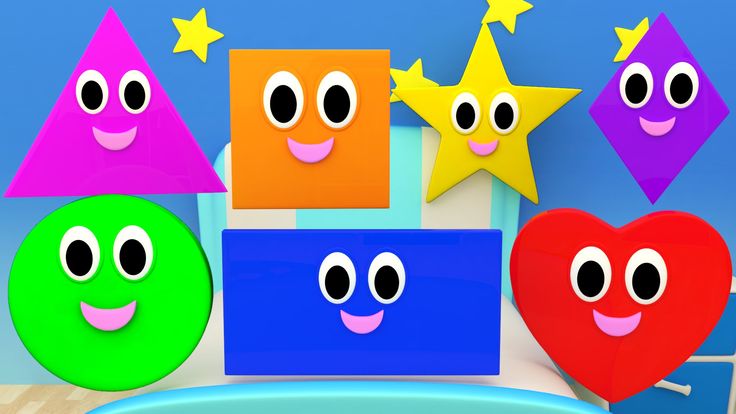
Shapes kids learn
Teaching Basic Shapes to Kids In an Interesting Way
Table of Contents
| 1. | Introduction |
| 2. | Why is teaching shapes so important? |
| 3. | What are the different types of shapes for kids? |
| 4. | How to teach kids with the help of games and activities |
| 5. | Conclusion |
| 6. | About Cuemath |
| 7. | Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) |
| 8. | External References |
Introduction
Kids have dynamic learning capabilities that are enhanced by their observation skills. However, parents need to take tiny steps while teaching preschool kids. Basic shapes and colors impact children. They try to understand their surroundings by looking at the different objects around them. All kinds of objects and structures help kids in learning shapes. As a parent one should introduce different shapes for kids at an early age. There are various shapes activities for kindergarten that can help kids learn and understand basic shapes.
Shapes for Kids
Here is a downloadable PDF that lists out various shapes for kids. Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. Different types of shapes for kids. Click on the download button to explore them.
Why is teaching shapes important?
Basic shapes for kids are being taught at every preschool today. It is important to understand the necessity of shaping activities for kindergarten kids. Few ways in which kids are impacted by basic shapes are:
- Visual Information
- Sign and symbols
- Alphabets and numbers
- Mathematical concepts
- Categorization and comparison
- Problem-solving
- Symmetry
- Kids Learn how to organize visual information
Children observe their surroundings very keenly and encounter different shapes every single day. Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. The visual information they gather comprises compound shapes that are formed by a combination of basic shapes. Shapes’ names for kids enable them to identify the basic shapes in compound shapes. For instance, when a child looks at a car it appears to be a rectangular box. However, children will learn to identify the compound shapes in a car once they learn basic shapes.
Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. The visual information they gather comprises compound shapes that are formed by a combination of basic shapes. Shapes’ names for kids enable them to identify the basic shapes in compound shapes. For instance, when a child looks at a car it appears to be a rectangular box. However, children will learn to identify the compound shapes in a car once they learn basic shapes.
- Helps to teach signs and symbols
Symbols are very important for kids. But it will take some time for kids to get used to it. Kids take some time before they can actually name the shapes they see. However, this does not indicate that the kid is unable to comprehend basic shapes. Signs on the other hand impart certain information and details. Basic shapes for kids help them store information in their minds. Kids are usually 5 to 6 years old when they start following signs and symbols
.
- Help kids identify different alphabets and numbers
Toddlers may get confused among all the alphabets they see. As parents, it can be challenging to teach various letters and numbers. Kids tend to mix up similar-shaped letters like “b” and “d”. Patience is important while correcting these mistakes. Learning shapes for kids help them differentiate among the letters. Therefore all the preschools cover learning shapes for kids before moving into Alphabets and numbers.
- Basic mathematical concepts can be taught
Once a child is comfortable identifying shapes for his /her own, they can start learning simple mathematical operations like addition and subtraction. It is always easier to teach addition than subtraction. Therefore we advise parents to start teaching addition and then venture into subtraction.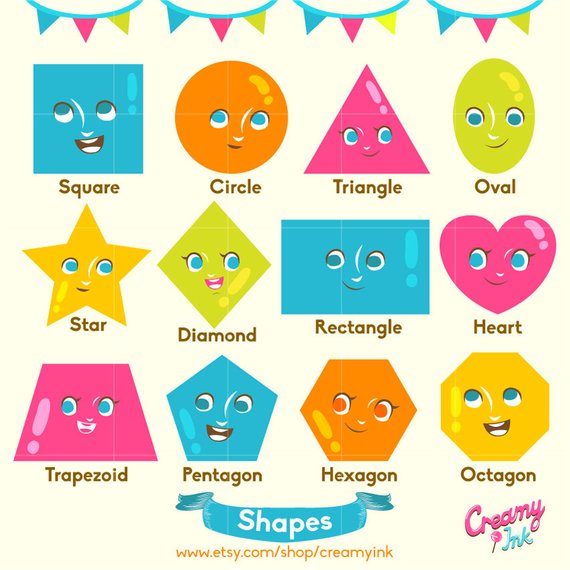 Basic shapes for kids include balls, matchboxes, dice, etc. So you can pick the object of your choice and start teaching simple maths to your kids.
Basic shapes for kids include balls, matchboxes, dice, etc. So you can pick the object of your choice and start teaching simple maths to your kids.
- Categorization and comparison
Facial recognition and navigation skills are swiftly developed among kids who can categorize and compare various shapes. As kids learn to differentiate shapes, they understand facial features and their differences. It is also important to note that different shapes for kids imply different geographical locations or features. Have you noticed, in kids’ drawing- mountains and hills are always triangles and houses have a square or rectangle structure with a triangular roof? We do suggest you take a look and understand how kids observe and compare the shapes around them.
- Problem-solving
Brain development and thinking skills are really important for a kid in preschool or kindergarten. Shapes and colors are directly responsible for brain development. Kids analyze structures and start with 2-D mental mapping and then gradually, as the year progresses, they start 3-D mapping. These mental mapping of shapes plays a crucial role in the development of problem-solving abilities in children.
Shapes and colors are directly responsible for brain development. Kids analyze structures and start with 2-D mental mapping and then gradually, as the year progresses, they start 3-D mapping. These mental mapping of shapes plays a crucial role in the development of problem-solving abilities in children.
- Symmetry
Kids love to play around the parks or fields. This is important for the development of their motor skills. However, kids tend to lose their balance more often than adults. Growing up, we all had cuts and bruises on our knees Over the years these injuries started disappearing even when sports activities became more rigorous. This happens when kids are unable to understand the basic concept of balance and center of gravity. Now even though terms like the center of gravity feel fancy for kids, it is important to teach symmetry with the help of basic shapes for kids. This will help them understand how to position themselves and develop motor skills.
This will help them understand how to position themselves and develop motor skills.
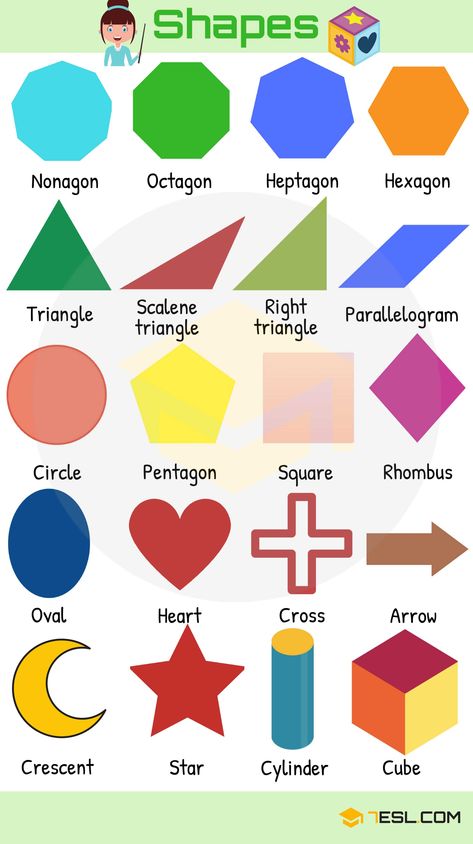
What are the different types of shapes for kids?
Different shapes for kids are available ranging from basic shapes to compound shapes. Basic shapes are simple shapes that can not be broken down into simpler shapes by general conventions, examples include square, circle, triangle, etc. Compound shapes can be split into simpler shapes, examples include Arrows, Starts, etc. Let us go through a few shapes to understand better.
|
Shape |
Image |
Number of Sides |
Example: |
|
Triangle |
3 Sides |
Mountains and Hills are Triangle in shape |
|
|
Square |
4 Sides |
Small houses or huts are square in shape |
|
|
Rectangle |
4 Sides |
Cars and buses are rectangle in shape |
|
|
Circle |
No Sides |
Wheels and Balls are circle in shape |
|
|
Arrow |
7 Sides |
Signs boards have an arrow shape |
|
|
Star |
10 Sides |
Starfish and star anise are star-shaped |
|
|
Diamond |
4 Sides |
Kites and crystals have diamond shape |
|
|
Heart |
No Sides |
Strawberries are heart-shaped. |
- Basic Shapes for kids
Shapes like squares, triangles, circles, and rectangles are taught first to kids. Once a child learns how to categorize and name these shapes, they are taught more complex shapes. However, it suggested that ample time is spent on basic shapes for kids. This is because all the shapes are taught at a later stage depending upon the concepts developed during learning basic shapes for kids. It may require a little while for kids to pick up the concept but we suggest parents be patient.
- Advanced Shapes for kids
Once a child is familiar with basic shapes he/she is ready to learn advanced shapes for kids. These shapes include arrows, stars, and hearts. Advanced shapes do not include 3-D structures in preschool as it may confuse them.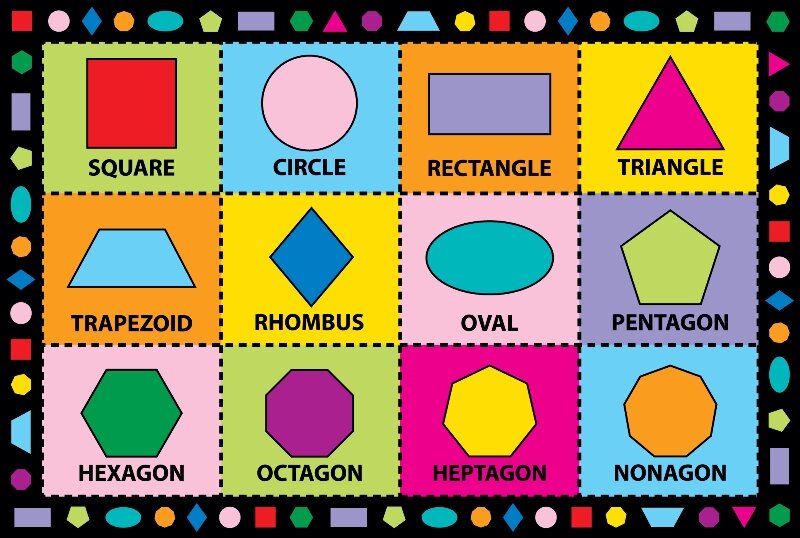 Kids with a clear conception of basic shapes will be able to ace this topic quickly.
Kids with a clear conception of basic shapes will be able to ace this topic quickly.
How to teach shapes to kids with the help of games and activities?
Till now, we saw how important basic shapes can be for a child's brain development. Teaching shapes can be cumbersome without activities as children find it difficult to comprehend something that can not be observed. Activities and games will help kids learn while having fun.
Now, we will look into a few activities and games to help your child play and learn.
- Flashcard shapes for kids
Flashcards are a really fun and interactive tool while teaching kids. They can be purchased in stores or prepared by hand. You can draw different shapes on cards made out of thick paper to prepare a set of flashcards. Use these cards to play with your child. Ask your kid to pick up a card and name the shape drawn on the card. Maintain a scoreboard and let them beat their own high scores.
Maintain a scoreboard and let them beat their own high scores.
- Shapes for kids chart
Bright and colorful shape names for kid's charts are available in the market. To prepare them at home, you need to draw shapes and write down their names. Colorful shapes are easier to remember for kids. Ask your kids to look at the beautiful chart every day in the morning before going to preschool or kindergarten.
- Shapes hunt
Just like a treasure hunt, shapes hunting is fun and easy for preschoolers. Use a set of flashcards with different shapes on them. Ask your kid to pick up one card and identify the shape and once he or she has identified the shape, ask them to find an object of the same shape around the house. This will keep the kids engaged and help them relate basic shapes to their surroundings.
- Puzzle games
Two types of puzzles are available for kids to learn basic shapes. The first one contains pieces of brightly colored basic shapes for kids. These shapes need to be fitted onboard with hollows similar to the shapes. These boards with pieces of basic shape for kids are available in preschool supply shops and toy shops.
The second type is a conventional puzzle with bigger pieces. Once a child is proficient in basic shapes for kids they can try to join the pieces of a picture together.
We suggest you go for basic puzzles with pictures of fruits and flowers to keep the level easy for your child.
Conclusion
In the former section, we came across the various benefits of teaching basic shapes for kids. It is one of the most important topics covered in the kindergarten and preschool syllabus. Even though your child may be learning shapes for kids in school, it is suggested that parents help them out with shapes games for kids. This is because the identification of shapes and naming shapes are two different objectives. Kids tend to forget shape names.
Even though your child may be learning shapes for kids in school, it is suggested that parents help them out with shapes games for kids. This is because the identification of shapes and naming shapes are two different objectives. Kids tend to forget shape names.
Start teaching basic shapes to your child and try to relate them with the objects around you. This will help kids relate the concept of basic shapes with their surroundings. We suggest parents start with basic shapes and gradually move into advanced shapes. Spend more time on basic shapes for kids to build the foundation for advanced shapes.
About Cuemath
Cuemath, a student-friendly mathematics and coding platform, conducts regular Online Live Classes for academics and skill-development, and their Mental Math App, on both iOS and Android, is a one-stop solution for kids to develop multiple skills. Understand the Cuemath Fee structure and sign up for a free trial.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between regular and irregular shapes?
- Regular Shapes are those which have equal sides as well as equal angles. Irregular Shapes are just the opposite,i.e, their angles and sides vary.
- Examples of Regular Shapes are Square, Circle, Equilateral Triangle, etc.
- Examples of Irregular Shapes are Rectangle, Heart, Right-angled triangle, etc.
- Cylinder - Circles
- Cuboid - Rectangles
- Cube - Squares
- Pyramid - Rectangles and Circles
- Tetrahedron - Triangles
- Geometric: These are simple shapes like rectangle, square, triangle, etc. which are geometric in nature.
 They form the basis of other types of shapes.
They form the basis of other types of shapes. - Organic: These shapes are curvier in nature and have a natural feel to them (for example, the shape made after the ink is spilled on a paper is of organic type). These are more soothing and relaxing to the eyes.
- Abstract: These shapes are complex in nature and are mostly used in graphics designing purposes. They are aesthetically beautiful but are not naturally found.
When Do Kids Learn Shapes?
Table of Contents
- 1 What Are the 2D and 3D Shape Names?
- 2 When Do Kids Learn Shapes?
- 3 What Are the Different Shapes Taught in Kindergarten?
- 4 Printable Resources For Teaching Shapes
- 5 Toys For Teaching Basic Shapes
Some of the links in this post are affiliate links. This means if you click on the link and purchase the item, I will receive a small commission at no extra cost to you. All opinions remain my own.
Today’s post will be all about shapes, such as “when do kids learn shapes?”, “what are the basic shapes?”, and the best toys and printable resources for teaching 2d and 3d shapes.
What Are the 2D and 3D Shape Names?
Basic shapes and common shapes are easy to remember. In fact, most children are familiar with most common shapes by the time they start school.
Squares, circles, and triangles are often a part of their repertoire. However, children have different exposure over those first few years of life. To fill that gap, shapes are taught in the classroom from the very beginning.
More practice doesn’t hurt anyone!
As knowledge in those 2D basic shapes is solidified, more complex shapes and advanced shapes are introduced and included in practice.
A list of 2D shapes and 3D shapes covered in the early years is listed below.
2D Shapes
- Square – A square is made by four equal sides and four equal angles.
- Circle – Circles are completely round and created by a single curved line.
- Triangle – Triangles have three sides and three angles.
- Rectangle – Rectangles are made of four sides.
 They are not even in length.
They are not even in length. - Pentagon – A five-sided shape.
- Hexagon – A six-sided shape.
- Octagon – An eight-sided shape.
- Nonagon – A nine-sided shape.
3D Shapes
- Cube – Cubes have six faces that are all squares.
- Cylinder – This shape has two round faces. One at the top and one at the bottom. It has a curved side.
- Cone – Cones have a flat circle base and a pointy top. Think of an ice cream cone!
- Pyramid – A pyramid can have a triangle, square, pentagonal, hexagonal, or octagonal base.
- Sphere – A sphere is a round and circular shape. It has one face and no edges.
- Cuboid – Cuboids have six faces. They are all rectangles. This may be a new shape to many!
When Do Kids Learn Shapes?
Whether you’re a parent or a new teacher, it’s important to know when do kids learn shapes.
Shapes, colors, numbers, and letters are often something introduced at an early age, long before children begin heading to school. As kids move into a more structured preschool and eventual elementary school program, those skills will become cemented into their long term memory and skill set.
As kids move into a more structured preschool and eventual elementary school program, those skills will become cemented into their long term memory and skill set.
The shapes covered before school are often basic 2D shapes, but children are introduced to 3D shapes as early as kindergarten! They will continue practicing their 3D and 2D shape skills and recognition throughout kindergarten and first grade.
Basic 3D shapes join the mix early on in their elementary school career. More specifically, 3D shapes are often taught in kindergarten.
To simplify it, kids should begin recognizing shapes as toddlers, then build upon their recognition of 2D and 3D shapes in kindergarten.
Critical milestones at a young age are learning colors and a variety of shapes, and knowing how to apply those skills in everyday life. Let’s look more into the milestone of learning shapes.
What Are the Different Shapes Taught in Kindergarten?
Kindergarten is the beginning of a long 13 year school career.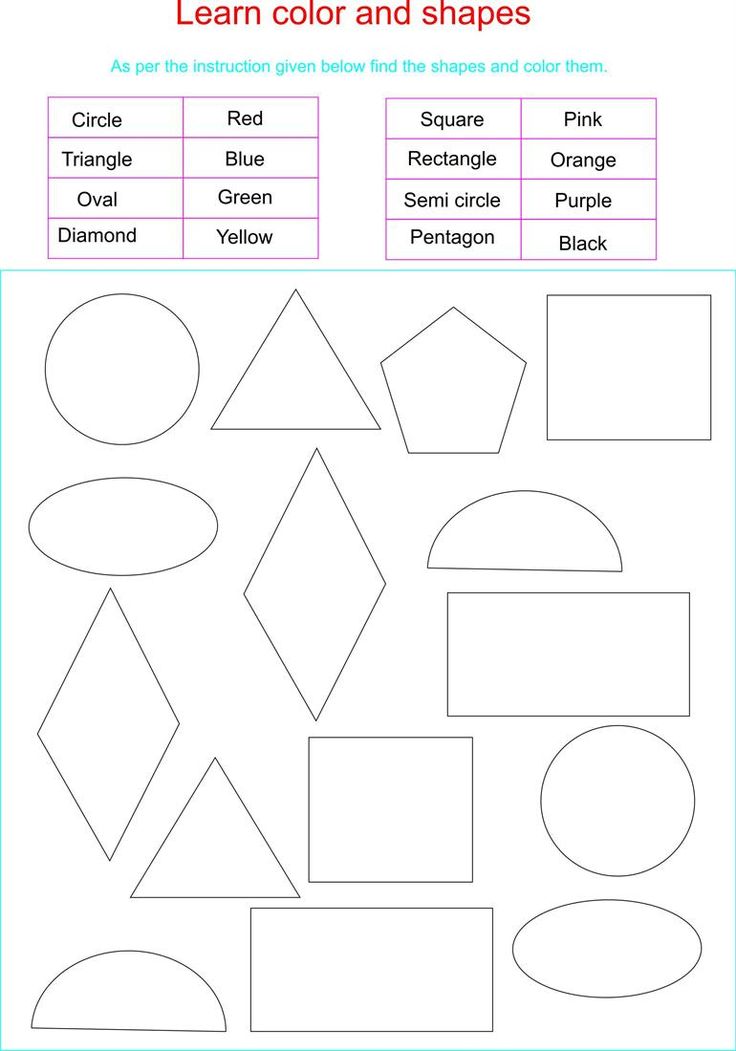 Learning the kindergarten curriculum will build a firm academic foundation.
Learning the kindergarten curriculum will build a firm academic foundation.
The shapes taught in those early school years vary by grade as laid out by grade level common core standards. The different shapes covered in kindergarten (based on common core standards) include:
- Squares
- Triangles
- Rectangles
- Hexagons
- Cubes
- Cones
- Cylinders
- Spheres
Kindergarteners will be expected to:
Identify and describe shapesThey need to be able to name shapes regardless of their size and whether or not they are 2D or 3D. They must be able to describe the environment the shapes are in and the positions of shapes (using words such as above, below, beside, in front of, and behind). What shapes do they see in real-life objects?
Analyze, compare, create, and compose shapesKindergarteners need to be able to compare and contrast shapes of different sizes and orientations. They should learn how to build and draw shapes using various materials and use smaller shapes to make larger shapes.
They should learn how to build and draw shapes using various materials and use smaller shapes to make larger shapes.
When teaching different types of shapes, I help the kids set learning goals with these kid-friendly “I Can” statements. The various shapes are covered under the geometry section of the common core standards.
Printable Resources For Teaching Shapes
Looking for no-prep printable shape resources? Below are some new and classic shape resources that you’ll love.
Most of these simple activities work really well as independent work or part of a center or activity rotation! All are great for at home or in the classroom!
Shape SuperStars
These superstar worksheets have children practicing 2D shapes in five different ways:
- Trace
- Find and color
- Tap and say the name of the shape
- Cut and paste shape sorting
- Draw the shape
Get these printables HERE or on Teachers Pay Teachers
Shapes Make and Trace Play Dough Mats
If you have a lot of tactile learners, this make and trace is a good idea. Children can use fine motor skills to make 2D shapes out of play dough and then practice drawing.
Children can use fine motor skills to make 2D shapes out of play dough and then practice drawing.
This type of sensory activities are great for shape recognition, and names of shapes, with young and older kids.
If you’re also teaching colors, you can have the kids match the play doh color to the color of the shape on the mat.
Get these printables HERE or on Teachers Pay Teachers
Superhero I Have, Who Has 2D and 3D Shapes
Group games and activities are the best way to work on skills in a classroom. This game includes cards for 2D and 3D shapes.
I Have, Who Has is a great all-class game that will have the whole room excited
Get these printables on Teachers Pay Teachers
Shapes Write the Room
Children can go on a hunt to find the shape cards around the room, color them, and then write and label the sheets.
Get these printables HERE or on Teachers Pay Teachers
Making Words and Shape Cards
With this making words set, children can learn to read, write, build, and illustrate 2D shape words.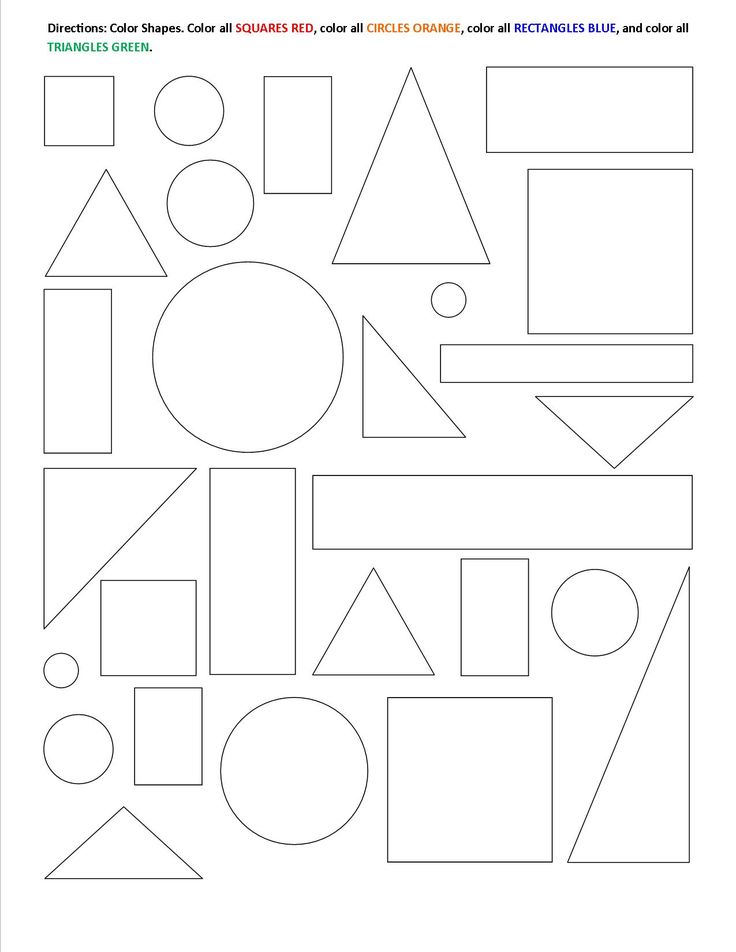
Kids will build, write, and draw each shape. Shape cards, or word wall cards, are included as a bonus!
Get these printables HERE or on Teachers Pay Teachers
Lucky Ducks Shape Game
In this game, children pull a duck from the pond and graph the shape found on the bottom of their duck. If they pull three ducks with the same shape, they win the game!
Get these printables on Teachers Pay Teachers
Toys For Teaching Basic Shapes
Young children learn best through play! Educational games are a hit for everyone. Toys keep children engaged. When kids are engaged and interested, learning is more likely to stick.
Shape toys and manipulatives are great for free play, but they are also a great companion to more structured written work or activities.
Combining structured, written work with tactile or kinesthetic opportunities is an easy to way to appeal to nearly everyone. Many of the toys below are great companions to worksheets, but several of them are great stand-alone shape practice!
- View-Thru Geometric Shapes
- 250 Shape Manipulatives
- Shape Bean Bags
- Shape Slide Puzzle
- Matching Egg Shape Toy
- 3D Jumbo Shape Solids
- Rubber-band Shape Boards
- Magnetic Sticks
- Shape Clock
- Color and Trace Activity Book
- Shape sorting block
Those plastic shape sorters are a popular toddler toy for a reason! It is an important skill to learn and important step in child development!
Before you go, here are more posts you’ll enjoy:
25 Printable Kindergarten Vocabulary Worksheets
15 Best Ways to Improve Fine Motor Skills
34 Best nursery Rhymes for Kids
The Benefits of Teaching Code to Elementary Kids
When Do Kids Learn Shapes?
How to motivate your child to learn: simple ways that will help you
Surely every parent has at least once wondered how to teach a child to be independent without hassle and disappointment? How to teach children to do homework with joy, to make the learning process exciting for the children themselves. Our new blogger Anna Chirkova tells how to work with children's motivation.
Our new blogger Anna Chirkova tells how to work with children's motivation.
In recent years, the practice of teachers shows that the number of children who do not seek knowledge is constantly growing. It appears even in primary school students.
Unwillingness to learn is manifested in the fact that children forget to do their homework, their textbooks and desks are messy, they draw in class, look out the window, talk to classmates, they are bored in class. Such children may blame teachers for their poor grades, but most often they do not care at all about poor performance.
Why do children not want to study? Even teachers with experience are not always ready to unequivocally answer this question, but we will try to give the simplest and most effective ways to motivate your child.
There are many reasons why children do not want to study. Let's analyze some of them.
What influences the unwillingness to study
1. The child is too small for school. Parents think that their children are ready for school if they see that they know a lot for their age. But even if your child is smart enough, and you think not to take him an extra year to kindergarten, this does not mean that he is psychologically ready for school. Most likely, the child will not be able to obey certain rules. In addition, it is more difficult for young children to sit for a long time in the classroom without moving.
Parents think that their children are ready for school if they see that they know a lot for their age. But even if your child is smart enough, and you think not to take him an extra year to kindergarten, this does not mean that he is psychologically ready for school. Most likely, the child will not be able to obey certain rules. In addition, it is more difficult for young children to sit for a long time in the classroom without moving.
2. Conflicts with teachers. Often, even the teachers themselves are not aware of the conflict with their pupils. They may notice that the student has poor academic performance, his behavior has changed, although, as it seems to the teacher, there was no conflict as such. In fact, the child could hear unpleasant words addressed to him or hold a grudge against the teacher's behavior. The child may feel depressed, feel fear, he develops a negative attitude towards the teacher. In most cases, children do not want to tell their parents about their fears related to school, this preserves the conflict and the difficulties associated with it.
3. Conflicts with students. If such a problem has already developed, then it can be very difficult to correct it without consequences for the child.
4. Physical defects. For example, stuttering, trembling of the limbs, and others. It is very difficult for children to get used to the idea that they are somehow different from their peers. It becomes especially difficult in cases where the shortcomings cause bullying and laughter from classmates. Knowing about his problem, the child does not want to become the center of attention, feel humiliated and once again appear at school.
5. Family conflicts. Scandals between parents and other family members. Often such a child closes in on himself due to experiences, he not only loses his motivation for learning, he is rarely interested in anything at all.
6. Pressure on the child from parents and relatives . We set high standards for children, sending them to the best schools where education is conducted at a higher level, we enroll in various sections.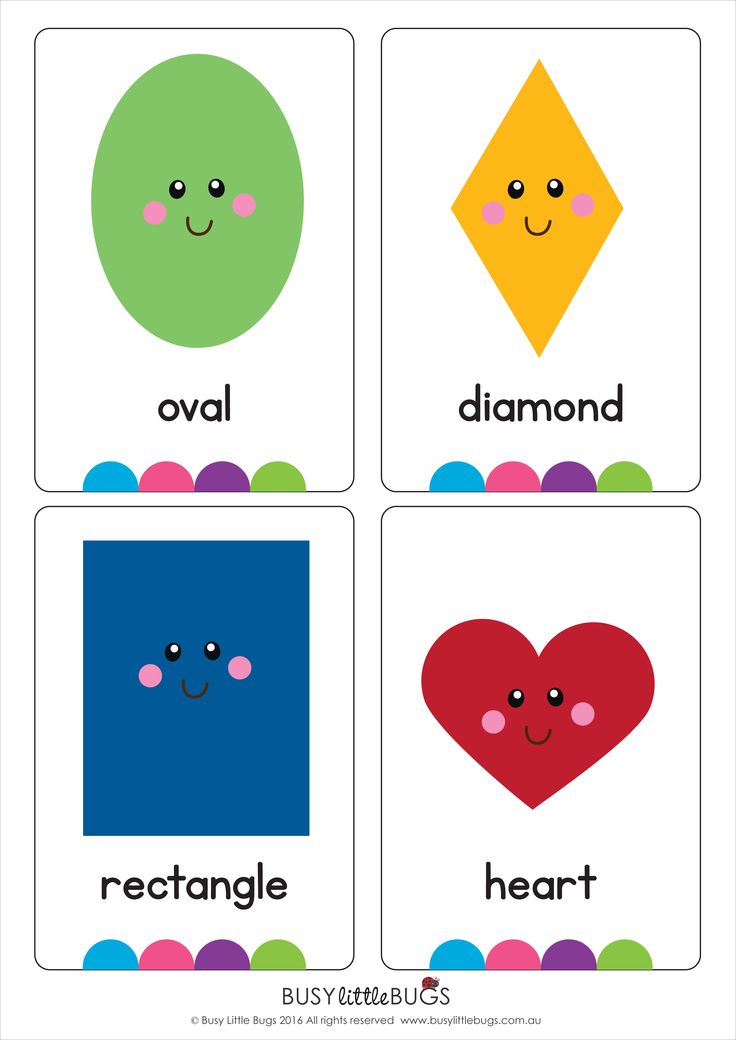 Just imagine how many sections parents try to send their children to without taking into account the opinion of the children themselves. Parents scream, get indignant, scold children if they bring bad grades or simply do not reach the results of their classmates. Think about it, maybe you are putting too much pressure on the children, forcing them to do what they do not want.
Just imagine how many sections parents try to send their children to without taking into account the opinion of the children themselves. Parents scream, get indignant, scold children if they bring bad grades or simply do not reach the results of their classmates. Think about it, maybe you are putting too much pressure on the children, forcing them to do what they do not want.
What factors influence interest in learning
1. Interest in the subjects studied . Often, children lose interest in studying some subjects just because they seem boring to children. However, you need to make it clear to the child that in all lessons they provide the necessary information that develops different skills, so it is important to study all subjects. There are many disciplines, the study of which requires more work. In this case, you need to find another motivation. Much depends on the teacher, who is able to explain complex things in simple language and thus simplify the learning process.
2. Method of studying objects . In elementary grades, it is much easier for children to learn with the help of active methods, discussions and games. The teacher should pay attention to the fact that tasks like “rewriting textbooks” and “working on our own” reduce interest in the subject, while creative and various unusual ones, on the contrary, increase.
3. Perception of information . Some children perceive information better through sight, others through hearing, others through images. The effectiveness of teaching children largely depends on the type of perception of information. Parents themselves can choose the ways of teaching the child if they understand his peculiarities of perception of information.
4. Teacher's interest . When a teacher intrigues students with a personal example, shows a positive attitude towards the subject, then children also become interested in what they are taught. When they know that they will hear something funny or interesting in class, they look forward to these items with joy.
What are the types of motivation
Motivation is one of the most important conditions for successful learning. The most significant for students are the following motives:
- cognitive, that is, the desire to know more, to become erudite;
- communicative - expanding the circle of communication through an increase in the intellectual level and new acquaintances;
- emotional;
- self-development - disclosure of one's abilities and talents;
- student position;
- achievements;
- external - rewards, punishments.
In addition, motives are divided into external (social) and internal (cognitive). An example of extrinsic motivation: "I need to pass the exam so that my parents don't scold me." Intrinsic motivation: "I really like literature lessons, so I read every free minute, I learn something new with every book I read."
There are two more types of motivation - stable and unstable. An example of sustainable motivation: "Since the day I entered the drawing school, I have never regretted that I chose this particular section." Unstable: “I went to a concert, I also wanted to play some instrument, I started studying, but after a while I quit.”
An example of sustainable motivation: "Since the day I entered the drawing school, I have never regretted that I chose this particular section." Unstable: “I went to a concert, I also wanted to play some instrument, I started studying, but after a while I quit.”
Most often, children's motivation is unstable due to the fact that they are very emotional. It is very easy to interrupt old ones with new emotions and impressions.
It is very difficult for a child who is not interested in learning to apply the acquired knowledge in practice, and the lack of motivation for the learning process leads to chronic academic failure. Why is this happening? Often the parents are to blame.
Of course, only you can choose how to properly raise your child, but his and your life depends on this choice. Not all parents realize what mistakes they make in the process of motivating their children. Consider not all, but the most relevant of them, which are most often found among parents.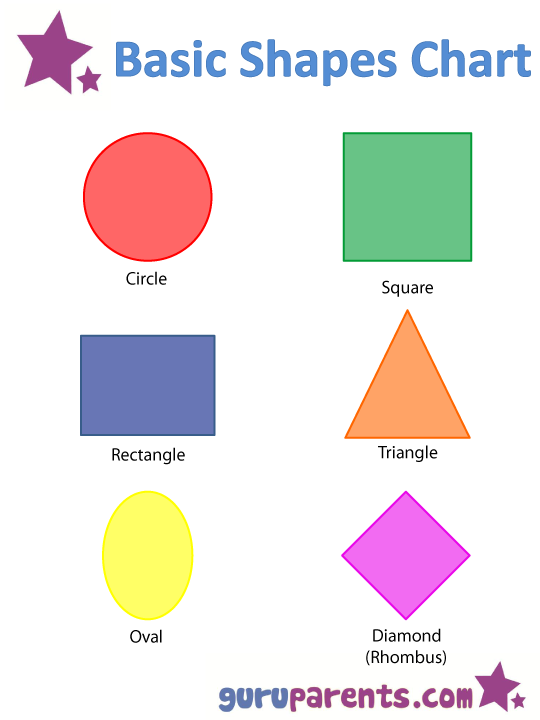
1. Lowering your child's self-esteem, programming for failure. This happens when you tell a child that nothing good will come of him, that he will become a janitor if he does not study well. Such words lead to an underestimation of self-esteem, in case of any failures, the child lets go of his hands, completes what he started at the slightest problem.
2. Deception and intimidation . If you use such methods, the connection and trust between you and your child will be destroyed.
3. Exaggerated demands, not taking into account the child's capabilities . The parent may think that the child is lazy or “not studying on purpose”, while there may be specific reasons (mental developmental features, illness, fatigue).
4. Gifts in exchange for good academic performance . There are many downsides to this method. The child quickly develops a habit of getting what he wants through good grades. In the future, he may begin to demand a reward and fulfill your requests only after receiving what he wants. Such children are only aimed at receiving presents, and not at good studies.
Such children are only aimed at receiving presents, and not at good studies.
5. Motivated by success . Often, parents assure the child that all his actions should be aimed at success and high status in society. In the future, such children grow up to be people who do everything for the sake of success and money, and not because it brings them positive emotions or is aimed at helping loved ones.
6. Excessive workload in various activities and sections . Modern parents like to plan their children's schedule as tightly as possible so that they spend their time with benefit every day. The child's psyche may not be able to withstand such a load, so you will get a complete lack of interest in classes.
How to increase motivation to study
1. Educate your child in a playful way
Play is a unique instrument of pedagogical influence. If the child does not want to learn or something does not work out for him, you can always come up with a game in which he will be able to complete the tasks you have given.
These can be intellectual exercise games, training games based on competition. They show schoolchildren the level of their preparedness and fitness. By comparing with the opposite team, students themselves see their gaps in knowledge, this encourages cognitive activity in them.
The game form does not involve standard student assessment, so even lagging children can be interested.
2. Support the child in his hobbies
Do not impose your favorite activities, let him pursue his hobby. Help children discover their hidden talents or develop those they already have, let them freely choose what interests them.
3. Small rewards, not big rewards
Encourage the child, praise for the result, but do not do it in the form of money and in the form of expensive gifts. Otherwise, the time will come when the child wants to sell you the results of his labor at a higher price. For example, the rule "For every correct task - 1 candy" works much better than "For every five in the diary - a cake. " Candy is a kind of guarantee that difficult homework is done in an atmosphere of trust, which in itself is already a motivation.
" Candy is a kind of guarantee that difficult homework is done in an atmosphere of trust, which in itself is already a motivation.
4. Be interested in what your child has learned in school, not in his grades
Show him how to apply what he has learned, discuss his stories together. Encourage your child to think and discuss as often as possible. Remember that any grades are a subjective thing, this is not an indicator of your child's knowledge, but only his assessment by teachers.
A child does not have to be an excellent student, he has the right to receive bad marks. If he himself was upset because of the deuce - support and never scold. After all, first of all, you should be his friend and partner.
5. Minimize stress
Tell the children how you yourself overcame difficulties in school, how you coped with difficult tasks. Show what you have achieved now that you have walked this path. Talk together about your failures and fears.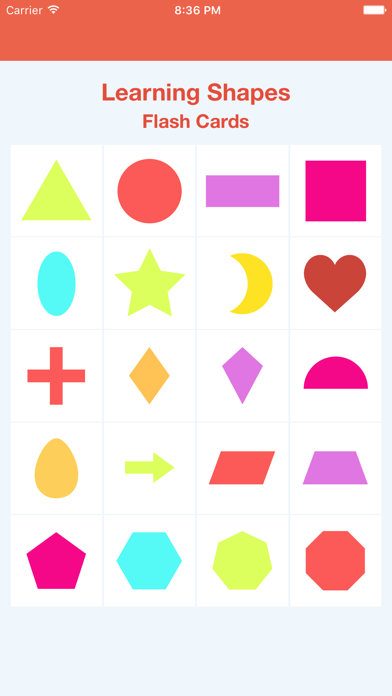
The child should always know that he will be heard, and problems will not be exaggerated. Explain that stress is an integral part of life, teach how to cope with it so that in the future the child can overcome it himself.
Motivation for learning does not develop overnight, sometimes it takes a lot of effort and time. If you have missed something in raising your child, it is never too late to start building your relationship on the basis of trust and understanding.
Do not motivate your child with distant and illusory goals incomprehensible to his age. Every parent must find where the potential of their children lies. Try to reveal his talents from different angles, give him the opportunity to prove himself. Look for inclinations in your children for some kind of activity, show by your own example that we are learning new things all our lives, that there are many interesting things in life.
Do not forget that in no case should you beat, humiliate, yell at a child, because school will end sooner or later, but your relationship will remain. According to the research of E. N. Volkova, the majority of children living in families in which severe physical, emotional, and other types of violence are used have signs of a delay in physical and neuropsychic development. Their memory deteriorates, the processes of memorization and retention are difficult, selectivity in memorization increases sharply. Attention becomes scattered, speech becomes poorer, stuttering appears. Children do much worse at school, the processes of school adaptation are more difficult.
According to the research of E. N. Volkova, the majority of children living in families in which severe physical, emotional, and other types of violence are used have signs of a delay in physical and neuropsychic development. Their memory deteriorates, the processes of memorization and retention are difficult, selectivity in memorization increases sharply. Attention becomes scattered, speech becomes poorer, stuttering appears. Children do much worse at school, the processes of school adaptation are more difficult.
Imagine what kind of person your child will be at the end of the learning journey. The time spent studying is very valuable for his formation as a person, do not miss it!
Photo: Shutterstock (granata68)
How to make students want to learn
home
Parents
How to raise a child?
How to make students want to learn
- Tags:
- Expert advice
- 3-7 years
- 7-12 years
- children in the family
- family relationships
Every person remembers his very first September 1st.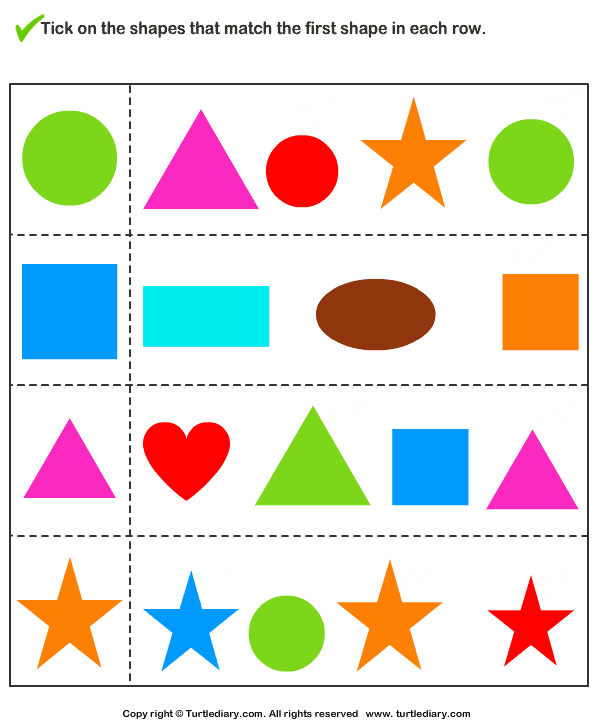 Happy and a little frightened first-graders in a brand new school uniform are sure that they will study only for one five.
Happy and a little frightened first-graders in a brand new school uniform are sure that they will study only for one five.
The first days at school are very interesting: new friends, fun breaks, a kind teacher. Later, the first difficulties, quarrels appear, and the teacher no longer seems kind, and the desire to go to school disappears. How can you make your child want to learn?
School motivation
Motivation drives the world. The word “motivation” itself comes from “movere”, which means “to move” in English. Achieving a goal is always accompanied by a feeling of happiness. The question is, what is the goal? What is important for the child - to solve the problem or to avoid doing homework?
The psychological phenomenon of motivation lies in success. We like to do what works. Formed school motivation develops into school success. However, for many modern parents, homework time is a real torture. Few people can boast that doing homework does not turn into a scandal, and only a few can say that children do their homework on their own.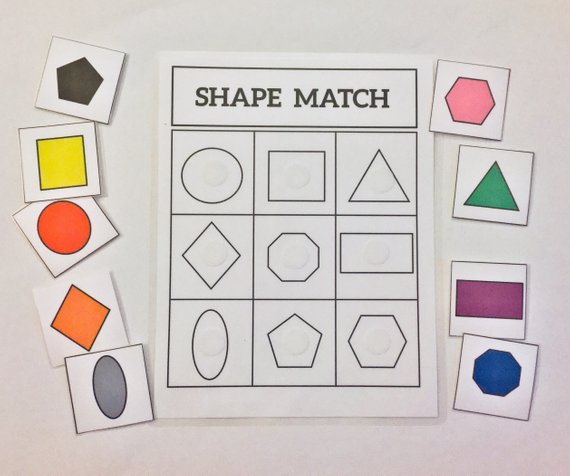
It is difficult to say at what point children's motivation disappears. For some, the desire to learn disappears in the first days at school, for others - with the appearance of the first difficulties, and for others - over time. Each parent tries to solve the problem in different ways: pays children for good grades, sets successful people as an example, punishes, scares them with a difficult future.
School failures are not always an indicator of intellectual development problems. Most often, school failure is the result of a complex chain of gaps in knowledge and poor mastery of the material. But at the heart of it all is a reluctance to learn. Agree that it is difficult to succeed in a business that is not interesting.
Reasons for lack of motivation
Motivation for cognitive activity should be formed long before school. The first folded cubes, assembled pyramids and mosaics should be accompanied by praise from parents.
Each new task should be a little more difficult than the previous one, so that the child learns to overcome difficulties and get joy from it.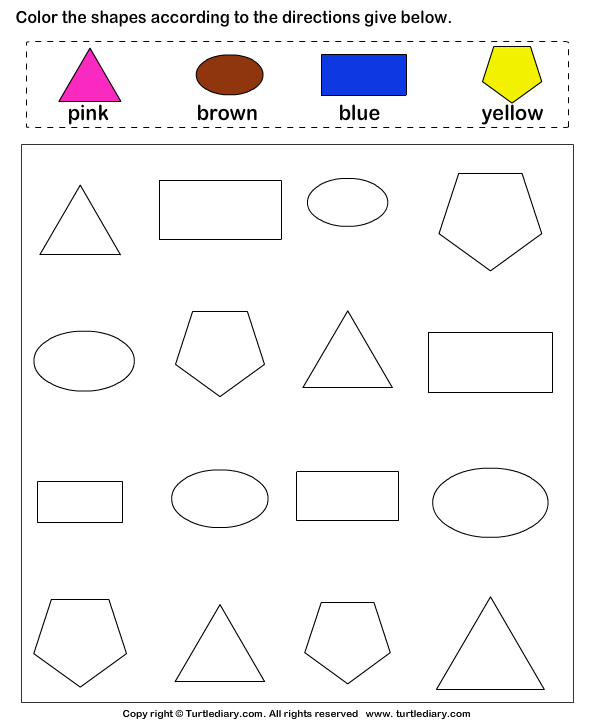
Junior school age is the most favorable period for the formation of interest in learning. But in practice there are few children who want to learn.
Cause 1.
Unformed voluntary behavior.The ability to read and write is not all that is needed at school. The child must be able to obey the rules, observe the regime, do what is necessary. The school curriculum does not involve physical education when you want - there is a school schedule for this. Of course, voluntary behavior is formed at preschool age, but it is never too late to start this work.
Reason 2.
Unjustified expectations.Children are often told about school in rainbow colors: many peers, breaks, games, competitions. As a result, the child will be greatly disappointed and convinced that he was deceived.
Reason 3.
Physiological unpreparedness. Many parents think that learning skills are the most important thing, but this is not true. It is important that the child is physiologically ready for school: he must have a strong hand with stable fine motor skills, immunity is formed, correct posture is developed, and the musculoskeletal system is developed. A weakened child will often get sick and miss lessons, which will cause gaps in knowledge, lower academic performance and "falling out" from the life of the class team.
It is important that the child is physiologically ready for school: he must have a strong hand with stable fine motor skills, immunity is formed, correct posture is developed, and the musculoskeletal system is developed. A weakened child will often get sick and miss lessons, which will cause gaps in knowledge, lower academic performance and "falling out" from the life of the class team.
Reason 4.
Poor communication skills.This problem often accompanies children who are raised at home. The child does not know how to listen to other people's adults, does not know how to interact with peers, and works unproductively in a team.
Reason 5.
Lack of a clear daily routine.The child may not get enough sleep and be tired. In this case, the material will be assimilated with difficulty.
Reason 6.
Wrong methods of education. Parents try to force their children to study through threats, ridicule, harsh punishments. There can be no motivation based on fear.
There can be no motivation based on fear.
Reason 7.
Excessive requirements for the child.It is important that your expectations match your child's abilities. Most often, the motivation of children is “killed” by their parents.
How to generate interest in learning
Is your child a poor learner? Does he not want to go to school and do his homework? Then it's time to take action.
Step 1.
Find the cause.This is the most difficult task. Try to drop all the accusations against the teachers and look at the situation from the outside. Motivation is absent in several cases:
- Lack of learning ability: low intelligence.
- Lack of formation of educational activities.
- Mistakes of upbringing.
In the first case, you need the help of a specialist - a correctional teacher or defectologist. Only they can confirm this version.
In the second case, the child may need to hire a teacher (tutor).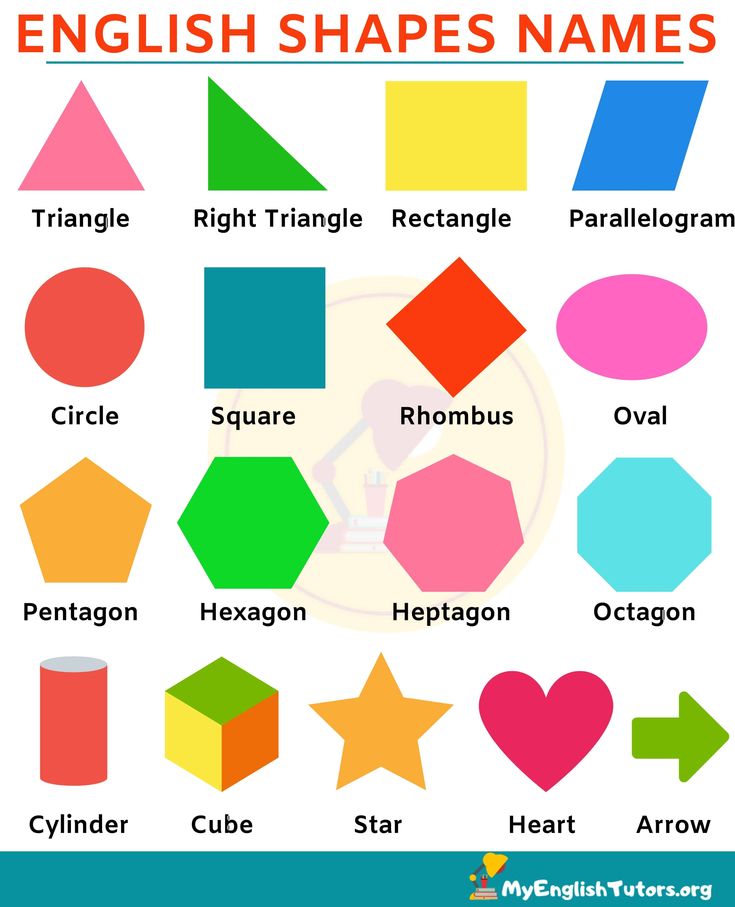 Or you yourself should try to return to the basics of knowledge in order to repeat the material with your child and adjust your learning skills.
Or you yourself should try to return to the basics of knowledge in order to repeat the material with your child and adjust your learning skills.
In the third case, you need to analyze your own behavior.
Step 2.
Admit your mistakes and change your behavior with the child.It is important to take into account the individual characteristics of the child, make changes in the daily routine, take breaks in activities, include “success situations” and in no case threaten your children.
Remember, a struggling child needs help.
Step 3.
Study with your child.Don't be afraid to take the time to learn the rules and learn new things. Find interesting additional material, discuss with your child what he is studying. You must show genuine interest in everything your child is learning.
Step 4.
Determine your child's zone of proximal development. Don't do for your child what he can do for himself with a little guidance.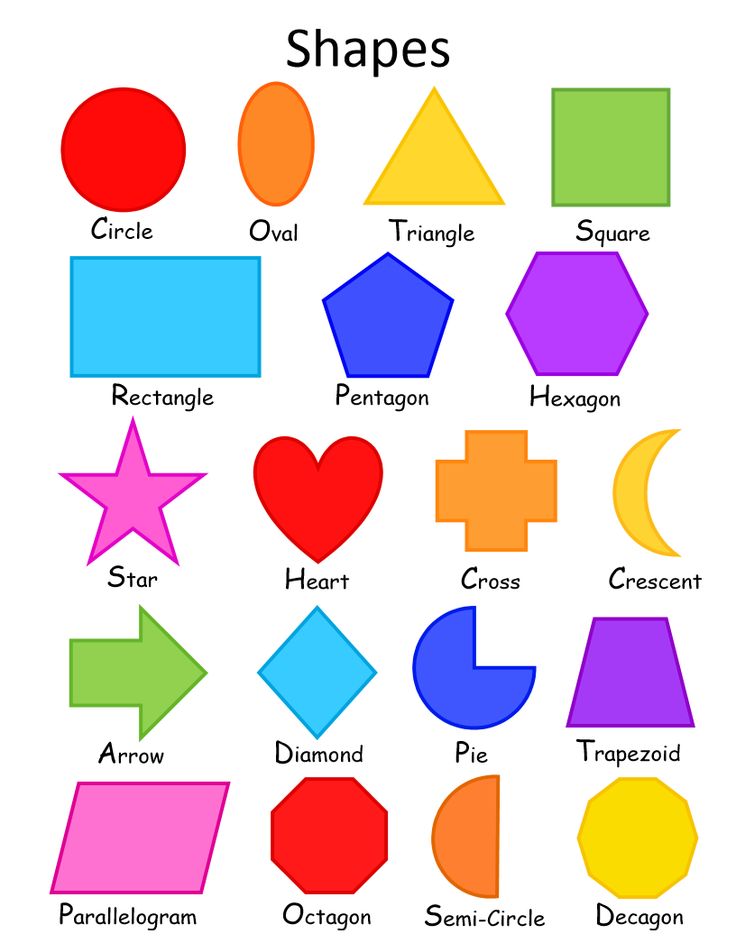 Teach your child to find their mistakes, give hints if necessary.
Teach your child to find their mistakes, give hints if necessary.
Step 5.
Support your child.You know that those who believe in achieve success. Use words of encouragement:
- Well done!
- You did it!
- You will succeed!
- We believe in you!
- Still ahead, we will succeed!
Reward your child for success and teach him to analyze the causes of failure. It is important that the child realizes from childhood that everything is in his hands.
Step 6.
Patience.Do not expect quick results: only long-term systematic work will lead to success. Do not allow yourself breakdowns and scandals.
It's no secret that much in life depends on academic success. Help your child develop a desire to learn.
Svetlana Sadovnikova
Is it good for the child at school? After passing this test, you will find out what kind of relationship your child has with classmates and whether he likes school life.