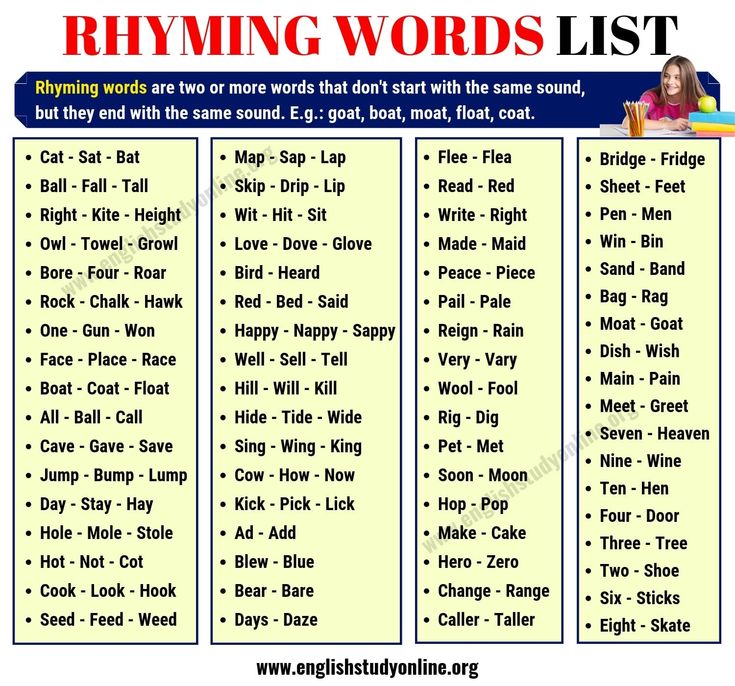
What is a complex sentence for kids
Complex Sentences for Kids with Examples
Jaymz Boanerges Repertoire
I have put up quite some posts on the complex sentence in English. There is the post on 25 Examples of Complex Sentences and also 10 Examples of Complex Sentences. This particular post presents complex sentences for kids with examples. Kids, who also read Akademia, deserve to be carried along in the explanation of a complex sentence.
The same goes for those who use this platform in teaching their kids at home or at school. In the light of this, I will not like to leave out the kids when it comes to a clear and simple understanding of what a complex sentence is. So if you have got some kids you need to teach complex sentence, whether your children, your pupils or students, this post complex sentences for kids is just appropriate for them.
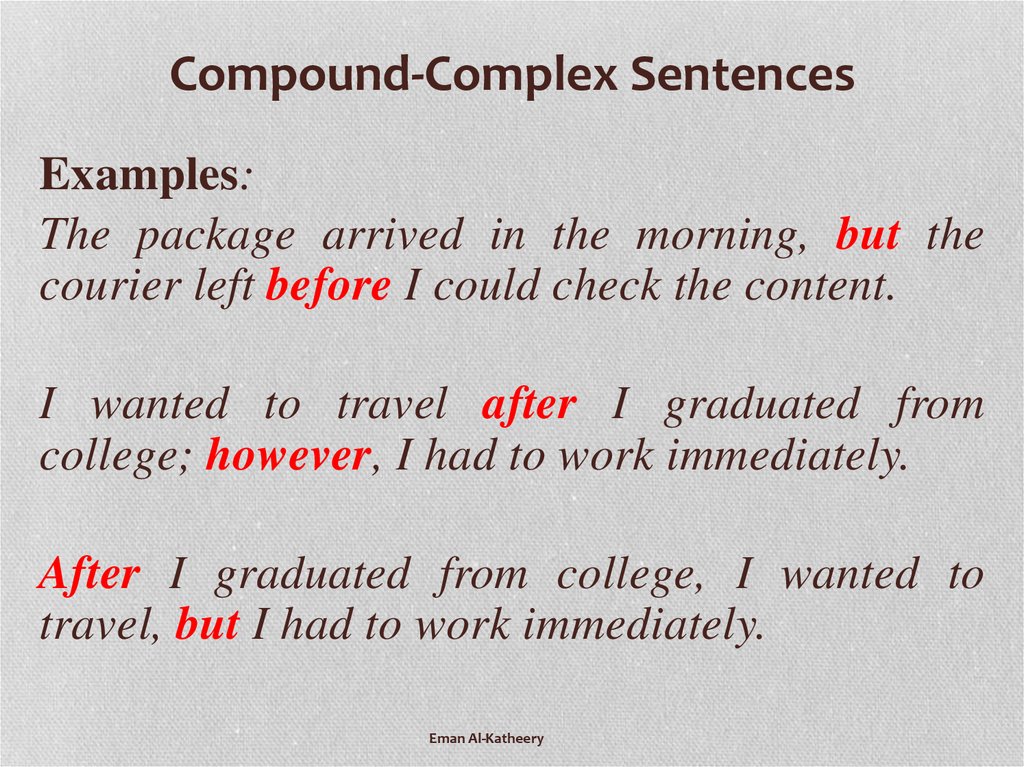
Complex Sentences for Kids with ExamplesIn explaining a complex sentence to a kid, what would you say it is? Well, let me provide a simple definition. A complex sentence is a type of sentence in English which has only one main clause, just like the simple sentence, but with, at least, one additional clause that cannot stand on its own.
The clause that cannot stand on its own, which we call a dependent or subordinate clause, can be more than one; but at least, such clause must be present in a sentence plus the main clause (that can stand on its own) for a sentence to qualify a complex sentence. How about that for a kiddo!
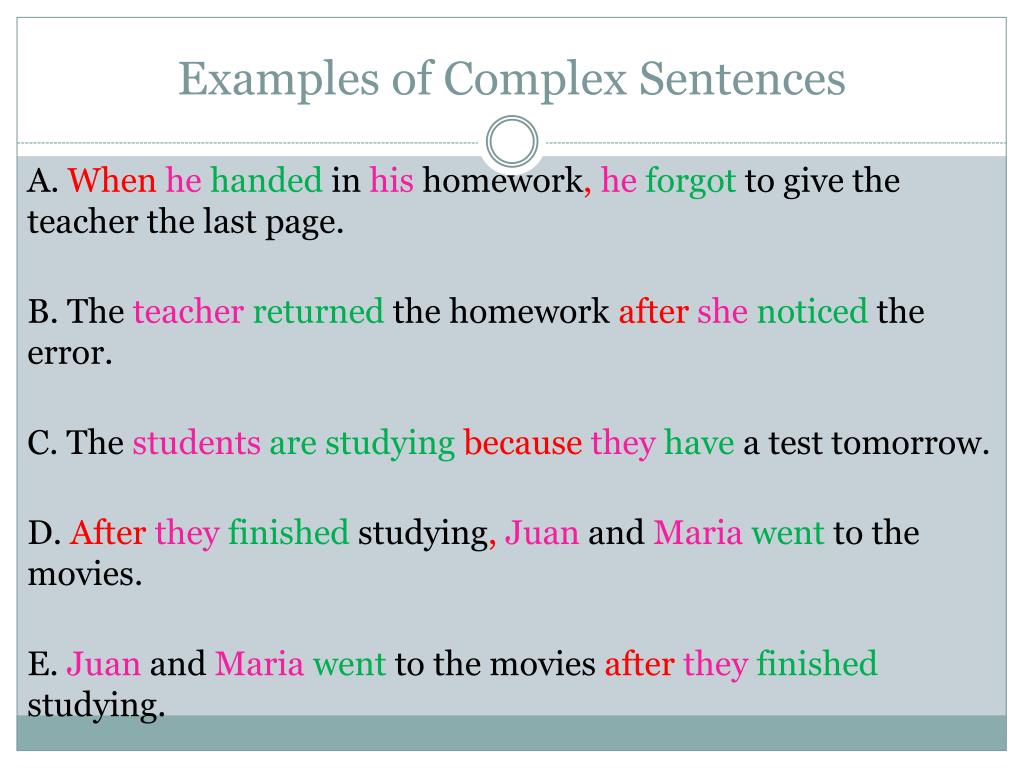
Complex Sentence Examples for KidsHaving given a description of complex sentence for kids, let us now provide kids’ friendly examples of a complex sentence…
- I will play games when I get home.
- I don’t like him because he beats me.
- When I finish my assignments, I will play outside.
- My parents hug me before they leave the house.
- While watching the television last night, I slept off.
- Whenever we go to the store, we always buy ice cream.
- Watching my friends board the plane, I felt lonely.
- When I grow up, I will become the president.
- If you do not come to school regularly, you will not do well in tests.
- After playing football for 30 minutes, the children became tired.
- While I was in primary school, I travelled to the village every weekend.
- If I don’t do my assignments, my teacher will punish me.
- If granny comes tomorrow, I will go back with her to the village.
- Anytime I see my uncle, I think of Santa Claus.
- While waiting for the school bus, the rain began to fall.
- The kids like animations because it entertains them.
- When my father returns from the office, he will take me out.
- Unless we pay our fees, we will not be allowed into the school.
- Before leaving the house every morning, we pray.
- After we collect our results, we must show them to our parents.

- 100 Examples of Compound Sentences
- Simple Sentence in English
- Complex Sentence in English
- 50 Examples of Simple Sentences in English
- 10 Examples of Complex Sentences in English
- Synonyms Words – 100 Examples You Need To Know
- 25 Examples of Complex Sentences in English
- What is a Compound Sentence?
- Compound Sentence Using Yet with Examples
complex sentence examples for kidscomplex sentences for kids
What are simple, compound and complex sentences?
Simple sentences, compound sentences, complex sentences... can you identify the different types of sentence construction your child will learn in KS1 and KS2? Our parent-friendly guide sorts out any confusion and explains how your child will be taught to put grammar into practice in the classroom.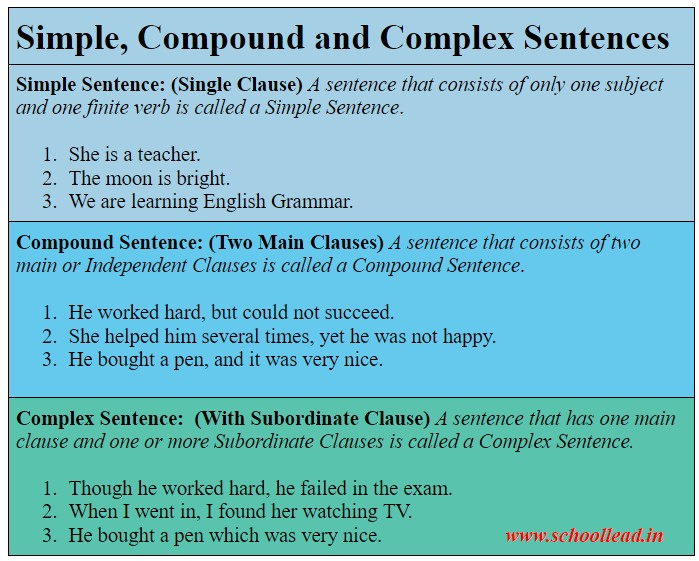
or Register to add to your saved resources
What is a sentence?
A sentence is a grammatical unit made up of one or more words (Go! is a sentence, as is The cat sat on the mat.). Sentences begin with a capital letter and end with a full stop, a question mark or an exclamation point.
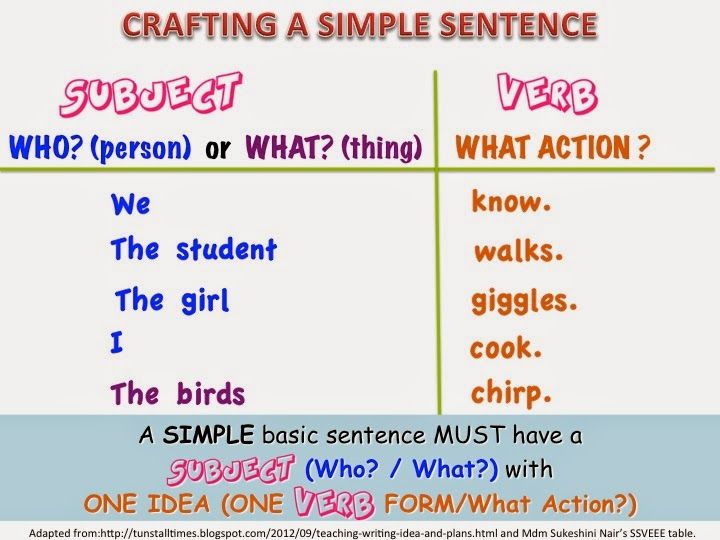
What is a simple sentence?
Sentences can be structured in different ways.
A simple sentence has a subject and ONLY ONE verb:
The girl sprinted after the tiger.
The cat purred.
Give Your Child The Gift Of Great Grammar
- Perfect Punctuation Workbook
- Grammar Games Pack
- PLUS 100s of other grammar resources
Download Now
What is a compound sentence?
A compound sentence is formed when you join two main clauses with a connective. In a compound sentence the clauses are linked by coordinating conjunctions / connectives (and, but, so, or).
I like bananas and I like grapes.
Zoe can be rude at times but she is a nice girl.
What is a complex or multi-clause sentence?
Complex sentences can also be referred to as multi-clause sentences.
A complex sentence is formed when you join a main clause and a subordinate clause with a connective. A subordinate clause is one that relies on a main clause to make sense.
The connectives in complex sentences are subordinating conjunctions and they tell us about the order or the place in which things happened or specify a cause or effect relationship between events. Connectives used in complex sentences include after, although, as, because, if, since, unless, when.
I love roast potatoes, although my mum prefers them mashed.
You need to prepare for the spelling test tomorrow if you want to get all your spellings right.
The big dog barked whenever I knocked on the door.
Complex sentences can also be constructed by including relative clauses (which are subordinate clauses), for example: Tom, who liked to read, settled down happily with his new book.
How are children taught sentence construction in KS1?
Children are not necessarily taught the concept of compound and complex sentences explicitly in KS1, but teachers will encourage children to notice the use of connectives in texts they are reading and how they make the writing more effective.
In Year 1, children need to start joining parts of sentences (clauses) using 'and'. For example:
There was a monster in my room and he was roaring.
In Year 2, children need to start using subordination, which occurs in a complex sentence. So instead of writing: 'I wanted some ice-cream,' they need to expand this using the connectives 'and,' 'or' and 'but,' to something like: 'I wanted some ice-cream but there was none.'
How is sentence construction taught in KS2?
Children continue to be expected to use compound and complex sentences. They will be expected to use more and more varied and sophisticated connectives.
In Years 3 and 4 they are expected to use 'when,' 'if,' 'because' and 'although'.
In Years 5 and 6 they are expected to use 'meanwhile,' 'therefore,' 'however,' 'consequently,' and other connectives.
By Year 6 children are expected to recognise, understand and be able to explain what simple, compound and complex sentences are, as this is likely to come up in the KS2 Grammar, Punctuation and Spelling test.
Teachers use a variety of methods for encouraging children to improve their sentence structure:
- Teachers often put lists of connectives up around the classroom to encourage children to remember to use them in their writing.
- They may also play classroom games, saying sentences out loud using connectives. An example of this is to give children the half-sentence: 'I would like to get a dog, however,' and then ask them to repeat it, adding their own half of the sentence, for example: 'I would like to get a dog, however my mum won't let me.
 '
' - Teachers will also model the use of compound and complex sentences on the board when they are drafting example text for the children.
- When a teacher marks a draft piece of writing, they may, in their marking, draw the child's attention to how two simple sentences could be joined by a connective, or how one simple sentence could be expanded by a connective and a second clause.
More like this
What is a sentence?
Primary grammar glossary for parents
Grammar in primary school
Sorting simple and complex sentences
What is a clause?
Adding clauses to sentences
Reading simple sentences
What is the Y6 Grammar, Punctuation and Spelling test?
Great Grammar Games
Compound sentence in Russian - types, types, examples
Today we will analyze a topic that is relevant for many 9th grade students. Namely: what sentences in Russian are called complex, what groups they are divided into and how to find them in the text.
Namely: what sentences in Russian are called complex, what groups they are divided into and how to find them in the text.
What is a compound sentence
| A compound sentence is a sentence that consists of two or more grammatical bases. |
An example of a complex sentence:
According to the connection between the parts, complex sentences are divided into two types - allied (compound and complex) and non-union. In the first case, the parts are connected by unions and allied words, in the second - by meaning.
In total, there are 3 types of complex sentences. Let's look at them in a table.
Demo lesson in Russian
Take the test at the introductory lesson and find out what topics separate you from the "five" in Russian.
Compound sentence
| Compound (CSP) is a complex sentence that has two or more independent simple sentences in its composition. This means that they can be broken with a dot, while the meaning is not lost. |
Parts of such complex sentences are connected by conjunctions and allied words: connecting (and, yes, also, etc.) , adversative (a, but, but, etc.) , separating (or, then ... then, not that ... not that, etc.) or combinations thereof.
Examples:
-
I wanted a pie, and the apples are already ripe.
-
I wanted a pie, but the apples weren't ripe yet.
-
Either mother will bake pies, or grandmother will come with buns.
Sometimes parts of compound sentences are connected without a coordinating union and a union word - in meaning. Such proposals are called non-union.
Example:
Punctuation marks in compound sentences
In sentences with conjunctions and, yes, however, either, etc. it is customary to put a comma. Except when:
Exception
If the parts of a complex sentence have a common minor member or subordinate clause, but they are connected by a repeating conjunction, a comma must be used.
Example:
In non-union compound sentences, parts are divided not only by commas, but also by dashes, colons and semicolons. We discussed this topic in detail in the article on compound sentences.
Compound sentence
| Compound sentence (CSP) is a type of complex sentence in which one simple sentence is subordinate to another in meaning and intonation. |
An example of a complex sentence:
Types of connection in a complex sentence
Usually parts of NGN in Russian are connected with each other by subordinating conjunctions, for example:
There are complex sentences in which the main clause is related only in meaning and separated by a punctuation mark, but a subordinating conjunction can still be inserted between them. Such proposals are called non-union.
Example:
Values of subordinate clauses in NGN
Compound clauses are divided into groups, and then into subgroups according to the meaning and type of connection with the main one.
You can read more about the differences between clauses in a complex sentence with examples in this article.
Types of subordination in a complex sentence
Sometimes in a complex sentence there are not one, but two or more subordinate clauses. This type of complex sentences is called polynomial. They have different types of submission.
We have already discussed this topic in more detail in the article on complex sentences.
Punctuation marks in complex sentences
It is customary to put a comma between the main and subordinate parts of a complex sentence. If one part is in the middle of another, it must be separated with a comma on both sides:
-
When we returned to the city, all the sorrows were left behind.
-
Now that we have returned to the city, all the sorrows are left behind.
If sentences with the words only, only, also, and, above all, precisely, obviously, are probably connected by a compound union, it is divided.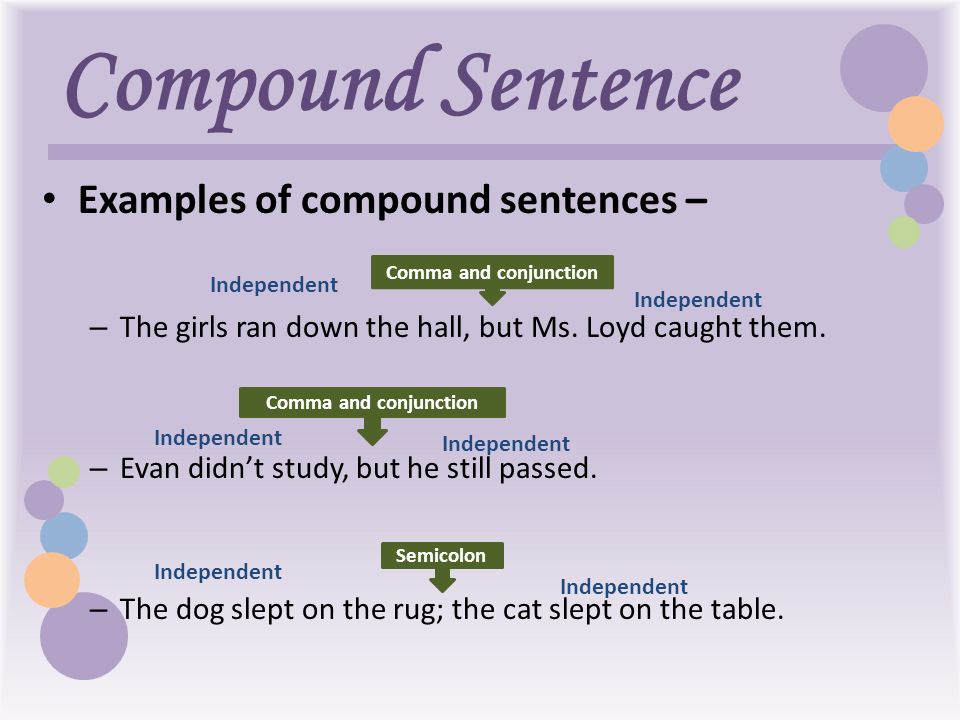 Then a comma should be put before the word what:
Then a comma should be put before the word what:
If we highlight indicative or conditional clauses with intonation and put them before the main clause, a dash is placed between them:
If it is clear from the main clause that the subordinate clause will explain it, you need to put a colon. The same rule applies to non-associative complex sentences:
Free English lessons with a native speaker
Practice 15 minutes a day. Learn English grammar and vocabulary. Make language a part of life.
Test yourself
Determine what type of compound sentence these examples refer to: complex or compound?
-
Mother had already cooked for the morning and went to bed when I returned from the theatre.
-
I knew it couldn't go on too long.
-
Snowflakes lay lightly on the palm, and the world around froze in snow-white splendor.

-
I went to the edge of the forest an hour later, but the travelers were gone.
-
I quickly found the place where the cuckoos were nesting.
Russian language exam preparation courses at the Skysmart online school - without stress and on real exam tasks. Try it for free with an introductory lesson!
Russian cheat sheets for parents
All the rules of the Russian language at hand
Simple and complex sentences with examples (Grade 4, Russian)
4.6
Average score: 4.6
Total scores: 9023 9025.
Average score: 4.6
Total ratings received: 925.
In this article, intended for grade 4, we will consider what complex and simple sentences are, what this division of sentences is connected with, how to distinguish a simple sentence from a complex one.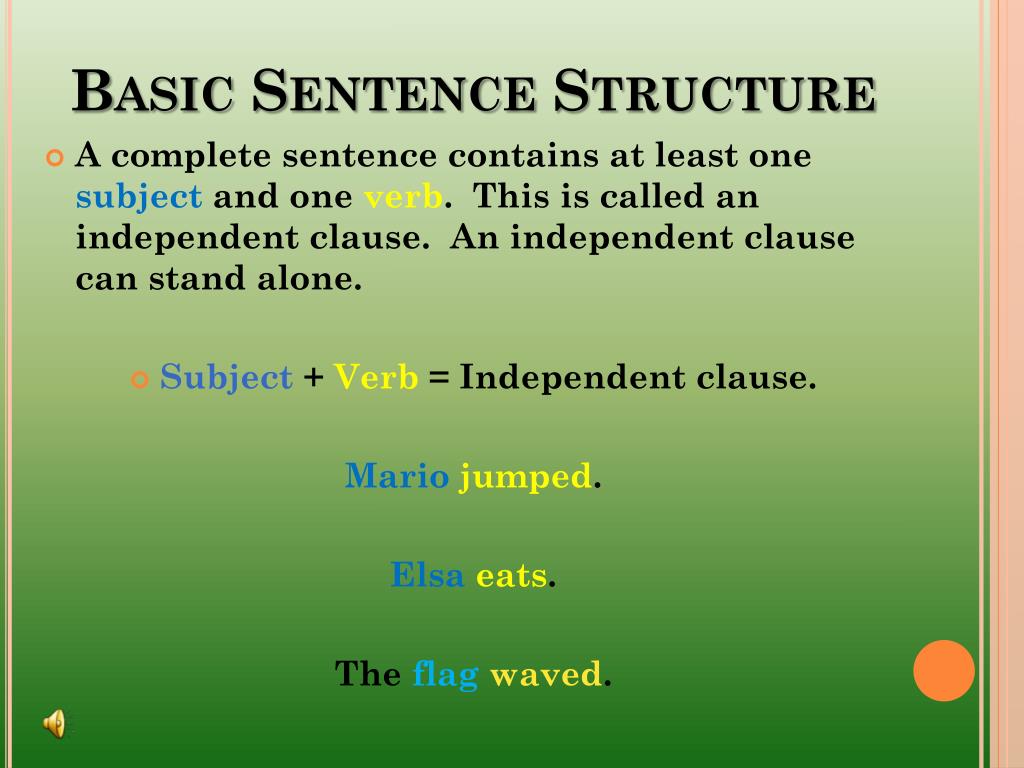
Simple offer
A simple sentence is a sentence with one grammatical basis.
In Russian there is only the term "simple sentences", the terms "light sentences" and "ordinary sentences" do not exist.
Complex sentence
A compound sentence is a sentence with two or more grammatical bases.
A complex sentence includes simple sentences. Simple sentences that are part of a complex sentence are related to each other in meaning and intonation.
Parts of a complex sentence complement each other, turn different information into one, more complete one.
Most often, commas are placed between parts of a complex sentence.
There may be conjunctions between the parts of a complex sentence, but they may also be absent. If there are no unions between parts of a complex sentence, then this is an union-free complex sentence; allied complex sentences are divided into compound (with coordinating unions) and complex (with subordinating unions).
How to tell?
A complex and simple sentence is closely related to the number of grammatical bases.
To understand when a sentence is simple and when it is complex, you need to count the number of grammatical foundations, which means that those who speak Russian must be able to correctly determine the grammatical foundations of sentences. Without the ability to find the grammatical basis of a sentence, it is impossible to determine whether a particular sentence is simple or complex.
It is necessary to distinguish between an independent grammatical basis and homogeneous subjects or predicates. You also need to understand that the grammatical basis can be only the subject or only the predicate.
Let's compare simple sentences and complex sentences.
Examples of simple sentences:
- We rode the rides (1 grammatical basis: we rode).
- I went to my grandmother for the holidays (1 grammatical basis: I left).


 In this case, the dependent clause is called the subordinate clause, and the independent clause is called the main clause.
In this case, the dependent clause is called the subordinate clause, and the independent clause is called the main clause.