upbringing of children;
2. mutual trust in relations between teachers and parents;
3. use of various forms of kindergarten with the family in their relationship;
4. forms of individual and group work with parents [2, p.81].
forms of individual and group work with parents [2, p.81].
The authors lay the foundations for organizing the interaction of preschool educational institutions on the principles of continuity of joint activities, feedback, as well as the individual approach of each family.
Today, the problem of interaction between teachers and parents in the educational process can be successfully solved through integrated approaches in planning a joint
activities, the choice of indicators
performance, a single
methodological, organizational, structural and methodological framework [5, p. 71].
It should be noted that today it is possible to qualitatively influence a child through games, i.e. joint games with a teacher or parents, in this regard, one of the forms of interaction of all participants in the educational process is interactive games
Advantages of interactive games:
1. interactive games create a motive for joint activities, arousing the curiosity of the participants, bringing them joy and increasing interest in the interaction between participants in the educational process;
2. they can create a long-term interest in self-development and in discovering their human and parental potential;
they can create a long-term interest in self-development and in discovering their human and parental potential;
3. interactive games promote the adoption of new standards of communication and behavior;
4. get acquainted with the details of the educational process in preschool [6, p.119].
Parents' meetings are considered one of the main forms of joint work of a teacher with parents, the purpose of which is to create the conditions necessary for the development of free communication, the establishment of mutual business, pedagogical and mutual friendly relations based on the interests of raising a child. No less interesting and necessary are such interactive forms as a group discussion - a joint discussion of any controversial issue, an attempt to move towards the search for truth, which allows you to clarify or change) the opinions, positions and values of parents; round table - a conversation in which a small group of parents participate and during which there is an exchange of views between them and teachers; "symposium" - a more formalized discussion than the previous one, during which parents and a psychologist make presentations presenting their points of view, and then answer questions from the audience. Any of the parents at the "symposium" can state the topic and speak with their vision of the situation or problem.
Any of the parents at the "symposium" can state the topic and speak with their vision of the situation or problem.
As a result, we can conclude that the interaction between the family and the preschool is a long and painstaking work that requires patience, creativity and mutual understanding on the part of teachers and parents.
Various forms of interaction with parents allow teachers to improve the pedagogical culture of parents, significantly improve relations with families, conduct joint partnership activities for the benefit of the educational process in kindergarten.
References:
1. Erofeeva T.I., Musienko S.I. Creation of a team of like-minded people in innovative pedagogical activity. Innovations in Russian education
: Pre-school education
. - 999-No. 4. -27 p.
2. Zvereva O.L., Krotova T.V. Communication between a teacher and parents in a preschool educational institution: a methodological aspect. - M.: TC Sphere, 2009. - 80 p.
3. Kozlova S. A., Kulikova T. A. Preschool pedagogy: Proc. allowance for students. avg. ped. textbook Institutions 3rd. ed., corrected. and additional - M .: Publishing Center "Academy", 2001. - 416a
4. Miklyaeva, N.V. Preschool pedagogy: a textbook for bachelors: Yurait Publishing House, 2013. - 510 p.
5. Tonkova Yu. M. Modern forms of interaction between preschool educational institutions and families // Problems and prospects for the development of education (II): Materials of the international. in absentia scientific conf. - Perm: Mercury, 2012. -71s.
TRAJECTORIES FOR DEVELOPING SOCIAL COMPETENCE OF HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS IN THE EDUCATIONAL SPACE OF SCHOOL
Natalia Vladimirovna Bushnaya
Candidate of Pedagogical Sciences, Associate Professor, Director of the State Educational Establishment “Gymnasium No. 1 named after F. Skorina, Minsk”, Republic of Belarus
THE TRAJECTORIES OF THE FORMATION OF SOCIAL COMPETENCE OF SENIOR STUDENTS
Bushnaya Nataliya Vladimirovna
Ph. D. in Pedagogy, assistant Professor, The principle of state educational establishment "Gymnasium № 1 named after F. Scorina of Minsk",
D. in Pedagogy, assistant Professor, The principle of state educational establishment "Gymnasium № 1 named after F. Scorina of Minsk",
Republic of Belarus
ABSTRACT
The article reveals the process of formation of social competence of high school students. The educational trajectory of the formation of social competence of high school students is represented by the stages of self-determination, self-development, self-realization and characterizes the features of the implementation of their subjectivity in the educational space of the school by solving social problems of individual, personal, social, life-futurological content through identifying their position in the educational space, their own change, development and independent activity on the formation of social competence.
ABSTRACT
The article describes the process of the formation of social competence of senior school students. The educational trajectory of the formation of senior school students' social competence is presented by stages of self-determination, self-development and self-realization and characterizes the peculiarities of their realization in school educational environment by means of solving social tasks of personal, public and life-futurological content identifying their own position, personal development and independent activities in the formation of social competence.
Keywords: social competence of high school students, social tasks of individual-personal, social and life-futurological content, self-determination, self-development, self-realization.
Key words: social competence of senior student, social problems of personal, public and life-futurological content, self-determination, self-development, self-realization.
Self-realization of a young person in the face of global challenges of our time is largely due to his social competence, the formation of which is currently included in the group of priority educational tasks at all levels and levels of the lifelong education system. This explains the high demands of society and the state to the formation of social competence of high school students. Students at this age are faced with the tasks of professional and life self-determination, determining their place in the system of social relations. School graduates, leaving the educational institution, plunge into the social world,
which provides them with a range of possibilities.