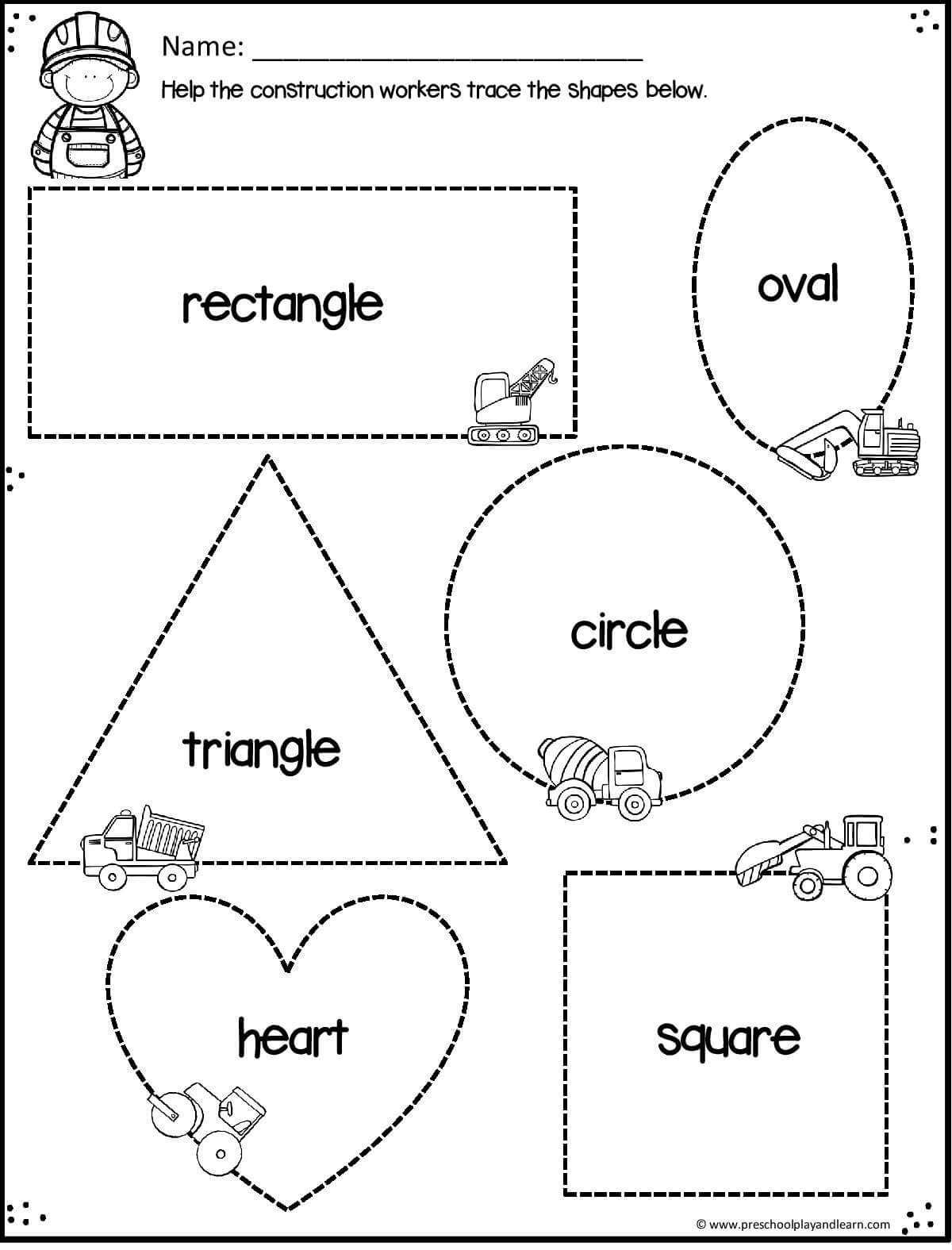
Shapes theme preschool activities
40 Easy And Fun Hands-On Shape Activities For Preschoolers
One of the first math concepts that preschoolers learn is identifying shapes. They begin to distinguish among the different shapes and categorize items according to shape. They learn the names of shapes and their characteristics. They find shapes in everyday items. This collection of shape activities for preschoolers can lead preschoolers to explore shapes in all kinds of ways.
Shapes Activities for Preschoolers
These activities will help your preschoolers learn their shapes. These shape activities for toddlers, will work in your preschool classroom and your kindergarten classroom.
1. Road Shapes with Cars (Pre-K Pages) – 22 printable road shape mats to help your litte learners identify shapes.
2. Making Shapes with Play Dough (Pre-K Pages) – A fun, hands-on playful learning experience that uses play dough to teach shapes!
3. Pattern Block Shapes (Pre-K Pages) – Pattern blocks can actually help your little learners build a strong foundation for learning geometry later.
4. Making Shapes with Geoboards (Pre-K Pages) – If you haven’t tried geoboard activities in your classroom yet, your kids are going to love them!
5. Create a Shapes Photo Book (Pre-K Pages) – To introduce shape concepts to my son, I grabbed the book So Many Circles, So Many Squares from our library as the anchor to our learning ship. Using this book, we went on a shape scavenger hunt and made a fun shape keepsake.
6. Perfect Square Shapes Art (Pre-K Pages) – This Perfect Square art activity is so easy to set up and totally open-ended. It goes perfectly with the book and would be an excellent addition to a shapes unit.
7. Building Shapes with Craft Sticks (Pre-K Pages) – Pair this activity with the book Shapes, Shapes, Shapes by Tana Hoban and you’ve got the perfect low-prep shapes lesson!
8. Teaching 3D Shapes (Pre-K Pages) – Here are some of my favorite ideas for teaching 3D shapes to young children in pre-k or kindergarten. I also wrote some very simple 3D shape songs for you that incorporate hands on learning; keep reading to download the 3D shapes printable song charts.
I also wrote some very simple 3D shape songs for you that incorporate hands on learning; keep reading to download the 3D shapes printable song charts.
9. Nature Shape Scavenger Hunt (Pre-K Pages) – A Star in My Orange is a great way to reinforce shape recognition with your preschoolers. They will also immediately want to run outside for their very own shapes scavenger hunt in nature!
10. The Shape of Things Chalk Drawings (Pre-K Pages) – Shapes are found, identified, and drawn in all preschool classrooms! Discovering just how often circles, squares, and triangles occur in our everyday life make them relevant to children.
11. Shape Wands (Pre-K Pages) – Make some shape wands and turn your home or classroom into the perfect place for kids to learn and identify shapes.
12. Shape Exploration (Pre-K Pages) – After reading the wonderful book Mouse Shapes by Ellen Walsh, I thought it would be fun to make a mouse that could be used in a shape game. The mice in the book explore shapes so, why shouldn’t we?
The mice in the book explore shapes so, why shouldn’t we?
13. Make a Tortilla Shape Snack (Pre-K Pages) – We have the perfect recipe for exploring a math concept. Read aloud one great children’s book. Make a healthy and yummy treat. Combine the two together and you have a lesson on shapes.
14. Shapes Word Chart (Pre-K Pages) – This word chart focused on shapes but you can make a word chart for any topic.
15. “I Have Who Has” Shapes Game (Prekinders) – You may have seen the “I Have, Who Has” card games circulating the internet a lot lately, so this is a fun twist for Pre-K to teach shapes.
16. Games and Activities for Teaching Shapes (Prekinders) – Here are a fun few ways to teaching shapes, like shape bingo and a memory game.
17. Tracing Shapes on the Flannel Board (Teach Preschool) – A wonderful way to introduce letters and shapes while building pre-writing skills!
18. Hunting for Shapes (Teach Preschool) -Explore shapes with a fun and interactive game!
19. Exploring Shapes with Blocks on a Table Top (Teach Preschool) – A simple and engaging exploration of shapes and colors!
Exploring Shapes with Blocks on a Table Top (Teach Preschool) – A simple and engaging exploration of shapes and colors!
20. Learning Shapes by Rolling a Ball (Hands On As We Grow) – Try a fun hands on activity for toddlers for a creative twist to learn shapes!
21. Finding Shapes at the Playground (Buggy and Buddy)- Just print out the free shape hunt printable and go searching for shapes at the playground with this fun geometry activity for children!
22. Geometric Shapes Math Activity (Little Bins for Little Hands) – This simple geometric shapes activity for kids is easy to do at home or as a math center in school. It also makes a terrific STEAM project including a bit of art and design too.
23. Gruffalo Themed Shape Animals (Educators’ Spin on It) – Exploring shapes with young children can be such fun when you involve a few animal friends from The Gruffalo.
Shapes Activities for Preschoolers
24. Feed the Shape Monster Game (Imagination Tree) – Make a fun activity for preschoolers and school aged kids with this feed the hungry shape monsters sorting game!
25. Sticky Shape Bugs Activity (Mom Inspired Life) – This was a great way to develop fine motor skills and critical thinking skills while learning about shapes.
Sticky Shape Bugs Activity (Mom Inspired Life) – This was a great way to develop fine motor skills and critical thinking skills while learning about shapes.
26. Learning Shapes with Spaghetti Noodles (Teaching Mama) – Looking for a fun way to teach shapes? Well here’s a very fun way using spaghetti noodles! This hands-on activity also is a great sensory activity.
27. Matching Shapes to Outlines (Busy Toddler) – Create this fun easy DIY shape mat to practice shapes with your preschoolers.
28. Chalk Shapes Jumping Game (Craftulate) – All you need for this shape activity is some sidewalk chalk!
29. Open and Closed Polygons Game (JDaniel4’s Mom) Grab some LEGOs and have fun with these polygon games, like hockey!
30. Shape Sensory Squish Bag (Still Playing School) – Create this sensory squish bag with triangles, circles, and squares. It’s irresistible to touch and talk about in the window or on the table. It’s super easy to make, too!
31. DIY Shape Puzzles (Munchkins and Moms) – If you have some Jenga blocks and markers, then this easy DIY shape puzzle will be a fun engaging activity for your preschoolers.
32. Stamping Shapes in Kinetic Sand (Still Playing School) – Stamping shapes into kinetic sand is a great opportunity to work on shape identification, count the sides and corners, and compare and contrast the shapes.
33. Making Trucks from Shapes (Powerful Mothering) – Using your wooden blocks to draw and create trucks!
34. DIY Waldorf Square (Rhythms of Play) – An easy DIY toy for kids made with wooden blocks and liquid watercolor paints.
35. Magazine Shape Hunt and Sort (Mom Inspired Life) – This magazine shape hunt is jam-packed with learning! Kids will learn shapes while they practice cutting, gluing and sorting. It’s also an awesome way to work on critical thinking and observation skills.
36. Building Rockets with Shapes (Stir the Wonder) – Building rockets with shapes is a fun way to review shapes and colors with toddlers and preschoolers!
37. Build on Shape Outlines (Brick by Brick) – Use wooden blocks in a new fun way and work on shapes at the same time!
38. Shapes in Our Neighborhood Book (Munchkins and Moms) – Go for a walk and look for shapes in the neighborhood and then create a photo book after!
Shapes in Our Neighborhood Book (Munchkins and Moms) – Go for a walk and look for shapes in the neighborhood and then create a photo book after!
39. Sorting Shapes in the Sensory Bin (Learning 4 Kids) – Your preschoolers will practice their shapes and fine motor skills while having fun with this shape sensory bin.
40. I Spy Shape Hunt (Munchkins and Moms) – Create these fun easy spy glasses and go on a shape hunt!
Follow my Shapes Pinterest Board for more great ideas!
2D Shape Activities for Preschool, Pre-K, and Kindergarten
Learning about 2D shapes is a must for every early childhood classroom. I’m here to share with you my favorite, go-to 2D shapes activities! Some teachers may do a shapes theme or unit (like me), some may do a shape of the week, and some sprinkle in shape activities all year long. These activities will work for all types of classrooms and teaching styles! Grab your lesson plan binder, and let’s get started! Want all shape printables now? You can find them in my Shapes Unit on TPT HERE.
This post contains affiliate links.
Shape Manipulatives
When setting up a shape activity, the first thing I do is go into my supply closet and pull out all my shape games, manipulatives, and puzzles. Pattern blocks, shape cookies, and shape magnet blocks are distributed into various classroom centers. Students need to be playing, manipulating and creating with shapes all over the classroom, not just in the math center!
I love this 2D & 3D shape building set! It’s a ton of fun and comes with shape cards.
Toothpick Shapes
Toothpick Shapes are a fun and interactive way to learn shapes! Students can make shapes with toothpicks and play dough or marshmallows. When teaching your little learners about shapes, it’s important to teach about the sides and vertices too. Use those big vocabulary words! Feel, touch and count the number of sides and vertices a shape has. Don’t forget that a circle doesn’t have any sides or vertices!
In the Discovery Center: Learning about math and science
In the discovery center, I set up a shapes exploration table. The wall has shape posters with real photographs, the back of the table is lined with shape building cards and manipulatives and translucent shapes. There is a sorting board with shape flashcards on top. It’s just a poster board I made with tape. Super simple! The basket is filled with real objects and shape cards students can sort. This exploration table gives students the opportunity to talk about, touch, feel, build, and manipulate shapes with a peer or independently.
Shape Building Blocks Cards! This is a close up of the building block shape cards. Students use the blocks to create the shape on the card. After the shape theme is over, put the shape building cards in with your manipulatives or STEM drawers!
Geoboard shape cards! I put these shape geoboard cards in my geoboard basket. Students can make the shapes with loom bands on the geoboard. To introduce this activity, I put it out for table time as an arrival activity. It’s also great to build those little fine motor muscles too!
Shape cover up! Cover up is a fun game to practice matching shape! Students spin the spinner and cover the matching shape. I love these translucent spinners for my math games. This game is in my Shapes pack. It comes in four different levels.
Shapes graph it! This is another fun shapes game that my students love. It’s also a great opportunity to talk about more, less and equal to. Try using magnet bingo chips to cover the graph then using a magnet wand at the end to make the game even more exciting.
In the Sensory Table
This shape sensory table is filled with shaped manipulatives and a few cupcake pans for sorting. It has foam shape beads, shape chains and translucent shapes. Perfect for sorting, lacing, and linking together. And you guessed it, it’s great for their fine motor, too!
Transition Activity
Shape sort! Transition activities are the perfect time to do a quick assessment or learning check. We have snack after music and movement time. I always plan a transition activity for that time for several reasons. The first is so the whole class isn’t lined up at the same time to wash their hands, which is just asking for crazy behaviors to occur. The second is because it’s another time I can squeeze in more learning! What I do is call on a student and give them a card to sort. It’s a quick and easy way for me to check and see if they know or don’t know a shape.
In the Library Center
Sand writing trays with shape flashcards! Students can write and draw shapes in the sand. This tray is from a lacing set but you can use any small tray you have. I know some teachers use foil pie plates or kid plastic divided dinner plates for writing trays.
Shape mini books! After we make a shape mini books together during small group or table time, I put them in the center. They LOVE making them! Staplers scare me a bit with my little learners so I put in this stapleless stapler! It’s amazing!
Shapes emergent reader! For a small group activity, students create their own shape emergent reader. After they are complete and we have read them a few times together, they are put in the library center for students to read.
In the Art Center
My students LOVE play dough trays so I try to make one for each theme we do. In this activity, they create play dough shape monsters. Students use the shape cookie cutters to create the body. Then add arms, legs, eyes and hair using cut up pipe cleaners, small popsicle sticks, toothpicks, and googly eyes. The tray is from the Dollar Tree.
Play dough shape mats! Students can create play dough shapes on these shape mats. They can make the shape by rolling play dough snakes or by molding the dough.
Shape Prints! It’s great fine motor and makes beautiful pieces of art for your classroom. We cut up paper towel tubes for this circle printing project.
We printed with wooden shape blocks too!
Shape collages! It’s important to provide activities for students to create new items using shapes. In fact, it’s a learning objective/standard in many states. Students need to be able to manipulate shapes to create new shapes, objects or pictures. Shape collages are the perfect activity to address this learning objective.
Single shape collages! You can also have students create shape collages using just one kind of shape. One year my students were struggling with triangles so we created triangle shape collages. Students were finding triangle shapes, talking about triangles (how they are alike and different), and making pictures with triangles!
Dramatic Play
You can change the dramatic play center to so many different things for a shape theme but my favorite thing to do is a Pizza Restaurant. There are shapes all over a pizza restaurant. The pizzas can be different shapes and the slices too! Then the toppings are so many different shapes too. You should totally try it!
Make learning about shapes FUN by providing your students with hands-on learning experiences and play! Want all the 2D Shape printables in this post? Click HERE to grab my 2D Shapes unit from my TPT store. It’s packed with over 200 pages of shape building cards (legos, geoboards, popsicle sticks, toothpicks, play dough), posters, sorting mats, worksheets, games & MORE.
Learning about shapes is a fun theme and concept to do with little learners and you can check more fun shape activities by clicking on the image below!
Love these shape activities? Pin this image!
Consultation for teachers on the topic: "Formation in children of senior preschool age of readiness for joint activities with peers in a preschool educational organization" | Consultation (senior group):
Published on 08/30/2020 - 02:17 PM - Galina Veniaminovna Tretyakova
the subject of relations with oneself, other children, adults and the world. Modern domestic pedagogy is actively building its new human-oriented paradigm. The personality of the child with its inherent originality of character and behavior is placed at the center of the modern educational process. The question of upbringing is not only a question of the means and methods of upbringing, but also a question of moral values, norms and rules that a person has perceived and which is guided in communicating with people. At the same time, there are negative trends in the system of preschool education: excessive focus on the intellectual development of the child, technologization of modern life, which lead to underdevelopment of the emotional and communicative spheres, and as a result of this, the formation of an inadequate attitude towards peers. Therefore, one of the main tasks in senior preschool age should be the formation of readiness for joint activities with peers. The priority of universal human values, the humanistic principle underlying the modern educational process, requires the development of such a type of human relations as joint activities, co-creation, partnership, the ability to work in a team, which contribute to the formation of a person who freely expresses himself in the social and spiritual spheres.
To form readiness for joint activities with peers, such forms as exercises for joint interaction (in pairs, triplets, small groups), individual exercises, role-playing games, discussion and playing out problem situations can be used. Such methodological methods of forming readiness for joint activities are used, such as: demonstrating "positive" and "negative" ways of interacting with a game character, another adult, a child and their subsequent discussion, switching the child's attention from an adult to a peer, creating a situation of lack of material, creating situations of choice: tasks, method of execution, material, partner, development of rules for interaction and fixing them with the help of symbols.
The program for the formation of readiness of children of senior preschool age for joint activities with peers in a preschool educational organization. Based on the results of primary diagnostics, we have developed a program for the formation of readiness for joint activities of older preschool children with their peers in a preschool educational organization. The purpose of the program: to increase the level of formation of the readiness of older preschoolers for joint activities with their peers. Program objectives: 1. Development of interest in each other and interaction with peers as a manifestation of the natural need for joint activities. 2. Formation among preschoolers of generalized ideas about the structure of joint activities and the development of a single "group language" that determines the interaction of partners in the process of jointly solving educational and cognitive problems. 3. Practical development of the basic methods of joint activities. 4. Development of the ability of older preschoolers to independently select a model of joint activity to solve an educational problem. This program is designed for children of senior preschool age (5-7 years). The program includes 10 lessons. The recommended duration of classes is 25 minutes once a week. Classes are held 48 in subgroups of up to 6 people. Class protocols are presented in Appendices 2-11. The program implementation period is from January 2017 to March 2017. Table 4 The program for the formation of the readiness of older preschool children for joint activities with peers No.
Name of the GCD Purpose of the GCD Time of the GCD Terms 1. Problem situations of staging with "talking dolls" Formation of basic ideas about the structure of joint activities 25-30 minutes 3rd week of January 2. Joint activity on the application "Children's World" To form practical skills of joint activity 25-30 minutes 4th week of January 3. Didactic game "Ladder" Recognize the need to control and coordinate each other's actions in the process of activity. 25-30 minutes 1st week of February 4. Modeling lesson “Confectionery shop” To form practical skills for joint activities 25-30 minutes 2nd week of February 5. Story from the picture “Bump to bump” Mastering speech structures for joint activities 25 -30 minutes 3rd week of February 6. Lesson on manual labor "Furniture factory" To form practical skills of joint activity 25-30 minutes 4th week of February 7. Lesson on manual labor "Repair of books" To form practical skills of joint activity 25-30 minutes 1st week of March 8. Compilation of a story based on the fairy tale "Cockerel - Golden Comb" Master basic communication skills for joint activities 25-30 minutes 2nd week of March 9.
Collective panel "In the sky, on earth and at sea" To form practical skills of joint activity 25-30 minutes 3rd week of March 10. Collective work "Spring clearing" To form practical skills of joint activity 25-30 minutes 4th week of March 49
Download:
Preview:
Formation of readiness in children of senior preschool age
for joint activities with peers
in a preschool educational organization
In the Federal State Educational Standard for Preschool Education, one of the tasks is to form readiness for joint activities with peers, develop the abilities and creative potential of each child as a subject of relationships with himself, other children, adults and the world. Modern domestic pedagogy is actively building its new human-oriented paradigm. The personality of the child with its inherent originality of character and behavior is placed at the center of the modern educational process. The question of upbringing is not only a question of the means and methods of upbringing, but also a question of moral values, norms and rules that a person has perceived and which is guided in communicating with people. At the same time, there are negative trends in the system of preschool education: excessive focus on the intellectual development of the child, technologization of modern life, which lead to underdevelopment of the emotional and communicative spheres, and as a result of this, the formation of an inadequate attitude towards peers. Therefore, one of the main tasks in senior preschool age should be the formation of readiness for joint activities with peers. The priority of universal human values, the humanistic principle underlying the modern educational process, requires the development of such a type of human relations as joint activities, co-creation, partnership, the ability to work in a team, which contribute to the formation of a person who freely expresses himself in the social and spiritual spheres.
To form readiness for joint activities with peers, such forms as exercises for joint interaction (in pairs, triplets, small groups), individual exercises, role-playing games, discussion and playing out problem situations can be used. Such methodological methods of forming readiness for joint activities are used, such as: demonstrating "positive" and "negative" ways of interacting with a game character, another adult, a child and their subsequent discussion, switching the child's attention from an adult to a peer, creating a situation of lack of material, creating situations of choice: tasks, method of execution, material, partner, development of rules for interaction and fixing them with the help of symbols.
The program for the formation of readiness of children of senior preschool age for joint activities with peers in a preschool educational organization. Based on the results of primary diagnostics, we have developed a program for the formation of readiness for joint activities of older preschool children with their peers in a preschool educational organization. The purpose of the program: to increase the level of formation of the readiness of older preschoolers for joint activities with their peers. Program objectives: 1. Development of interest in each other and interaction with peers as a manifestation of the natural need for joint activities. 2. Formation among preschoolers of generalized ideas about the structure of joint activities and the development of a single "group language" that determines the interaction of partners in the process of jointly solving educational and cognitive problems. 3. Practical development of the basic methods of joint activities. 4. Development of the ability of older preschoolers to independently select a model of joint activity to solve an educational problem. This program is designed for children of senior preschool age (5-7 years). The program includes 10 lessons. The recommended duration of classes is 25 minutes once a week. Classes are held 48 in subgroups of up to 6 people. Class protocols are presented in Appendices 2-11. The program implementation period is from January 2017 to March 2017. Table 4 The program for the formation of the readiness of older preschool children for joint activities with peers No.
Name of the GCD Purpose of the GCD Time of the GCD Terms 1. Problem situations of staging with "talking dolls" Formation of basic ideas about the structure of joint activities 25-30 minutes 3rd week of January 2. Joint activity on the application "Children's World" To form practical skills of joint activity 25-30 minutes 4th week of January 3. Didactic game "Ladder" Recognize the need to control and coordinate each other's actions in the process of activity. 25-30 minutes 1st week of February 4. Modeling lesson “Confectionery shop” To form practical skills for joint activities 25-30 minutes 2nd week of February 5. Story from the picture “Bump to bump” Mastering speech structures for joint activities 25 -30 minutes 3rd week of February 6. Lesson on manual labor "Furniture factory" To form practical skills of joint activity 25-30 minutes 4th week of February 7. Lesson on manual labor "Repair of books" To form practical skills of joint activity 25-30 minutes 1st week of March 8. Compilation of a story based on the fairy tale "Cockerel - Golden Comb" Master basic communication skills for joint activities 25-30 minutes 2nd week of March 9.
Collective panel "In the sky, on earth and at sea" To form practical skills of joint activity 25-30 minutes 3rd week of March 10. Collective work "Spring clearing" To form practical skills of joint activity 25-30 minutes 4th week of March 49
Preview:
Formation of readiness in children of senior preschool age
for joint activities with peers
in a preschool educational organization
In the Federal State Educational Standard for Preschool Education, one of the tasks is to form readiness for joint activities with peers, develop the abilities and creative potential of each child as a subject of relationships with himself, other children, adults and the world. Modern domestic pedagogy is actively building its new human-oriented paradigm. The personality of the child with its inherent originality of character and behavior is placed at the center of the modern educational process. The question of upbringing is not only a question of the means and methods of upbringing, but also a question of moral values, norms and rules that a person has perceived and which is guided in communicating with people. At the same time, there are negative trends in the system of preschool education: excessive focus on the intellectual development of the child, technologization of modern life, which lead to underdevelopment of the emotional and communicative spheres, and as a result of this, the formation of an inadequate attitude towards peers. Therefore, one of the main tasks in senior preschool age should be the formation of readiness for joint activities with peers. The priority of universal human values, the humanistic principle underlying the modern educational process, requires the development of such a type of human relations as joint activities, co-creation, partnership, the ability to work in a team, which contribute to the formation of a person who freely expresses himself in the social and spiritual spheres.
To form readiness for joint activities with peers, such forms as exercises for joint interaction (in pairs, triplets, small groups), individual exercises, role-playing games, discussion and playing out problem situations can be used. Such methodological methods of forming readiness for joint activities are used, such as: demonstrating "positive" and "negative" ways of interacting with a game character, another adult, a child and their subsequent discussion, switching the child's attention from an adult to a peer, creating a situation of lack of material, creating situations of choice: tasks, method of execution, material, partner, development of rules for interaction and fixing them with the help of symbols.
The program for the formation of readiness of children of senior preschool age for joint activities with peers in a preschool educational organization. Based on the results of primary diagnostics, we have developed a program for the formation of readiness for joint activities of older preschool children with their peers in a preschool educational organization. The purpose of the program: to increase the level of formation of the readiness of older preschoolers for joint activities with their peers. Program objectives: 1. Development of interest in each other and interaction with peers as a manifestation of the natural need for joint activities. 2. Formation among preschoolers of generalized ideas about the structure of joint activities and the development of a single "group language" that determines the interaction of partners in the process of jointly solving educational and cognitive problems. 3. Practical development of the basic methods of joint activities. 4. Development of the ability of older preschoolers to independently select a model of joint activity to solve an educational problem. This program is designed for children of senior preschool age (5-7 years). The program includes 10 lessons. The recommended duration of classes is 25 minutes once a week. Classes are held 48 in subgroups of up to 6 people. Class protocols are presented in Appendices 2-11. The program implementation period is from January 2017 to March 2017. Table 4 The program for the formation of the readiness of older preschool children for joint activities with peers No.
Name of the GCD Purpose of the GCD Time of the GCD Terms 1. Problem situations of staging with "talking dolls" Formation of basic ideas about the structure of joint activities 25-30 minutes 3rd week of January 2. Joint activity on the application "Children's World" To form practical skills of joint activity 25-30 minutes 4th week of January 3. Didactic game "Ladder" Recognize the need to control and coordinate each other's actions in the process of activity. 25-30 minutes 1st week of February 4. Modeling lesson “Confectionery shop” To form practical skills for joint activities 25-30 minutes 2nd week of February 5. Story from the picture “Bump to bump” Mastering speech structures for joint activities 25 -30 minutes 3rd week of February 6. Lesson on manual labor "Furniture factory" To form practical skills of joint activity 25-30 minutes 4th week of February 7. Lesson on manual labor "Repair of books" To form practical skills of joint activity 25-30 minutes 1st week of March 8. Compilation of a story based on the fairy tale "Cockerel - Golden Comb" Master basic communication skills for joint activities 25-30 minutes 2nd week of March 9.
Collective panel "In the sky, on earth and at sea" To form practical skills of joint activity 25-30 minutes 3rd week of March 10. Collective work "Spring clearing" To form practical skills of joint activity 25-30 minutes 4th week of March 49
On the topic: methodological developments, presentations and abstracts
Consultation for teachers on the topic: “Formation of spatial representations in preschool children with visual impairment as the basis of mental activity”
Consultation for teachers on the topic: "The formation of spatial representations in preschool children with visual impairment as the basis of mental activity" ...
Consultation for teachers "The development of intellectual abilities in children of senior preschool age through the organization of chess games in kindergarten"
Chess is a very ancient game.0045
Program content Tasks: Educational: to clarify, summarize the knowledge of children about the features of some professions: journalist, doctor, actor, photographer, policeman, salesman. Show the importance of labor ...
Synopsis of joint activities with preschool children using modern educational technologies: information and communication, personality-oriented
Synopsis of joint activities with preschool children "What are the professions" using modern educational technologies: information and communication, personality-or...
Consultation for teachers on the topic: "Formation of a healthy lifestyle in preschool children"
The main thing for teachers should be the formation of a culture of health as part of the general culture of a person - awareness of health as a vital value, fostering a responsible attitude ...
Pedagogical cognitive research project to familiarize children of senior preschool age Topic: "Formation of initiative in children of senior preschool age with the help of experimental research activities"
A preschool child is a tireless researcher who wants to know everything, understand everything, understand everything, he has a peculiar, special vision of the world around him, he looks around at what is happening . ..
Consultation for teachers on the topic:
In kindergarten, the concept of tolerance is not given, such concepts as friendship, compassion, love, understanding and peace are more common. These concepts are a component of tolerance. Tolerance is an evil topic...
Share:
Theme 4. Child development at preschool age
Theme 4. Child development at preschool age
1. Physical and mental development of a preschooler.
2. Development of the personality of a preschooler.
1. Physical and mental development of a preschooler
Chronological framework (age limits) - From 3 to 6-7 years.
Physical development. During this period, the anatomical formation of tissues and organs, an increase in muscle mass, ossification of the skeleton, the development of the circulatory and respiratory organs, and the weight of the brain increase. The regulatory role of the cerebral cortex increases, the rate of formation of conditioned reflexes increases, the second signaling system develops
Social situation. The child has a great desire to comprehend the semantic basis of the actions of adults. The child is excluded from active participation in the activities and relationships of adults.
Leading activity Role-playing game. At the age of 2-3 years, “single games” are pronounced in children, the child is focused on his own actions. Gradually, children begin to “play side by side”, uniting purely outwardly, since everyone should have their own toy.
At the age of 3-5, “short-term associations” appear, the duration of communication depends on the ability to create and implement a game plan and on the possession of game actions; the content of the game is not yet conducive to sustainable communication.
At the age of 4-6, “long-term associations of players” arise, the child strives to reproduce in the game the actions of adults and their relationships. The child has a need to have a partner. In the game, there is a need to negotiate with each other, to organize a game with several roles together.
Mental development. The development of differentiated sensitivity is noted. There is a development of sensory standards , the formation of perceptual actions. At 3 years old, the child manipulates the object without trying to examine it, they name individual objects. At 4 years old, the child examines the object, highlights the individual parts and features of the object. At 5-6 years old, the child systematically and consistently examines the subject, describes it, and establishes the first connections. At the age of 7, the child already systematically, systematically examines the subject, explains the content of the picture
perception of space, time and movement develops, the child perceives works of art.
Social perception develops as the ability to perceive and evaluate relationships with other people.
Stability of attention depends on the nature of perceived objects. This age period is characterized by a different ratio of involuntary and voluntary attention in different types of activity. There is a formation of stability and concentration of attention.
Ideas are being developed as the basis of figurative memory. There is a transition from involuntary memory to arbitrary. The productivity of memorization is affected by the attitude and nature of the activity. Children develop eidetic memory. The past and the future appear in the structure of the child's self-consciousness.
thinking is characterized by a transition from visual-effective to visual-figurative thinking (4-5 years), the formation of the simplest forms of reasoning (6-7 years), causal thinking appears at the age of six. There is a development of methods of mediation, schematization, visual modeling (6-7 years). At the age of 4, thinking is formed in the process of objective actions. At the age of 5, thinking precedes objective action. At 6-7 years old, children transfer a certain mode of action to other situations, elements of verbal-logical thinking appear.
The development of imagination depends on the experience of the child, imagination affects the creativity of children. Imagination is accompanied by a bright emotional coloring. Game and visual activity affects the development of the imagination.
Speech is mastered as the main mechanism of the child's socialization. Phonemic hearing, active and passive vocabulary develops, the vocabulary and grammatical structure of the language are mastered. At the age of 5 there is an awareness of the sound composition of the word, at the age of 6 children master the mechanism of syllabic reading.
2. Personal development of preschoolers
Personal development . There is a development of self-consciousness, it is formed due to intensive intellectual and personal development. There is a critical attitude to the assessment of an adult and a peer. Peer assessment helps you evaluate yourself. In the second half of the period, based on the initial purely emotional self-assessment and rational assessment of someone else's behavior, self-assessment. By the end of preschool age, a correct differentiated self-assessment, self-criticism develops. At 3 years old, the child separates himself from the adult; about himself, about his qualities yet does not know. At the age of 4-5, he listens to the opinions of other people, evaluates himself on the basis of the assessments of the elders and his attitude to the assessments; seeks to act in accordance with his gender. At 5-6 years old, assessment becomes a measure of the norms of behavior, evaluates on the basis of accepted norms of behavior, evaluates others better than oneself. At 7 years old, the child tries to evaluate himself more correctly.
The development of arbitrariness of all processes takes place - one of the most important moments of mental development. The volitional behavior of a preschooler is largely due to the assimilation of moral attitudes and ethical standards. Capriciousness, stubbornness and negativism in crisis periods of development do not indicate a weak development of the will.
At this age, children are characterized by variability in the manifestation of temperament, the maturation of the properties of the nervous system, the type of temperament affects behavior in various activities. The basic qualities of the personality develop, personal qualities are formed under the influence of self-awareness, and imitation affects the development of character. In various activities, abilities, talent is manifested in activity. Creativity is being formed as a basic characteristic
Communication motives develop at preschool age. There is a formation of subordination (hierarchy) of motives. Children are guided by the assessment of adults, this serves as the basis for the development of motives for achieving success.
The main influence on the development of emotions and feelings is exerted by one of the neoplasms of age - self-consciousness (inner world). The inner experiences of the preschooler become more stable, feelings develop. Participation in gaming and other activities contributes to the development of aesthetic and moral feelings.
Communication with adults differs at different ages: at 3-5 years old, communication is extra-situational-cognitive (objects and phenomena of the surrounding world are learned). At the age of 5-7 years - extra-situational-personal (recognize the features of the relationship between peers and adults and the characteristics of their personality). Communication with peers has the character of game cooperation, children learn empathy.
Neoplasms at preschool age. The beginning of the development of arbitrariness. The ability to generalize experiences. Moral development. Ability to perceptual modeling. socialized speech. The development of visual-figurative and the emergence of verbal-logical thinking. The emergence of the "inner world".
Crisis 7 years - is a crisis of self-regulation, reminiscent of a crisis of 1 year. According to L.I. Bozovic is the period of the birth of the social "I" of the child. The child begins to regulate his behavior by rules. Basic need - respect. Loss of childish spontaneity (mannering, antics). Generalization of experiences and the emergence of inner mental life. The ability and need for social functioning, for occupying a significant social position.
Assignments for independent work
1. Get acquainted with modern research on the problem of preschool childhood. List the main issues considered by the author of the article you like.
- Dyachenko OM On the main directions of the development of the imagination of preschoolers // Questions of psychology.
- 1988. - №6. - P.52.
- Yakobson S.G., Doronova T.N. Psychological principles of the formation of initial forms of educational activity in preschoolers // Questions of Psychology. -1988. - No. 3. -WITH. 30.
- Yakobson S. G., Moreva G. I. Self-image and moral behavior of a preschooler // Questions of Psychology. - 1989. - №6. - P.34.
- Sokhin F. A. Psychological and pedagogical problems of the development of speech of preschoolers // Questions of psychology. - 1989. - №3. - P.39.
- Sinelnikov VB Formation of figurative thinking in preschoolers // Questions of psychology. - 1991. - №5. – P.15.
- Kataeva A. A., Obukhova T. I., Strebeleva E. A. On the genesis of the development of thinking in preschool age // Questions of Psychology. - 1991. - №3. – S. 17.
- Veraksa IE, Dyachenko ON Ways of regulation of behavior of preschool children // Problems of Psychology. - 1996. - №3. – P.14.
- Kolominsky Ya. L., Zhuravsky BP Socio-psychological features of joint play and work activities of preschoolers // Questions of Psychology.
- 1986. - №5. - P.38.
- Yakobson S. G., Safinova I. N. Analysis of the formation of the mechanisms of voluntary attention in preschoolers // Questions of Psychology. - 1999. - №5. – C.3.
- Ermolova T. V., Meshcharikova S. Yu., Ganoshenko N. I. Features of personal development of preschoolers in the pre-crisis phase and at the stage of the crisis of 7 years // Questions of Psychology. - 1999. - №1. – P.50.
- Poddyakov NN Dominance of integration processes in the development of preschool children // Psychological journal. - 1997. - No. 5. - P.103-112.
- Kamenskaya V. G., Zvereva S. V., Muzanevskaya N. I., Malanov L. V. Differential psychophysiological signs of motivational influence on the efficiency of intellectual activity of older preschoolers // Psychological Journal. - 2001. - №1. – S. 33.
- Sergienko E. A., Lebedeva E. I. Understanding of deception by children of preschool age in the norm and with autism // Psychological journal.
-2003. -#4. –p.54.
- Elkonin D. B. Children's game // World of psychology. - 1998. - No. 4. - S. 58-64.
- Smirnova E. O. Playing with the rules as a means of developing the will and arbitrariness of a preschooler // World of Psychology. - 1998. - No. 4. – P.64-74.
- Abramenkova VV The game forms the child's soul // World of Psychology. - 1998. - No. 4. - P.74-81.
- Tendryakova M. V. Game and expansion of semantic space (mutual transitions of game and reality) // World of Psychology. - 2000. - №3. - P.113-121.
- Zanchenko N. U. Conflict characteristics of interpersonal relationships and conflicts between children and adults // World of Psychology. - 2001. - №3. - P.197-209.
- Senko T.V. The relationship of personal behavior, the emotional-need sphere and the sociometric status of an older preschooler // Adukatsia i vykhavanne. - 1997. - №3. - P.35-44.
- Korosteleva MM Improving the quality of preschool education in Belarus // Education and training.
- 2004. - №10. – P.28.
- Lebedeva IV Psychological analysis of manifestations of aggression and anxiety in a preschooler // Education and Excercise. - 2004. - №11. – C.3.
- Ermakov VG On the problems of developmental education in the field of mathematical education of preschoolers // Education and training. - 1996. - No. 8. –S.9-19.
- Abramova LN Peculiarities of interrelations between preschoolers in joint activities // Education and training. - 1996. - No. 10. - P.43-55.
- Abramova LN Influence of the nature of contacts between an adult and a child on the behavior and emotional manifestation of complaints of a preschooler. - 1998. - No. 4. - P.24-30.
2. Give answers to the following questions:
a) why, when communicating with peers, even dull ones, the child expands his vocabulary much better than when communicating with parents?;
b) children aged 5-6 were shown films. In them, men and women performed work that is usually done by members of the opposite sex. The man was a nanny, and the woman was the captain of a large ship. After watching the film, they asked the question: “Who was the nanny and who was the captain?” Give a forecast of possible answers;
c) in young children, behavior is strictly determined by the situation they perceive. Each object pulls the child to touch it, feel it. Objects dictate to him what and how to do. Yes, the door can be opened and closed. This continues until about 3-4 years. How to teach a preschooler to perform an objective action consciously and voluntarily?
List of recommended literature
- Developmental psychology: Textbook for students of higher education. textbook institutions / Ed. V.E. Klochko. - M .: Publishing house VLADOS-PRESS, 2003.
- Kulagina I.Yu., Kolyutsky V.N. Developmental psychology: The complete life cycle of human development: A textbook for students of higher educational institutions. - M.