What are the different types of shapes
Different Shape Names (with Useful List, Types) • 7ESL
Pin
Are you looking for different shape names in English? Here you will find a list of shapes with different types and useful example sentences. If you work in a business that requires the use of mathematics, for example then it would be very important that you are aware of the English names for shapes.
However, this may not be the only reason that you need to learn this information. When taking part in day-to-day conversations, you will need to learn the shape names in order to describe something or be able to understand what someone is talking about, for example, if a person tells you about ‘the square plate.’ Here, you can learn shape names and further expand your vocabulary.
Table of Contents
Shapes
What Are Shapes?
Shapes are geometric figures, or the pattern an outline falls into. Shapes are often drawn (whether by ink, pencil, or digitally), but they occur in life, also. Frequently, people picture 2D (two-dimensional, or flat) images when they hear the word “shapes,” so most of the objects listed in this lesson will be 2D shapes, but some will be 3D as well.
Different Types of Shapes
There are many, many different types of shapes, and there are names for basically all of them. The following list focuses on more common shapes that you’re more likely to encounter or to need or want to know the name of.
Shape names with pictures
Pin
Two-Dimensional (Flat) Shapes
- Circle: A circle is an equally round shape. Picture the lid of a jar, flat, from above. That is a circle. The wheels on a car are circular, as well. So are the holes in most lined paper and notebooks.
- Oval: An oval is basically a circle that’s been a little squished. The cups of over-the-ear headphones are generally referred to as oval. So is the profile of an egg.
 Some make a distinction between circles that have been squished in the middle versus circles that have been squished at the top, the former being called an ellipse, but common usage treats both as ovals.
Some make a distinction between circles that have been squished in the middle versus circles that have been squished at the top, the former being called an ellipse, but common usage treats both as ovals. - Rectangle: A rectangle is a shape with four sides, made up of two sets of parallel lines, with four right angles (90 degree angles; picture a capital L). It doesn’t matter whether the sets of sides are the same length. Picture a plain piece of printing paper. This is a rectangle, with one set of sides (generally the top and bottom) shorter than the other set of sides (generally the left and right).
- Square: A square is a very specific type of rectangle, one with four equal sides. Some boxes have a square footprint. Origami paper is square.
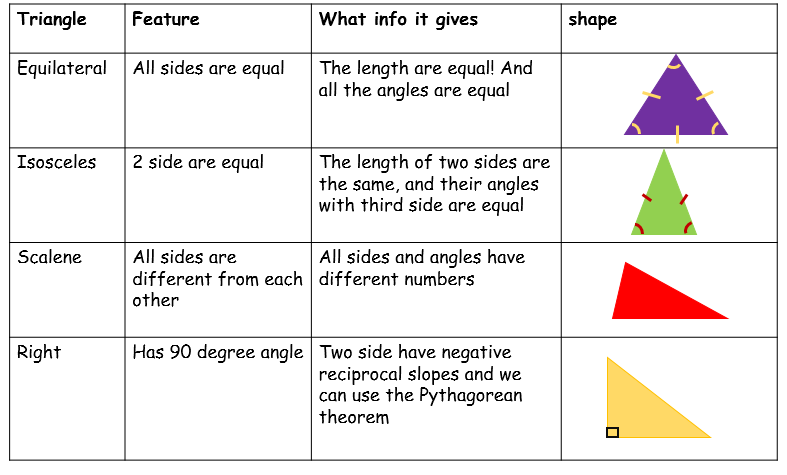
- Triangle: A triangle is a shape with three straight sides. These sides can be any length, with any degree of angle, as long as the three sides are joined at their ends. Many warning signs are triangular.
 A slice of a round pizza is mostly triangular (the crust is a little too rounded to be perfect).
A slice of a round pizza is mostly triangular (the crust is a little too rounded to be perfect). - Pentagon: A pentagon is a shape with five sides. A basic drawing of a house, with two lines for the roof, a line for each side, and a line for the bottom is generally a pentagon.
Shapes with more sides are generally named based on how many sides they have. A hexagon has six sides, heptagon has seven, and an octagon has eight.
Three-Dimensional Shapes
Three-dimensional shapes are ones that aren’t just flat on paper, but also take up room vertically. Only a few are really commonly named.
- Sphere: A sphere is a 3D circle, like a ball.
- Cube: A cube is a 3D square, like a box.
- Pyramid: A pyramid is a 3D triangle. The giant structures in Egypt are pyramids, as is the Luxor in Las Vegas.
Shape Names
It’s important to build a good vocabulary, in any language. The more words you know and understand, the better you can communicate. Even if you don’t use the words often, understanding them allows you to follow along with a conversation, even if it ventures a little outside of your comfort zone. This lesson is specifically focused on different types of shapes.
The more words you know and understand, the better you can communicate. Even if you don’t use the words often, understanding them allows you to follow along with a conversation, even if it ventures a little outside of your comfort zone. This lesson is specifically focused on different types of shapes.
- Nonagon
- Octagon
- Heptagon
- Hexagon
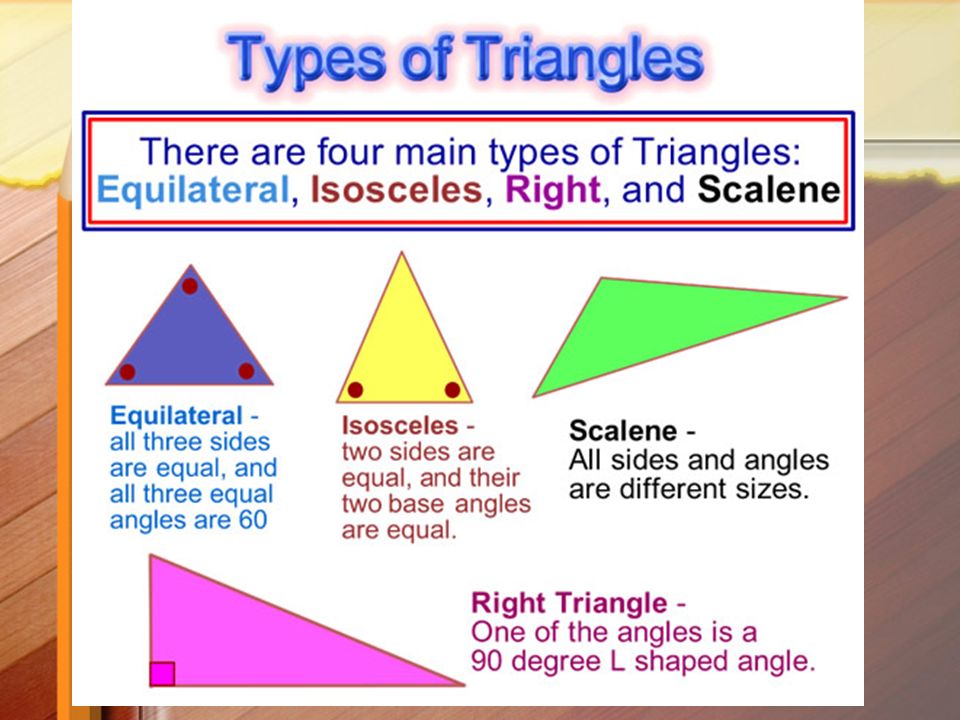
- Triangle
- Scalene triangle
- Right triangle
- Parallelogram
- Rhombus
- Square
- Pentagon
- Circle
- Oval
- Heart
- Cross
- Arrow
- Cube
- Cylinder
- Star
- Crescent
The math student measured each side of the nonagon until he had measurements for all nine edges.
Pin
OctagonThe sectional shape is a quarter of an octagon.
Pin
HeptagonThe pagoda has a base of heptagon.
Pin
HexagonA hexagon is a six – sided figure.
Pin
TriangleThe sum of all the angles of a triangle is 180 degrees.
Pin
Scalene triangleA scalene triangle is a triangle that has three unequal sides.
Pin
Right triangleThe hypotenuse is the longest side of a right triangle.
Pin
ParallelogramThese are the opposite sides of the parallelogram.
Pin
RhombusA rhombus is a simple quadrilateral whose four sides all have the same length.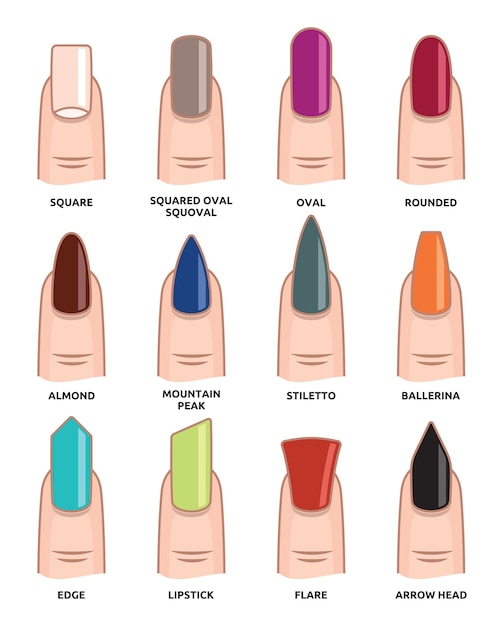
Pin
SquareThe interior angles of a square are right angles or angles of 90 degrees.
Pin
PentagonDraw a pentagon, a regular five-sided figure.
Pin
CircleThe students sit in a circle on the floor.
Pin
OvalThe shape of the earth is an oval.
Pin
HeartThe pool was in the shape of a heart.
Pin
CrossThe cross is the symbol of Christianity.
Pin
ArrowIt flew straight as an arrow.
Pin
CubeThe box was cube-shaped.
Pin
CylinderThe cylinder is rotated 180 degrees.
Pin
StarShe cuts these paper into star-shaped.
Pin
CrescentHe has a crescent–shaped knife.
Pin
Shapes | PictureLearn different shapes with images to improve and expand your vocabulary, especially shapes and colors vocabulary words in English.
PinShapes: Different Shape Names (with Useful List, Types)Shapes Names VideoThere are shapes everywhere, and so references to them happen frequently. Hopefully, after this lesson, you’re feeling prepared to deal with shapes!
Hopefully, after this lesson, you’re feeling prepared to deal with shapes!
Shapes- Definition, Types, List, Examples
LearnPracticeDownload
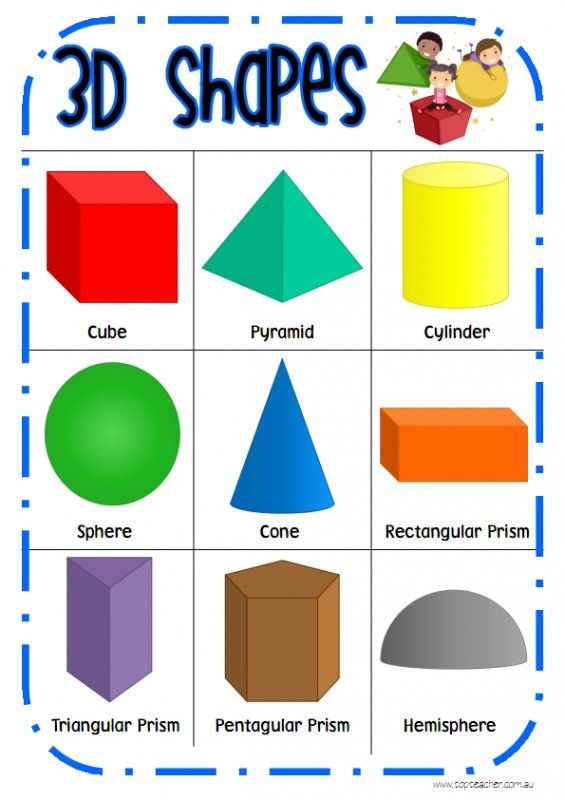
The shape can be defined as the boundary or outline of an object. It is the surface we see and does not depend on the size or the color of the object. Everything around us has a different shape, such as the square, rectangle, or three-dimensional sphere. Have you seen the model of the Earth called the globe? What is the shape of this globe? Have you noticed the shape of a pizza? It is round in shape. If we cut out a slice from the pizza, the slice gets a triangular shape. Let us learn all about shapes, types of shapes, and geometric shapes.
| 1. | What are Shapes? |
| 2. | Types of Shapes |
| 3. | List of Shapes |
| 4. | FAQs on Shapes |
What are Shapes?
Shapes define the boundary of an object and can be differentiated in many ways based on their properties. These shapes are closed by a boundary which is made by combining the curves, points, and line segments. Each shape has a name depending upon the structure. Few shapes are circle, square, rectangle, triangle, and so on.
Types of Shapes
Shapes can be classified into various categories. Before classifying shapes further in separate structures the basis of each shape depends on the following classification:
- Open Shapes: Open shapes are not continuous and are made up of line segments or curves which do not meet.
 Letter C is an example of an open shape.
Letter C is an example of an open shape. - Closed Shapes: Closed shapes can be traced without any break. They start and end in the same place. Letter D is an example of a closed shape.
Further, each shape is classified on the basis of dimensions it has. In this section, we will discuss the two major types of shapes:
- Two-dimensional (2D): 2D shapes, as the name suggests, have only two of these measurements, i.e., length and breadth.
- Three-dimensional (3D) shapes: 3D shapes have a length, a width, and a height. You can learn more about it here.
A square is a 2D shape, whereas, a cube is a 3D shape.
List of Shapes
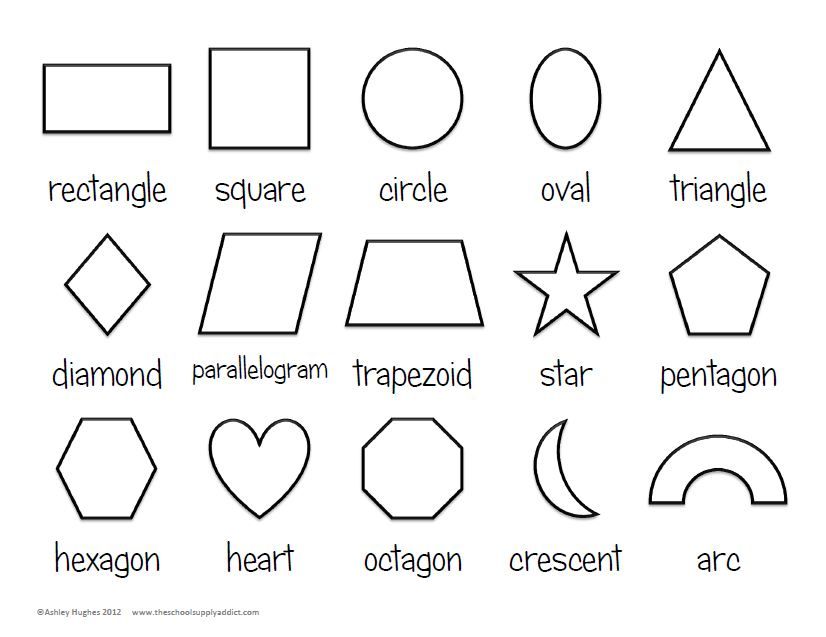
We know that shapes are made of straight lines or curved lines and they can be open or closed. Lines are defined as a collection of points. In other words, many points are put together to form a line. They may form a straight line or a curved line. Shapes are closed shapes that are created by joining lines together. Closed shapes made of four straight lines are called quadrilateral shapes. Given Below is the list of shapes with real-world examples.
They may form a straight line or a curved line. Shapes are closed shapes that are created by joining lines together. Closed shapes made of four straight lines are called quadrilateral shapes. Given Below is the list of shapes with real-world examples.
- Circle: A circle is a closed shape. It is categorized as a two-dimensional geometric shape that is round in structure. It does not have any lines or corners. For example, the wheel of a vehicle, pizza base, dartboard.
- Oval: An oval is an elongated shape slightly similar to a circle. It has no straight lines or corners. For example, the number zero (0).
- Square: A square is a closed 2-D shape that is formed by four sides. The length of each side is equal in measurement. For example, a chessboard and a carrom board.
- Triangle: A triangle is a shape with three sides and is categorized as a two-dimensional geometric shape. For example, the shape of tangy nachos, one slice of cheese burst pizza.

- Rectangle: A rectangle has four sides. It is a two-dimensional geometric shape in which the length of the opposite sides is equal. For example, laptop screen, touch screen mobile phones etc.
- Polygons: A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure with three or more straight lines. For example, windows, doors.
- Cube: A cube is a closed three-dimensional geometric shape. It is made up of six squares. It has six faces. For example, a Rubik's cube, a ludo dice, an ice cube.
- Cuboid: A cuboid is another three-dimensional shape that is formed using rectangles. For example, a duster, a book, a pencil box.
- Sphere: A sphere is a solid shape that is similar to a ball. It is a closed three-dimensional shape formed using a circular base. For example, football, basketball, etc.
- Cylinder: A cylinder is a solid shape that has two flat ends of circular formation. It is a three-dimensional figure which is formed by folding a rectangle.
 For example, coldrink cans, pool noodles, water bottles.
For example, coldrink cans, pool noodles, water bottles. - Cone: A cone is a solid three-dimensional geometric shape with a flat base. The base is circular in shape. It has a pointed edge at the top called the apex. For example, ice-cream cone, clown hat, etc.
☛Related Articles
Check out the following articles to learn more about different shapes in detail.
- Plane Shapes
- Closed Shapes
- 2-D Shapes
- 3-D Shapes
- Geometric Shapes
- Shapes Worksheets
Shapes Examples
-
Example 1: Solve the following riddles and write the name of the shapes.
a) I have three sides and a complete plane surface. Who am I?
b) I am a closed 3D shape formed with six squares. Who am I?Solution:
a) Triangle is a plane 2D shape with three sides.
b) Cube is a closed 3D shape with 6 squares.
-
Example 2: Eva is holding a gaming gadget. Its screen has 4 sides. Can you name the shape of the gadget screen?
Solution: Since Eva has a gaming gadget with specifically four sides. It could be a mobile phone screen or a tablet screen. Hence the shape of a gadget screen is rectangular.
-
Example 3: Name two letters that are perfect examples of a closed shape and an open shape.
Solution: Letter O is a perfect example of a closed shape. It is round in shape hence it is also an example of a circle.
Letter U is an open shape. It is open at the other end.
go to slidego to slidego to slide
Breakdown tough concepts through simple visuals.
Math will no longer be a tough subject, especially when you understand the concepts through visualizations.
Book a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions on Shapes
go to slidego to slide
FAQs on Shapes
What are Shapes in Geometry?
Shapes are also known as geometric shapes and figures made up of fixed lines or curves.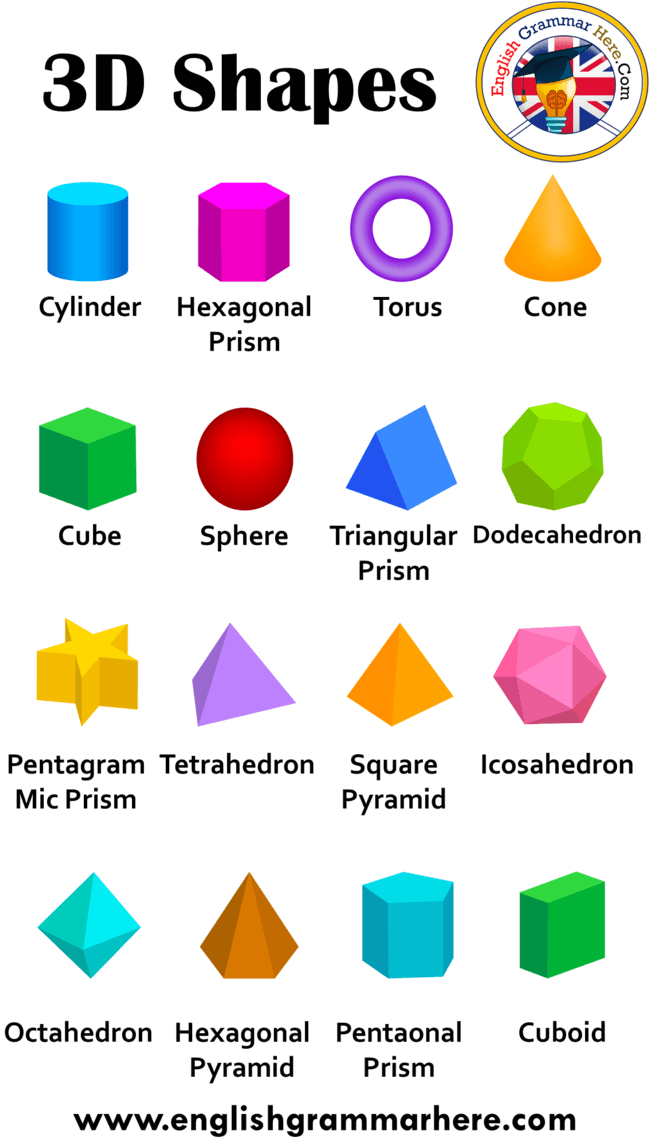 Shapes are categorized as closed shapes or open shapes. In our real-life, the example of shapes are, the Sun, Earth, Doors, Windows, Watch, Wall clocks, and so on.
Shapes are categorized as closed shapes or open shapes. In our real-life, the example of shapes are, the Sun, Earth, Doors, Windows, Watch, Wall clocks, and so on.
What are the Different Types of Shapes?
The shapes have two major types:
- The two-dimensional shapes
- The three-dimensional shapes
What are Two-Dimensional Shapes?
A 2D shape is also written as a two-dimensional shape is a shape that has length and width but no depth. Examples of two-dimensional shapes are Circle, square, rectangle, triangles.
What are Three-Dimensional Geometric Shapes?
In geometry, a three-dimensional shape is a solid shape that has three dimensions, length, width, and height. We generally write it as 3D- shapes. For example, cylinder, sphere, cuboid.
Write the List of Shapes.
There are various shapes categorized on the basis of their dimensions. Given below is the list with one real-world example.
List of 2D geometric shapes:
- Triangle: traffic signboards
- Square: chessboard
- Rectangle: UNO game cards
- Circle: dinner plates
- Oval: Number 0 (zero).
List of 3D geometric shapes:
- Cube: ice cubes
- Cuboid: bricks
- Cylinder: Cold drinks straws
- Sphere: oranges
- Hemisphere: bowls
- Cone: birthday party caps
Why are Shapes Important for Kids?
Shapes help children develop the understanding of identifying visual information about structures revolving around them. It also helps kids in building navigation skills by easily comparing various shapes.
What is the Use of Geometric Shapes?
Shapes refresh our visual senses in an interesting way. They developed and generate a logical sense of any piece of work in our everyday life. Things around us need a definite shape to recognize and to maintain the balance in nature.
How Many Dimensions Are There in a 2D Shape?
There are only two dimensions in a 2D shape that is a length and breadth.
How Many Dimensions Are There in a 3D Shape?
There are only three dimensions in a 3D shape that is a length, width, and height.
How do you Identify Shapes?
A great way to identify a shape is by knowing the number of sides and points in it. For example, a triangle has 3 sides and 3 points. So, we can easily identify it as a triangle.
☛ Also Check:
- Solid Shapes Worksheets
- 2d and 3d Shapes Worksheets
Is Square a Closed Shape?
Yes, a square is a closed shape as all the sides of the square are connected at all the vertices.
Download FREE Study Materials
Shapes Worksheets
Math worksheets and
visual curriculum
what are the forms of government, territorial structure and political regime of the state
How states appeared
Millions of years ago our ancestors lived in communities. They did not have clear boundaries, instead of laws there were customs, and power rested on the authority of the elders. But centuries passed, people became more and more, and the relationship between them became more complicated. To maintain order, a centralized authority arose - people who control society. They created laws and imposed penalties for breaking them. They set boundaries and equipped an army to guard and expand them. They protected the interests of their people and levied taxes from them. So the tribes turned into states.
To maintain order, a centralized authority arose - people who control society. They created laws and imposed penalties for breaking them. They set boundaries and equipped an army to guard and expand them. They protected the interests of their people and levied taxes from them. So the tribes turned into states.
There are several theories about how exactly the state arose:
- Theocratic is the most ancient theory; it was believed that the right to power comes from higher powers.
- Conquest theory - according to it, strong people subjugated the weak and began to rule over them.
- Social contract theory - according to this version, people voluntarily limited themselves in their rights in order to avoid arbitrariness and permissiveness.
- Class - created by the German philosopher and sociologist Karl Marx. According to him, the state is the result of the struggle between the upper and lower classes.
 Marxists believe that slave owners and feudal lords created states to protect themselves from slaves and peasants.
Marxists believe that slave owners and feudal lords created states to protect themselves from slaves and peasants.
The creation of statehood is one of the greatest achievements of mankind, which allowed the development of culture, science, medicine, and raising the standard of living of people. In any case, a more effective way to organize society has not yet been invented.
Definition and features of the state
The state is the main political institution that organizes and controls people's lives.
Any state must have the following features:
- Unity of territory . The state controls a certain territory in which its laws apply.
- Public authority. It extends to all people living in it.
- Legislation. The state issues laws to which everyone who is in its territory must obey.
- Control and coercion apparatus.
 The state monitors compliance with laws and performs other functions: provides social guarantees (benefits, pensions), encourages scientific and cultural achievements, ensures the safety of citizens, and much more.
The state monitors compliance with laws and performs other functions: provides social guarantees (benefits, pensions), encourages scientific and cultural achievements, ensures the safety of citizens, and much more. - Sovereignty . No external forces interfere in the domestic and foreign policy of the state.
- Tax system. The state collects money from its citizens and companies in order to spend them on the implementation of its functions.
<
The concept of the form of the state
The form of the state is a way of organizing state power. This concept includes:
- form of government,
- form of government,
- political regime.
Consider all items in order.
The form of government of the state
It depends on whose hands the power is. There are two forms of government: monarchy and republic .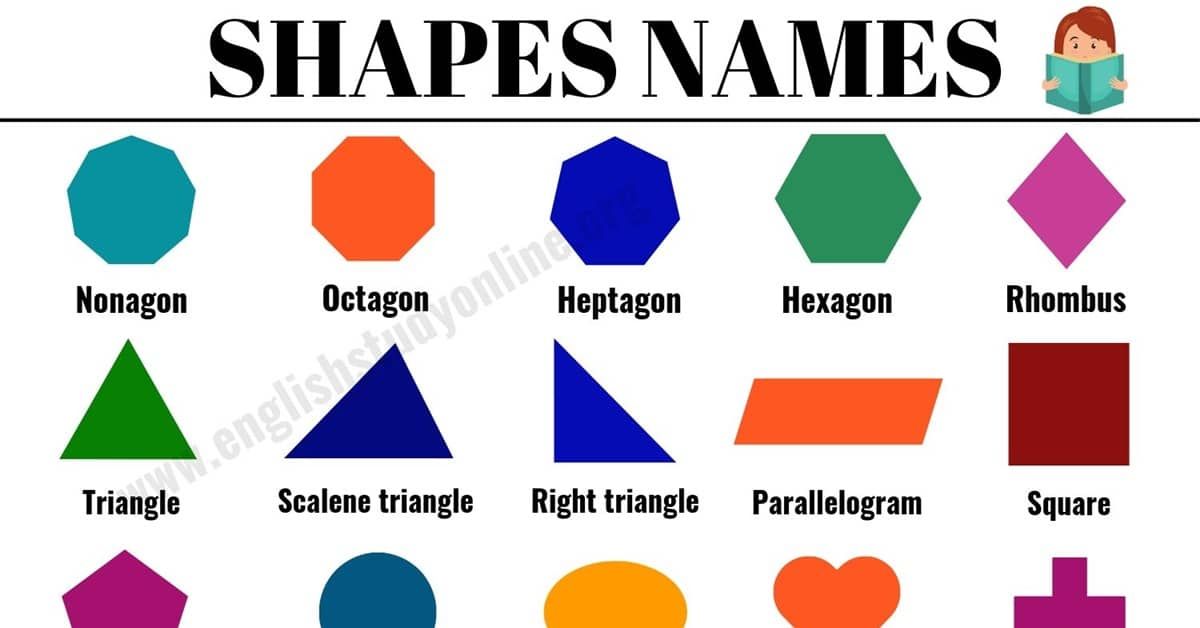
Monarchy
This word is translated from Greek as “one rule”. Monarchies appeared in ancient times and reached the peak of power during the time of feudalism. At the head of such a state is a monarch (king, king, emperor, sultan, shah, raja), who rules the country throughout his life, receiving and passing power by inheritance (although in Malaysia the king is elected for five years).
In absolute monarchy all power (legislative, executive, judicial and sometimes spiritual) belongs to one person who is above the law. This form of state was common from ancient times to modern times, and now there are only six absolute monarchies. These are the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Oman, Qatar, Brunei and the Vatican (the Pope has absolute power in the territory of the Holy See).
B Dual Monarchy The ruler appoints ministers to rule on his behalf. Laws are made by Parliament, but the monarch can veto any of them, dissolve Parliament and convene a new one.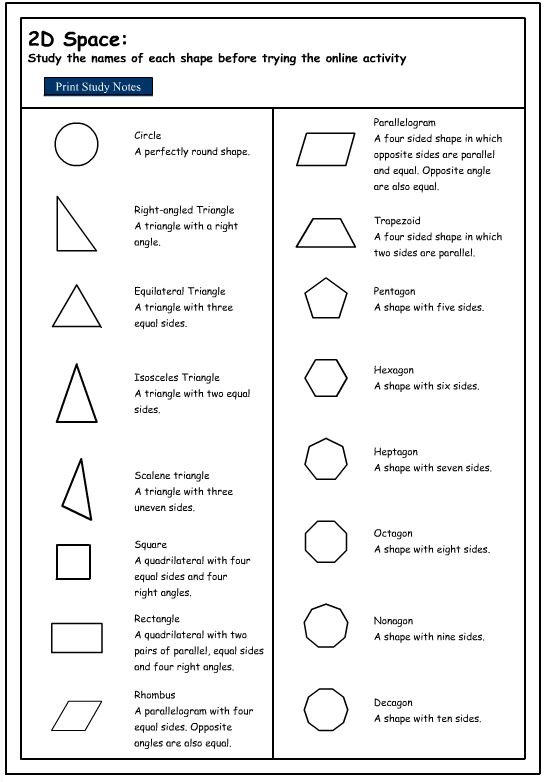 In addition, he himself can issue decrees that have greater legal force than other laws. This form of government was widespread at the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries as a transitional form of government from an absolute monarchy to a parliamentary one. Today there are nine dualistic monarchies in the world, and with the exception of the kingdom of Morocco, they are all small states: the kingdoms of Bahrain, Bhutan, Jordan, Tonga and Eswatini, the principalities of Liechtenstein and Monaco, as well as the emirate of Kuwait.
In addition, he himself can issue decrees that have greater legal force than other laws. This form of government was widespread at the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries as a transitional form of government from an absolute monarchy to a parliamentary one. Today there are nine dualistic monarchies in the world, and with the exception of the kingdom of Morocco, they are all small states: the kingdoms of Bahrain, Bhutan, Jordan, Tonga and Eswatini, the principalities of Liechtenstein and Monaco, as well as the emirate of Kuwait.
In the parliamentary monarchy the supreme ruler has a symbolic meaning. The monarch signs decrees and appoints ministers, but does so at the suggestion of parliament. All judicial, legislative and executive power is vested in constitutionally formed bodies. This is how most modern monarchies, such as Great Britain, Japan, Spain, Norway and Sweden, are arranged.
Learn social studies with Foxford Home Online School! By promo code
SOCIETY92021 you will receive free access to the 9th grade social studies course, which studies the forms of government.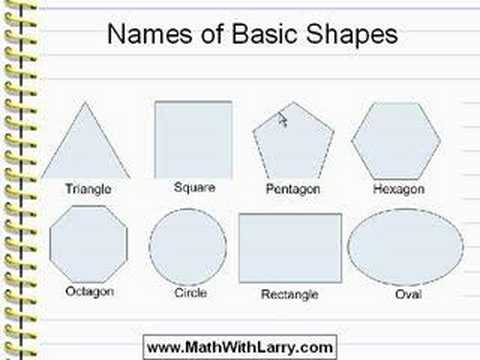
Republic
The phrase “res publica” is translated from Latin as “common cause”. Formally, power in the republic belongs to the people, but in no country are decisions made by the entire population at once. The citizens of the republic elect the parliament and other authorities that govern the country and are responsible to the voters.
The first republics appeared in ancient times (Athenian, Spartan, Roman). In the Middle Ages, city-states (Venice, Florence, Novgorod) were governed in this way. From the end of the 18th century to the middle of the 20th century, many monarchies became republics in the course of reforms or revolutions. Now most of the countries of the world are governed by this model.
There are three types of republics: presidential, parliamentary and mixed. They differ depending on who forms the government and to whom it reports.
In the parliamentary republic the supreme power belongs to the parliament, which is elected from among the political parties.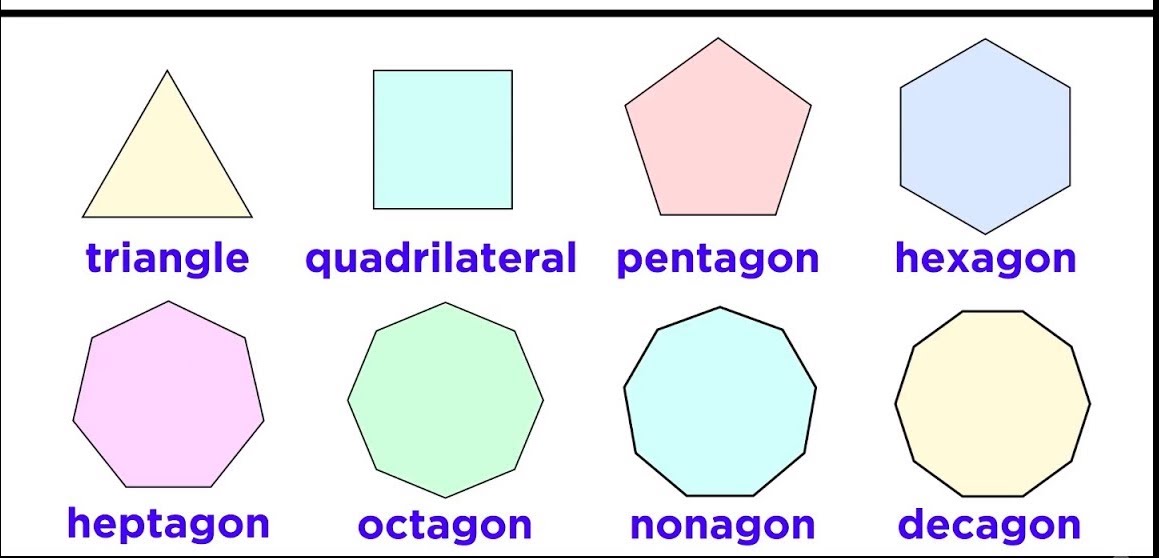 Parliament forms and dissolves the government, elects the president, and makes laws. The president in such a republic represents the state in the international arena and participates in official events. The head of state is the prime minister, usually the leader of the party that won the election. The parliamentary republics are Germany, Turkey, India, Iraq, Poland and Greece.
Parliament forms and dissolves the government, elects the president, and makes laws. The president in such a republic represents the state in the international arena and participates in official events. The head of state is the prime minister, usually the leader of the party that won the election. The parliamentary republics are Germany, Turkey, India, Iraq, Poland and Greece.
In the presidential republic the head of state and government is the president. He appoints and controls ministers, can issue decrees, influence the decisions of parliament and even dissolve it. This form of power in the state resembles a dualistic monarchy, with the difference that the president does not receive power by inheritance and is elected by the people or electors for a limited term. According to this system, power is arranged in the United States and most countries of Latin America.
In mixed republics there is a balance between presidential and parliamentary power.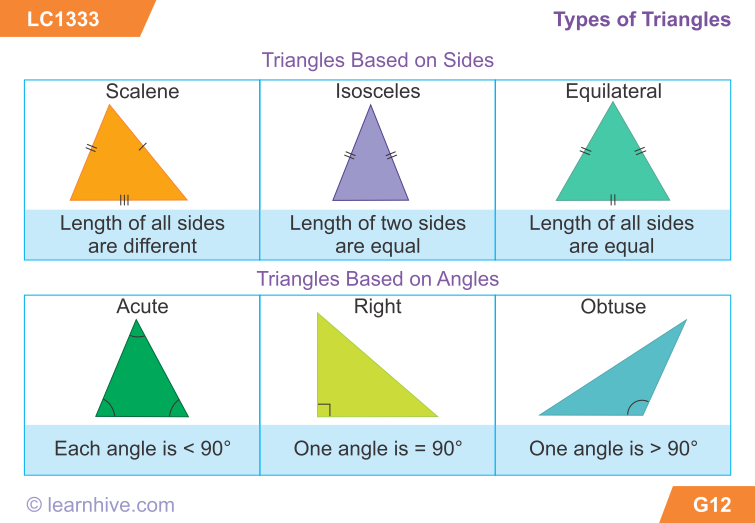 The head of state is the president, but he coordinates all important decisions with parliament. Both the president and parliament are elected by popular vote. Mixed republics are France, Finland, Russia, Ukraine, the Baltic countries.
The head of state is the president, but he coordinates all important decisions with parliament. Both the president and parliament are elected by popular vote. Mixed republics are France, Finland, Russia, Ukraine, the Baltic countries.
Form of government
It determines how power is distributed throughout the country.
Unitary state
The word "unitary" comes from the Latin unis - "one". In such a country, all territories are subject to a single government and a parliament located in the capital. They have the same legislation, constitution and judicial system. This is the case for most countries in the world.
Federal state
The federal state (from the Latin feodus - "union") is more complicated. It is divided into subjects (regions, territories, republics, states), each of which may have its own government, legislation and even constitution. There are 26 federations in the world: Russia, USA, India, UAE, Mexico and other countries.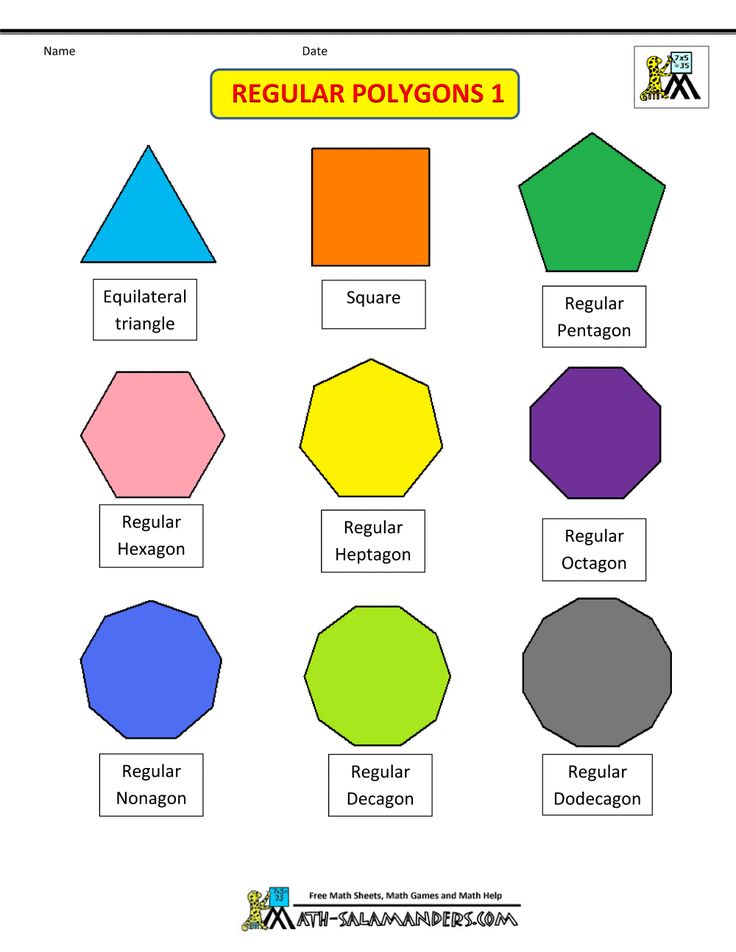
Political regime
This is a complex of methods of governing the country, the nature of the relationship between the authorities and the people. There are usually three types of regime - totalitarian, authoritarian and democratic.
Totalitarianism
Under a totalitarian regime (from the Latin totalis - "complete") the state seeks to control all spheres of people's lives. The basic principle is “ everything that is not allowed by is prohibited”. Only one political party is declared legal in the country, it is forbidden by law to criticize it. Any content (up to personal correspondence) is checked by the state for "dissent". The private life of people is under the supervision of special services, mutual surveillance and denunciations are encouraged in society. The opposition is absent or driven into deep underground. Disobedience to the regime is punishable. The authorities intimidate the population to protect themselves.
In the first half of the 20th century there were many totalitarian states - fascist Italy, Nazi Germany, the USSR under Stalin.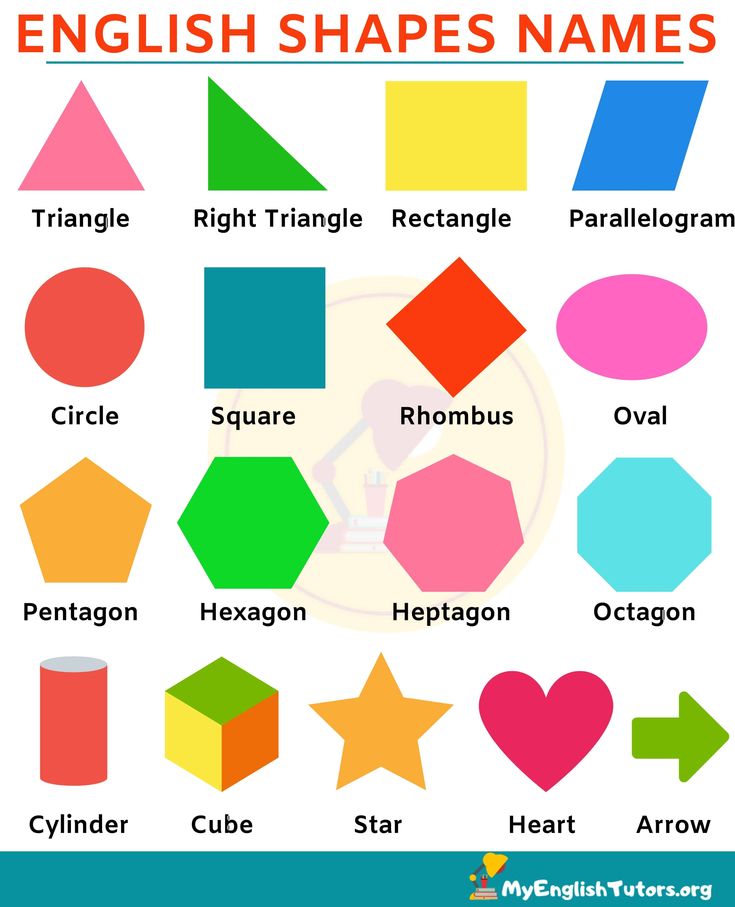 In our time, this regime is preserved in the DPRK.
In our time, this regime is preserved in the DPRK.
Authoritarianism
This word comes from the Latin autoritas - "influence, power, opinion." The principle of an authoritarian regime is " everything is allowed, except for the policy of ". In an authoritarian regime, power, as a rule, belongs to a one-man dictator. The importance of the parliament is insignificant, and the opposition, if it exists, has no real power. Any threats to the current government are immediately destroyed.
The main difference between an authoritarian regime and totalitarianism is more freedom. The authorities tightly control only the political sphere. In addition, if the totalitarian regime openly terrorizes the population, then the authoritarian regime relies on religion and traditional values. As a rule, authoritarianism does not recognize itself as such and disguises itself as democracy.
Examples of authoritarian states: Cuba, Venezuela, Belarus.
Democracy
Translated from Greek, “democracy” means “rule of the people”. The principle of this mode is " everything is allowed that is not prohibited by . In a democracy, society can effectively influence government through elections and referendums. The media are not subject to the political regime, the opposition and all kinds of public organizations exist freely. A person in a democratic state has a number of rights and freedoms - to elect and be elected, to conduct entrepreneurial activities, to profess any religion, to publicly express their thoughts. The most important feature of democracy is the equality of all citizens before the law.
Most states are officially democracies, but this is not always the case. For example, in the name of the most totalitarian country in the world, the DPRK, there is the word "democratic." There are few true democracies in the world. Among them are the states of Scandinavia, Canada, Australia and New Zealand.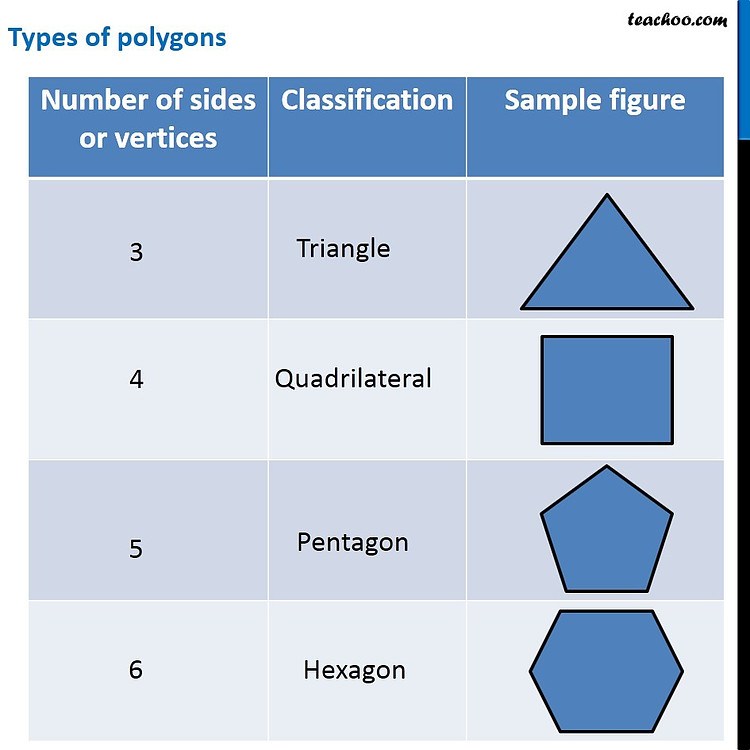
Nail shapes and how to choose the right one
Content:
- What are the forms of nails
- Natural nail shapes
- Unusual nail shapes
- How to choose a nail shape
To begin with, it is worth saying that the shape of the nails can be natural or acquired. The first category includes the forms that nature gives to nails: oval, square, soft square. To the second - the forms that the master will have to work on in the salon.
Square: suits everyone, looks especially good with dark nail polish.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by ISLA Berlin (@islaberlin)
Rounded: is ideal for a wide nail plate, easy to care for and requires only a few movements of the nail file to maintain.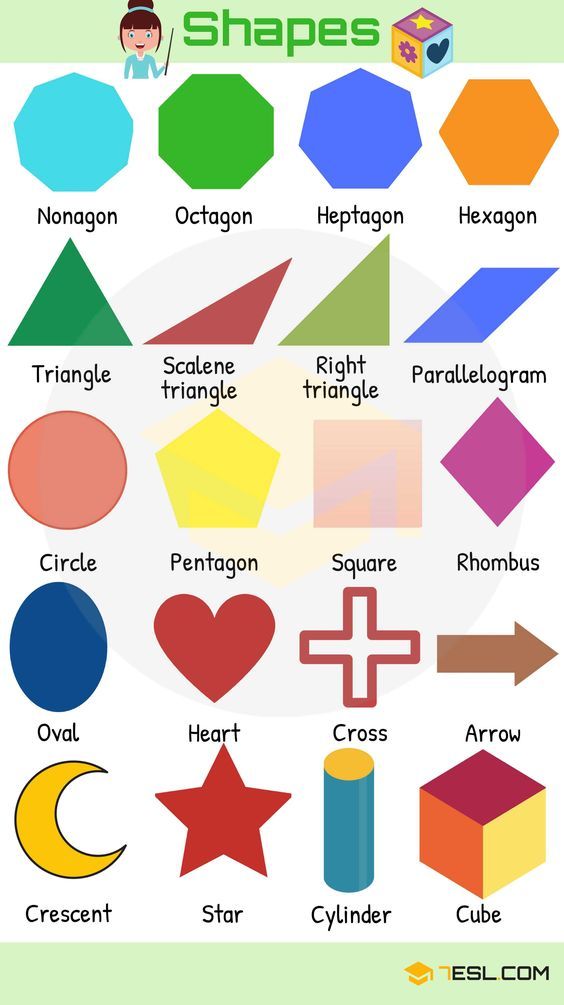
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Nail Artist (@_moon_nails_)
Oval: differs from round in that the edge of the nail is slightly tapered. To get this shape, you need to grow your nails a little. Looks great on long thin fingers, visually lengthens the short nail plate.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by IMARNI NAILS (@imarninails)
Soft square: is a universal choice.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Sylvie Macmillan (@sylviemacmillan.nails)
- Ballerina: is shaped like pointe shoes - oval along the cuticle line and square at the tips.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by culturamanicura (@culturamanicura)
- Almond-shaped: , as the name suggests, resembles an almond. Visually lengthens the fingers and makes the nails look like claws.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by culturamanicura (@culturamanicura)
- Stiletto (stiletto): this nail looks like a stiletto heel. It will come in handy as a weapon of self-defense, but in everyday life this is not the most convenient thing.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by MANICURE IDEAS (@_i.d.o.l.g.i.r.l_)
- Edge (from the English edge - "blade", "blade"): these nails look like a cut of the blade, forming an acute angle.
 You can make them by building up with the help of special forms-blanks.
You can make them by building up with the help of special forms-blanks.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Daria - Nails - Kharkiv (@nikolenko_kislinskaya_lookym)
- Beveled: in the West, this form is called lipstick, that is, lipstick, because outwardly the nails resemble exactly it - new, in a stick and only from the package.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Nails by Tinashe (@dollnailsbytinashe)
The classic advice when choosing a nail shape is that the tip of the nail should follow the oval of the cuticle.