Teach children social skills
How can I teach my child social skills?
Some children may find socialising more difficult than others. If your child struggles or seems reluctant to be with other people, they may need some support to learn social skills. There are some things you can do to help.
Practise talking
Practise talking through role play, puppets and storytelling. Talk to your child through the day. You can also narrate what you’re doing, to help develop their language.
Let your child see you using good manners, like please and thank you. This will encourage them to act this way with their peers.
Listen and take turns
Children learn both verbal and non-verbal skills from the people around them. To help your child to listen well, you can:
- Try showing them what good listening looks like through your own behaviour.
- Use games like ‘Simon Says’.
- Read some ideas for listening games for toddlers.
Find ways to make taking turns fun. Choose an object and tell your family they have to be holding it when they talk. Pass it between you. If your child is a little older, take it in turns to make made up sounds as if you are having an alien conversation.
Show the importance body language
Practise making eye contact and smiling with your child. If they are old enough to understand, ask them to talk about something while you use poor body language. This could be crossed arms, looking away, or fidgeting.
Ask them how your actions made them feel. Then show them attentive body language. Take it in turns.
Teach them about personal space
Consider teaching your child about personal space. Try:
- Asking them to put their hands on their hips and stick their elbows out – this is their personal space.
- Getting everyone in the room to walk around with their elbows out, to see how to give others space.
Introduce the idea of boundaries by asking if you can come into their space. You could say things like, “Can I give you a hug?” or ‘I know you don’t like hugs so shall we high five?”
You could say things like, “Can I give you a hug?” or ‘I know you don’t like hugs so shall we high five?”
Develop their emotional skills
Help your child understand, express and cope with emotions. This develops their empathy for others and helps them sense how to react to the emotions of others.
Teach them to problem-solve. If they’re old enough, ask them how they think they could tackle any issues they have. Guide them with questions like “What could you do?” or “What could you say?” Try to avoid fixing it for them.
You can also talk to them about friendships and what it is to be a good friend. If you can, arrange and support opportunities for socialising.
Find moments for learning in play
Children use lots of social skills when playing. It can be helpful to spot opportunities in play for learning. You can:
- Ask your child to help with tasks, and see if they’ll try activities with others, to build teamwork skills.

- Teach your child positive ways of responding to winning, losing or not getting their way.
- Show them you understand when they’re upset, but help them see what the positives could be (might the outcome have made their friend happy?).
- Show them what sharing looks like when playing at home.
If your child hits or bites, help them recognise how others feel when they’re hurt. Praise your child when you see them playing well. You can also gently encourage your child to apologise if they do hurt someone during play. Or if they don’t feel comfortable doing this, model apologising for them until they feel more confident. You could say something like, “Freddie feels sad that he’s hurt you and he wants to say he’s very sorry.”
You can read more on hitting and biting or playing well with others. We also have advice on teaching your child to share.
6 Ways to Improve Your Child's Social Skills
Few things can be more frustrating than watching your child struggle to
make friends or having a difficult time fitting into certain social settings.
There are several steps parents can take to improve their child's social skills.
1. Follow Their Interests
Enjoying others will come more naturally when a child is doing something they are genuinely interested in. Whether it's participating in a favorite sport, playing an instrument they like or being part of a club they're interested in, this is the first step toward building social skills. It also places a child around like-minded individuals that the child will probably feel more at ease with. While it's important to be able to socialize with those of varying interests, starting out with other kids who like the same things is an excellent way to more easily build social skills.
2. Learn to Ask Questions
Sometimes when children get nervous or a conversation lags, they may become more introverted and ultimately struggle in future social situations. According to the Center for Development & Learning there are several ways children can initiate and carry on positive conversations with others. One important way is to ask questions. The best way to find out about others and form connections is to ask questions that specifically pertain to the person the child is talking with. Encourage your child to ask questions that can't be answered with just a yes or no.
One important way is to ask questions. The best way to find out about others and form connections is to ask questions that specifically pertain to the person the child is talking with. Encourage your child to ask questions that can't be answered with just a yes or no.
3. Practice Role Playing
Pretend-play, with both younger and older children, is a great way for kids to actively practice their social skills. LD Online gives parents practical tips for effective role-playing. Have your child pretend to be the person they have difficulty talking to or getting along with. This will give you an idea of what this person is like, or at least how your child perceives this particular person. Then switch roles to see how your child does when pretending to interact with the person. Suggest ways your child can more effectively talk with the individual. Don't forget to include body language, such as smiling and making eye contact, when advising your child.
4. Teach Empathy
If children have a better understanding of how others feel, they are much more likely to feel connected to other people and form positive bonds. Parents suggest teaching empathy by talking about different situations and scenarios with your child. Ask how other people might feel when each of these things happen. Part of teaching empathy is to help children learn how to actively listen to others. This involves focusing on what others are saying and then thinking about what the speaker has said once the conversation is over.
Parents suggest teaching empathy by talking about different situations and scenarios with your child. Ask how other people might feel when each of these things happen. Part of teaching empathy is to help children learn how to actively listen to others. This involves focusing on what others are saying and then thinking about what the speaker has said once the conversation is over.
5. Know Your Child's Limits
Some children are simply more social than others. A child who is shy and introverted should not be expected to interact in the same way as a child who is naturally outgoing. Some children are comfortable in large settings, while others find it easier to relate to their peers when in smaller groups. It's also important to understand a child's time limits. Younger children and those with special needs may only feel comfortable socializing for an hour or two.
6. Be a Good Role Model
It's important to be consciously aware of how you interact with others when your child is watching. Are you asking questions of others and then taking the time to actively listen? Do you show genuine empathy for friends and family in your life? The Center for Parenting Education states that being an effective role model requires conscious effort and forethought. Children are constantly watching the adults in their lives.
Are you asking questions of others and then taking the time to actively listen? Do you show genuine empathy for friends and family in your life? The Center for Parenting Education states that being an effective role model requires conscious effort and forethought. Children are constantly watching the adults in their lives.
It's important to remember that it will take time for your child to develop good social skills. Social skills are something that are developed and improved upon over a lifetime.
Contact us today to schedule an assessment. You can also view the research and results of the program on the website.
How to develop social intelligence in a child: 7 tips from a psychologist
Publishing house "Alpina Publisher" 123007, Moscow, st. 4th Magistralnaya, 5, building 1 +74951200704
next article
December 13, 2017
2385 views
6 minutes to read
Success in life is often achieved by people from whom neither teachers nor parents expected it.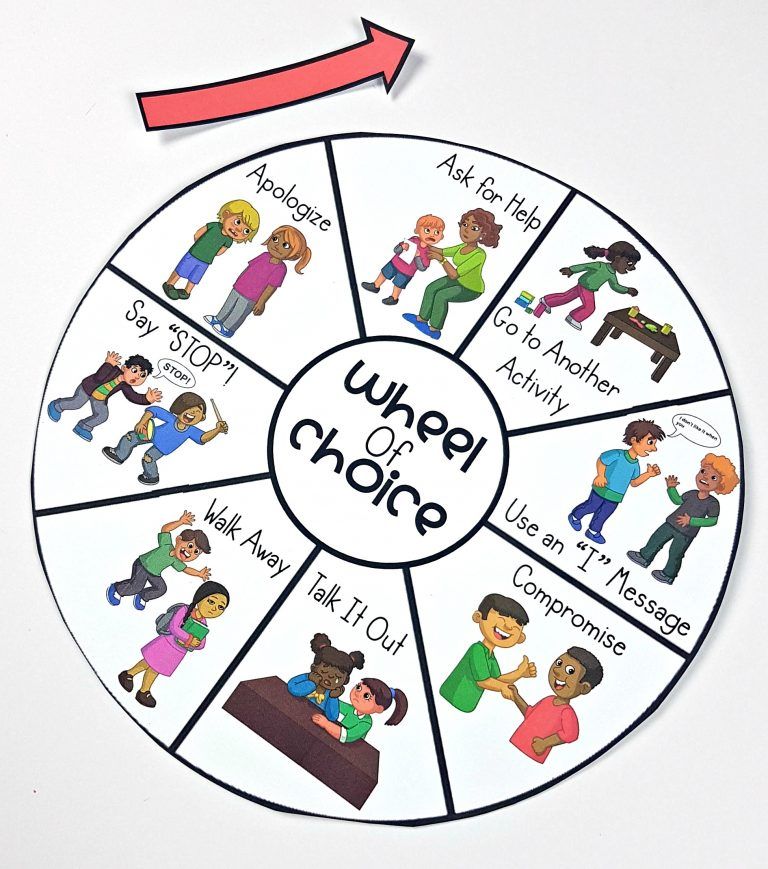 “A bully, a slacker, a C student” suddenly turns out to be much more successful than his classmates, who spent all their childhood sitting at textbooks. The answer is not in "accidental luck" or "happy fate", but in social intelligence. Our social adaptation, the ability to understand people and, ultimately, success depend on how developed it is.
“A bully, a slacker, a C student” suddenly turns out to be much more successful than his classmates, who spent all their childhood sitting at textbooks. The answer is not in "accidental luck" or "happy fate", but in social intelligence. Our social adaptation, the ability to understand people and, ultimately, success depend on how developed it is.
Social intelligence, unlike formal intelligence, can be developed. And it is better to start doing this from an early age. How exactly?
- Pay attention to who and how the child communicates. To begin with, we need to take the most objective position and look at the child's social circle. Where and with whom does he spend his free time? Does he have real (and not virtual) friends with whom he meets regularly, visits them? Does he have the opportunity to choose friends on his own? Or do we conduct a thorough audit of his acquaintances and, in an attempt to protect him from bad influence, we forbid him to communicate with "unequal", "bad" boys and girls? Does he know how to get out of difficult situations, resolve conflicts, or does he run to his parents for help?
- Expand the child's social circle.
 By limiting the child's contacts, we inhibit the development of his social skills. Growing up, he goes out into the world, not understanding how to live in it and how to interact with people who live in this world. There is a rule in aikido training: each athlete must work out the same technique with the maximum number of sparring partners, because with each of them it will be a little different - the athlete learns to see the strengths and feel for the weaknesses of the opponent, adapt to his height , weight, speed, and at the same time find their advantages. That is why the child must communicate with people of different ages, different material wealth and cultural levels. He must practice his social skills.
By limiting the child's contacts, we inhibit the development of his social skills. Growing up, he goes out into the world, not understanding how to live in it and how to interact with people who live in this world. There is a rule in aikido training: each athlete must work out the same technique with the maximum number of sparring partners, because with each of them it will be a little different - the athlete learns to see the strengths and feel for the weaknesses of the opponent, adapt to his height , weight, speed, and at the same time find their advantages. That is why the child must communicate with people of different ages, different material wealth and cultural levels. He must practice his social skills. - Give experience of various social situations. Relationships with people are always a risk. We are all different, someone likes you, and someone annoys and repels you. Someone can treat you kindly, and someone can intrigue. For full development, children need unplanned, unexpected, sometimes even conflict situations.
 The experience of getting into and out of such situations helps to develop social immunity. The child got into a fight - let's not rush to figure out who is right and who is wrong. It’s better to ask him what happened, and together we will discuss how it was possible to resolve the conflict peacefully and how to behave in the future.
The experience of getting into and out of such situations helps to develop social immunity. The child got into a fight - let's not rush to figure out who is right and who is wrong. It’s better to ask him what happened, and together we will discuss how it was possible to resolve the conflict peacefully and how to behave in the future. - Use social equipment. Even if a child is driven in a car with a personal driver, it is useful for him to take a ride on the subway or tram from time to time. Traveling by public transport is an ideal option for practicing social skills. Despite the apparent simplicity, even the ability to correctly find a place in the cabin is developed gradually. Which one is considered good? The place where we do not interfere with others and no one interferes with us, from where you can clearly see what is happening around. The task of “squeezing between people” is solved much easier if you turn to your neighbors with the words: “Are you not going out now? Please let me pass!” The child learns from experience that words are much more effective than brute force.

- Teach communication boundaries. For successful social interaction, it is very important for a child to learn to understand the boundaries of the personal space of other people and try not to violate them. This is especially true for the boundaries of strangers - in public places, on the street, in a restaurant, on an airplane, on a train. For example, a child rushes screaming around the restaurant from table to table - you need to stop him and say that he is bothering everyone. And if he does not understand, punishment should follow. Demanding compliance with external boundaries, we thereby give impetus to the formation of internal self-control, that is, the ability to monitor ourselves, cope with our impulses, emotional outbursts.
- Learn to understand your feelings and the feelings of other people. Life sets tasks for the child, for the fulfillment of which it is necessary to achieve something from people with different views, values and characters.
 To successfully cope with these tasks, it is necessary to be able to understand and anticipate the behavior of other people, evaluate their motivation, intentions and determine who can be trusted and who cannot. But often we ourselves do not know what we feel - resentment or anger, annoyance with ourselves or envy of another, joy or satisfaction. The ability to recognize your feelings is a very useful skill. Only by learning to understand our feelings can we learn to empathize, that is, to understand the feelings of other people.
To successfully cope with these tasks, it is necessary to be able to understand and anticipate the behavior of other people, evaluate their motivation, intentions and determine who can be trusted and who cannot. But often we ourselves do not know what we feel - resentment or anger, annoyance with ourselves or envy of another, joy or satisfaction. The ability to recognize your feelings is a very useful skill. Only by learning to understand our feelings can we learn to empathize, that is, to understand the feelings of other people. - Teach the child to respond adequately in various communication situations. In the big world, the child will have to solve his own problems, win a place under the sun, determine who is a friend and who is not. Somewhere you have to step aside, somewhere you need to agree and compromise, somewhere you need to actively insist on your own and directly express your opinion. To do this, the child's arsenal should have many ways to respond and cope with different situations.
 The more diverse the child's experience, the more rehearsals he had, the more convincingly he will play the performance called "life".
The more diverse the child's experience, the more rehearsals he had, the more convincingly he will play the performance called "life".
Our poor rich children
Marina Melia
Cover with valves
Out of stock
More
Issue
The most interesting thing is in your mail.
We send a digest of the best articles every two weeks.
By completing this form, I confirm that that I have read the Rules of the site, and I consent to the processing personal data.
reCAPTCHA is used in accordance with the Google Policies and Terms of Use.
Thank you for subscribing!
See also
How to bring up initiative in a child: 7 tips from a psychologist
See also
How to talk to a child to make contact
See also
"Silver Spoon Syndrome": we gave the child everything, but he is not happy
When copying materials, place
an active link to www. alpinabook.ru
alpinabook.ru
Social skills of preschoolers - the development of social skills in children
The development of social skills is a necessary point of education. A child with a high degree of socialization will quickly get used to kindergarten, school, any new team; in the future will easily find a job. Social skills have a positive effect on interpersonal relationships - friendship, the ability to cooperate.
Understand what social skills are.
What are social skills and why develop them?
Social skills - a group of skills, abilities that are formed during the interaction of a person with society and affect the quality of communication with people.
Man is a social being: all our talents and aspirations are realized thanks to other members of the group. Others evaluate our actions, approve or condemn our behavior. It is difficult to reach the pinnacle of self-actualization alone.
This is why social skills are important. They should be developed from early childhood and honed throughout life.
Social skills are a reflection of the child's emotional intelligence, to which educators and teachers assign an important role in the process of personality development. Without this group of skills, a smart child will not be able to apply the acquired knowledge in practice: it is not enough to create something outstanding, you need to be able to correctly convey thoughts to the public.
Sometimes people mistakenly believe that social skills relate exclusively to the topic of communication, communication. In fact, skills include many multidirectional aspects: an adequate perception of one's own individuality, the ability to empathize, work in a team, etc.
Why do we need social skills?
- Regulate the area of interpersonal relationships: the child easily makes new friends, finds like-minded people.
- Minimize psychological stress: children with developed social skills quickly adapt, do not feel sad due to changes in external circumstances.

- They form an adequate self-esteem from childhood, which positively affects life achievements and development in adulthood.
- Social skills cannot be separated from building a successful career: the best specialists must not only understand the profession, but also have high emotional intelligence.
Development of social skills in a child
Social skills need to be developed from preschool age, but older children and even teenagers may well learn to interact with the world.
It is recommended to pay attention to areas of life that bring discomfort to the child, significantly complicate everyday life.
- Friends, interesting interlocutors: the kid does not know how to join the team, he prefers to sit in the corner while the others play.
- Verbal difficulties. The child does not understand the rules of conversation, is poorly versed in the formulas of etiquette (when you need to say hello, say goodbye, offer help).

- Problems with the non-verbal side of communication. Such a baby does not recognize the shades of emotions, it is difficult to understand how others relate to him. Cannot "read" faces and gestures.
- Does not know the measure in expressing a point of view: too passive or, conversely, aggressive.
- The child bullies classmates (participates in bullying) or is a victim.
In case of severe moral trauma, one should consult a psychologist: for example, school bullying is a complex problem that children are not able to cope with on their own. The involvement of parents and teachers is required.
In other cases, family members may well be able to help the child develop social skills.
What are the general recommendations?
1. Be patient
Don't push your child to get the job done. Let them take the initiative: for example, do not rush to help during school gatherings, let the baby work on the problem on his own. The same goes for lessons and other activities.
The same goes for lessons and other activities.
2. Support undertakings
Children's dreams seem trifling to adults, but the initiative turns into a habit over the years and helps to discover new projects, meet people, and experiment.
3. Criticize the right way
When making negative comments, remember the golden rule of criticism: you need to analyze the work, highlighting both positive and negative aspects in a polite manner. Commenting on the specific actions of the child, and not his personality or appearance - this will lead to problems with self-esteem.
4. The right to choose
It is important for children to feel that their voice is taken into account and influences the course of events. Invite your child to personally choose clothes, books, cartoons. Ask about ideas, plans: “We are going to have a rest together at the weekend. What are your suggestions?
5. Personal space
Make sure that the baby has a place where he can be alone and take a break from talking. Personal things should not be touched: rearrange without prior discussion, read correspondence with friends, check pockets, etc.
Personal things should not be touched: rearrange without prior discussion, read correspondence with friends, check pockets, etc.
Children, noticing the respectful attitude of adults, quickly begin to pay in the same coin; the atmosphere in the family becomes warm and trusting.
What social skills should be developed in a child?
Let's dwell on the main qualities and skills, the development of which is worth paying attention to.
1. The ability to ask, accept and give help
Without the ability to ask for help, the child will deprive himself of valuable advice; the lack of the ability to accept help will lead to losses, and the inability to provide help will make the baby self-centered.
- Let the child help those in need: for example, a lagging classmate.
- Explain to your child that getting help from friends and teachers is not a shame.
- Show by personal example that mutual help enriches experience: tell how you exchange advice with colleagues, friends.

2. The ability to conduct a conversation and get the right information
Being a good conversationalist is difficult, but the skill is honed over time and brings a lot of benefits.
- Prompt the child for dialogue development options: for example, you can start a conversation with an appropriate question, a request for help.
- Do not leave the child in the role of a silent listener: when discussing pressing issues at home, ask the opinion of the baby.
- Support children's public speaking: reports at school, performances, funny stories surrounded by loved ones will add confidence.
3. Empathy
Empathy is the ability to recognize the emotions of others, put yourself in the place of another person, empathize.
This ability will make the child humane, prudent. How can it be developed?
- Start by recognizing the child's feelings - it is useless to listen to people if the person does not feel personal experiences.
 Ask your baby: “How do you feel after a quarrel with friends?”, “Do you want to relax today?”
Ask your baby: “How do you feel after a quarrel with friends?”, “Do you want to relax today?” - After conflicts with classmates, ask your child how the children with whom the quarrel may feel now.
- While watching cartoons, reading books, pay your child's attention to the emotional state of the characters.
4. Ability to work in a team
Many children can easily cope with tasks alone, but this is not a reason to refuse to work in a team. It gives the opportunity to exchange ideas and experience, delegate tasks, achieve goals faster and more efficiently.
- If the child does not communicate with members of the team, try to introduce him to another social group: for example, the lack of communication with classmates can be compensated by a circle of interests, where the child will feel calmer.
- Make the family a friendly team in which the child has his own "duties": for example, do housework, remind parents of upcoming events.
 Any activity related to the well-being of other family members will do.
Any activity related to the well-being of other family members will do.
5. Respect for personal boundaries
The absence of an obsessive desire to interfere in other people's lives is a valuable skill that helps to win people's sympathy.
- Respect the child's personal boundaries: do not enter the nursery without warning, do not rummage through personal belongings and correspondence, if the life and safety of the baby is not at stake.
- If the child violates other people's boundaries (takes toys without permission, asks uncomfortable questions), talk about it in private.
6. Ability to overcome conflict situations
It is difficult to imagine our life without conflicts. The task of the child is to learn how to culturally enter into a discussion, defend his point of view, and not be led by the provocations of his interlocutors.
- Talk about problems calmly, without raising your voice. Do not put pressure on the child with parental authority unnecessarily: the child is a separate person who has the right to an opinion.

- Do not judge people for views that differ from those of your family but do not affect your well-being. Show your child that the world is very different.
- You can demonstrate to children the basics of a civilized dispute, explain what arguments are, etc. It is advisable to teach this child in kindergarten.
7. Self-confidence
Stable and adequate self-esteem is a quality that not all adults possess.
It is formed under the influence of many factors: relationships between parents, the role of the child in the family circle, the characteristics of the environment that surrounded the child in early childhood.
It is important that the child does not grow up to be either a narcissistic narcissist with fragile self-esteem, or an overly shy person. How can you help your child find balance?
- Praise your child for personal progress: to receive a compliment from parents, it is not necessary to win prizes in school competitions.

Learn more