Why reading strategies are important
10 Best Reading Strategies for Students
Reading is one of the essential skills students need to learn to succeed in school and college. However, not all students are good readers, and that is where reading strategies kick in, and even among those who are, there are different types of good readers.
Teachers have to be concerned with the unique learning styles of students. Learning styles can be visual, auditory, and tactile. However, cognitive styles can also be verbal or non-verbal and sequential or global. These various learning styles play an essential role in helping teachers decide how to teach each student best to learn and comprehend lessons.
If you are trying to get your students to be better readers, use some reading strategies when teaching reading to your students.
10 Effective
Reading Strategies to Enhance your Students’ Cognitive AbilitiesRelated Reading: Strategies for Implementing Scaffold Learning in the Classroom
1.
The first strategy to implement is teaching your students to use their voices when reading. If they read a sentence with an exclamation point at the end, they should read it in an excited voice. If they read a sentence with a question mark at the end, they should use an interrogative voice. This takes very little instruction and practice, but it helps your students understand what they are reading better by engaging in the text. This can drastically improve their comprehension skills and help them build fluency skills.
2. Set a Purpose for Reading Strategies
Setting a purpose for reading is another effective strategy for teaching reading comprehension. When students are assigned a novel or short story to read, have them write out their purpose beforehand.
3. Schema
One of the most effective strategies for teaching reading is called Schema. This strategy asks students to connect what they already know with new concepts presented within the text. The idea is that when you can associate further information with what you already know, you will learn it faster and retain it longer.
The idea is that when you can associate further information with what you already know, you will learn it faster and retain it longer.
For example, if you know how to drive a car and are told that your car has four cylinders under the hood, you will understand that these objects allow your engine to work correctly because you already understand how an engine works. This can help you learn more quickly than someone who knows nothing about cars or engines.
4. Teaching Students to Read a Text
This is very important because it helps them develop their reading and writing skills to read better when they are older. It also helps them learn how to spell things correctly, which will help them in school and tests later on in life.
5. Make Reading Fun
One of the most important strategies is to make reading fun. You can do this by playing games, doing crafts, and getting the children involved in other activities that include reading. This is especially helpful if you have an older child struggling with reading. They will be more likely to participate in activities that involve reading when they are having fun at the same time.
They will be more likely to participate in activities that involve reading when they are having fun at the same time.
Preparing for Reading with Pre-Reading Activities:
- Read the title, subtitle, and table of contents.
- Read any questions that come before the text.
- Look over headings and pictures or illustrations.
- Skim the reader to get an idea of the general topic or theme.
Related Reading: Best Tips for Creating a Healthy Student-Centered Learning Environment
1. Questions & Doubts
Have students stop periodically during their reading and write down questions about characters or events in the story or text. Ask them questions to help activate prior knowledge and engage their critical thinking.
2. Connect & Predict
Have students connect what they already know and the topic of the story or book they will be reading. Ask them to predict what might happen in the story or text based on the title, illustrations, or cover.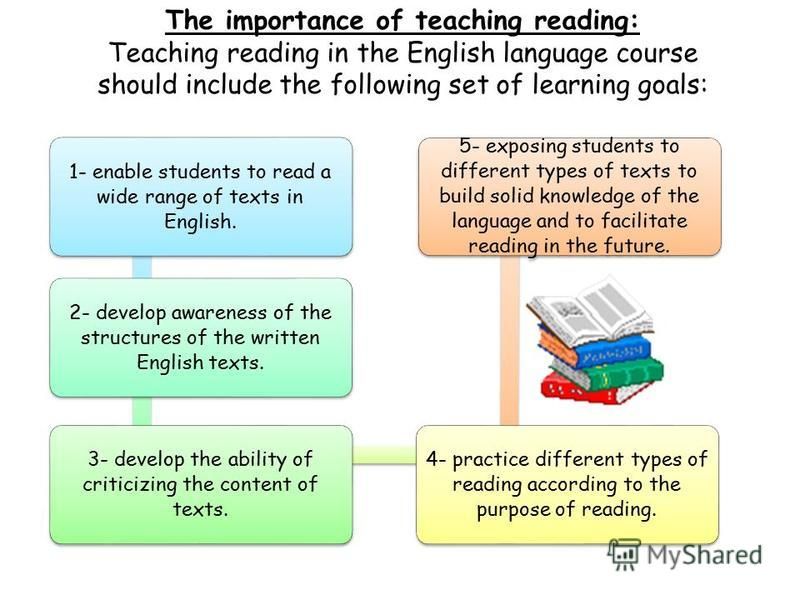 Ask them if they think characters will change as the story progresses.
Ask them if they think characters will change as the story progresses.
3. Reading Aloud
Model fluent reading by reading aloud a part of the text for your students. This is important for English learners and all readers since it demonstrates how fluent readers sound when they read.
Enhance your students’ reading skills with fun games, courses & worksheets on SplashLearn. Sign up to access the teacher dashboard & assign fun activities!
Teachers, sign up & use for free!
4. Conducting Discussions
Reading and discussion are linked, as one enhances the other. When we discuss a text we’ve read, we better understand it, see new things in it that we hadn’t noticed, gain insights into the writing process, and hear different perspectives on what it is saying.
Discussions are a way to assess the students’ understanding and help them understand texts more completely.
The Benefits of Using
Reading StrategiesReading strategies as a mental process helps the reader efficiently comprehend text. In other words, they’re the tools readers use to understand what’s written on a page. These strategies can be taught directly to students and are critical for literacy development.
In other words, they’re the tools readers use to understand what’s written on a page. These strategies can be taught directly to students and are critical for literacy development.
There are several benefits to using reading strategies before, during, and after reading:
- Understanding how text is organized can help kids understand what they read. A reading strategy like previewing can give an overview of the text organization before reading and using this information. In contrast, reading can help you read a passage in detail or skim it.
- Reading strategies can help monitor comprehension by checking what kids understand during and after reading. Asking questions during reading enables them to check to understand. Summarizing and retelling helps review understanding after reading.
- There are several ways to retrieve information from memory that can enhance comprehension. For example, retrieving data from the text is easier if kids use some mnemonic device to create a link between the new information and familiar information already stored in your long-term memory.

- Reading strategies can help students access information that is not explicitly stated. They help readers infer meaning, make conclusions and generalize information. Reading strategies are beneficial for texts that have complex ideas and vocabulary. Students can use them to develop comprehension skills and become better readers.
The Opportunities that Come Along Using
Reading StrategiesRelated Reading: Ways to Implement Restorative Practices in the Classroom
Reading strategies are actions that a reader takes to help construct meaning from text. The term reading comprehension refers to the understanding of what is read.
Early childhood education programs provide the opportunity to learn to read. It has been shown that early intervention can significantly improve a child’s success in reading.
The opportunities available when one uses reading strategies are endless. Reading strategies provide a way for readers to make sense of the text. This can be difficult for some students who have not been taught specific strategies to help them grasp the meaning of what they are reading.
This can be difficult for some students who have not been taught specific strategies to help them grasp the meaning of what they are reading.
There are simple, easy-to-use strategies to help you become a successful reader. Reading strategies can give kids a roadmap to become better readers. Your students will be more involved in the books they read, which will keep them interested in what they are reading.
Bottom Line
Boy in libraryReading is one of the biggest and most important subjects in any school or university curriculum. Students are encouraged to read as much as they can, but many people still find it hard to read a book, and some even find reading boring. However, reading is one of the critical factors to succeed in academia because good readers are also good writers.
Reading strategies help students understand what they read in terms that are easy for them to understand. They also help students find new ways to make reading more fun and more accessible to comprehend what they just read. Any educator can use SplashLearn to teach reading and language arts skills.
Any educator can use SplashLearn to teach reading and language arts skills.
What are the three main types of reading strategies?
The three different types of reading strategies are skimming, scanning, and in-depth reading.
What are reading strategies?
Reading strategies is the broad term used to describe the planned and explicit actions that can help readers translate print to meaning.
Why are reading strategies important for readers?
Reading strategies are solely used to boost comprehension of the text. Reading strategies are essential to teaching students how good readers think.
How can reading strategies be improved?
By implementing reading strategies and changing how students read, teachers can improve their reading comprehension and make reading more accessible and enjoyable.
What Are Reading Strategies and Are They Important?
Teachers | 0 comments
I remember when I first started teaching I fantasized that I would have a gaggle of kids sitting at my feet while I read books aloud to them and we would marvel at the literature (of Kindergarten???) and have deep conversations about the meaning of the literature and connect the text to the world and basically just live out every English teacher’s fantasy (or at least THIS English minor’s teaching fantasy!)
And then my students showed up.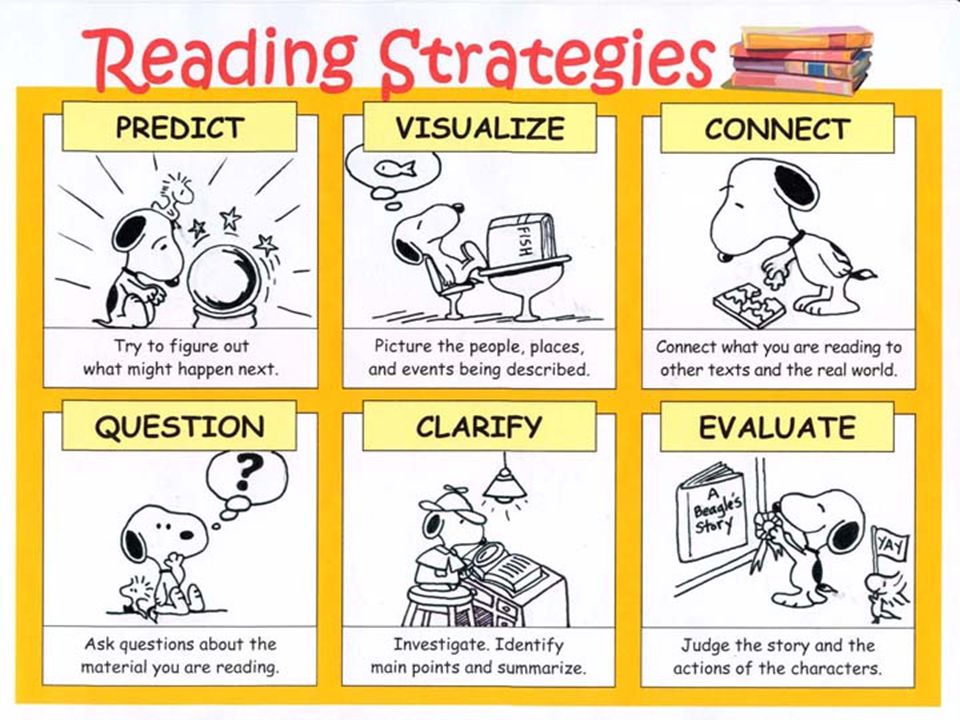
And I cried.
And my mom had to come and help me.
Like moms do.
And then I pulled it together!
So what do I mean by “pulled it together”?
I got real about what my students needed and what I would have to do to provide it to them. Gone were the sitting at the teacher’s feet for hours on end, discussing the deeper meaning of Goodnight Moon and onto really teaching these kids WHAT good readers do and HOW to do what good readers do.
I came to understand much more clearly what reading strategies are for and why I needed to start teaching them – especially in Kindergarten!
So, here’s what I’ve learned and incorporated into my practices in Kindergarten and upper elementary, middle school and high school classrooms – these are ideas that work in REAL LIFE classrooms!
- Reading strategies (like compare and contrast, prediction and inference, summarizing, etc.
 ) are solely for the purpose of boosting comprehension of the text.
) are solely for the purpose of boosting comprehension of the text. - Reading strategies are super important to teach because by teaching them we show students how good readers think. This is so important because learning to read is NOT a natural process. If it were, we wouldn’t have such high illiteracy rates!
- Reading strategies need to be modeled, modeled, modeled to kids of all ages before they become automatic. Just like you wouldn’t give a car to a 15 year old learning to drive, you don’t hand over comprehension of text to students without lots of hand holding!
- Reading strategies are a process, not a check on a checklist. Prior to reading ANY text, you should model and think aloud for students how you, as a successful reader, approach and attack the text. Things like “Hmm…this has me thinking that I’m a little confused, let me use my reading comprehension strategy of re-reading to see if I can make more sense of this.” Think-alouds like this give kids permission to ask questions about the text.
- Reading strategies give kids TOOLS to figure out difficult text – this is the whole point! Teaching reading comprehension shouldn’t been a shot in the dark – we need to ARM kids with the big guns (proven reading comprehension strategies) to be able to take on new text with lots of new vocabulary and lots of new content knowledge.
- Reading strategies give kids confidence. Have you ever seen a strong, confident reader cower at the thought of difficult text? Probably not! They go rip-roarin’ into the text because they’re thinking, “I’ve got this!” – and what you see is them regularly and appropriately applying reading comprehension strategies!
So, what are reading strategies?
Reading strategies are flexible tools designed to help facilitate text comprehension.
And why are they so important for all kids?
Reading strategies are critical to develop in order to boost comprehension, confidence and clarity while reading text.
So, where do you start with all of this? Start by reflecting on your lessons from last year – did you make assumptions that kids already knew/had the reading strategies? Were there multiple opportunities each day in different kinds of text where you modeled the strategies? Where do you see obvious opportunities to model next year?
Now, I’ve got to go and get back to prepping my Proust lesson for my kindergarten demo tomorrow. *wink wink*
*wink wink*
Techniques for teaching the strategy of semantic reading and working with text
1. Introduction
The global processes of informatization of society, the increase in the amount of textual information every year, the presentation of new requirements for its analysis, systematization and processing speed have put theorists and practitioners of education in front of the need development of new approaches to teaching reading.
Problems:
- children have low reading speed, as a result of which they spend a lot of time doing homework,
- they often do not understand the meaning of what they read due to reading errors and incorrect intonation,
- they cannot extract the necessary information from the proposed text, highlight the main thing in the read,
- they find it difficult to briefly retell the content,
- when performing independent work, tests of different levels, students make mistakes due to misunderstanding of the wording of the task,
- rarely refer to cognitive texts.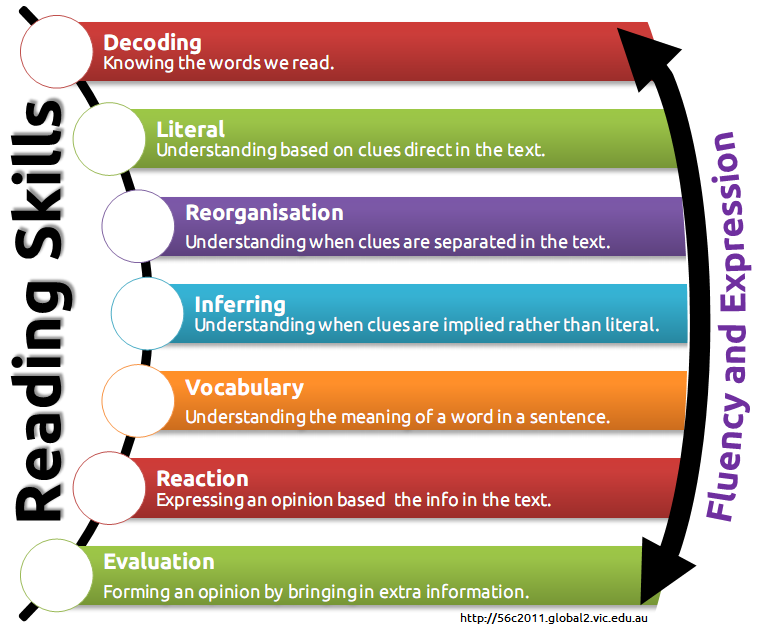
That is, a serious contradiction arises: on the one hand, the modern world brings down a huge amount of information on us, on the other hand, our children do not read much, do not have the skills of semantic reading, and do not know how to work with information.
It is not so important to read a lot, it is much more necessary to process what you read in your mind in a quality manner. Having comprehended and structured the text in a certain way, it is much easier to convey its content and learn the main thing.
The current interdisciplinary curriculum, provided for by the new educational standards, is the program "Fundamentals of semantic reading and working with text." The program is aimed at forming and developing the foundations of reading competence necessary for students to implement their future plans, including continuing education and self-education, preparing for work and social activities. Today, reading, along with writing and computer skills, is one of the basic skills that allow you to work productively and communicate freely with different people. Reading is a universal skill: it is something taught and something through which one learns. As scientists have established, about 200 factors affect student performance. Factor #1 is reading skill, which has a far greater impact on academic performance than all of them combined. Research shows that in order to be competent in all subjects and later in life, a person needs to read 120-150 words per minute. This becomes a necessary condition for the success of working with information. Reading is the foundation of all educational outcomes.
Reading is a universal skill: it is something taught and something through which one learns. As scientists have established, about 200 factors affect student performance. Factor #1 is reading skill, which has a far greater impact on academic performance than all of them combined. Research shows that in order to be competent in all subjects and later in life, a person needs to read 120-150 words per minute. This becomes a necessary condition for the success of working with information. Reading is the foundation of all educational outcomes.
2. Semantic reading in the context of the new Federal State Educational Standards
Federal standards include in the meta-subject results of OOP mastering as a mandatory component "mastering the skills of semantic reading of texts of various styles and genres in accordance with the goals and objectives."
Semantic reading is a type of reading aimed at understanding the semantic content of the text by the reader. For semantic understanding, it is not enough just to read the text, it is necessary to evaluate the information, respond to the content.
For semantic understanding, it is not enough just to read the text, it is necessary to evaluate the information, respond to the content.
In the concept of universal educational activities (Asmolov A.G., Burmenskaya G.V., Volodarskaya I.A., etc.) actions of semantic reading associated with:
- understanding the purpose and choosing the type of reading depending on tasks;
- definition of primary and secondary information;
- by formulating the problem and the main idea of the text.
For semantic understanding, it is not enough just to read the text, it is necessary to evaluate the information, respond to the content. The concept of "text" should be interpreted broadly. It can include not only words, but also visual images in the form of diagrams, figures, maps, tables, graphs.
Since reading is a meta-subject skill, its constituent parts will be in the structure of all universal learning activities:
- personal UUD includes reading motivation, learning motives, attitude towards oneself and school;
- in the regulatory UUD - the student's acceptance of the learning task, arbitrary regulation of activity;
- in cognitive UUD - logical and abstract thinking, working memory, creative imagination, concentration, vocabulary volume.
- in communicative UUD - the ability to organize and implement cooperation and cooperation with a teacher and peers, adequately convey information, display subject content.
The diagram shows groups of meta-subject results related to semantic reading.
3. Strategies for semantic reading
To work with the text at each stage, the reader chooses his own strategies. Learning strategies are a set of actions that a learner takes in order to facilitate learning, make it more effective, efficient, faster, more enjoyable, aim and bring learning activities closer to their own goals.0007
The term "reading strategies" was born at the dawn of psycholinguistics, and its appearance is associated with the work of Kenneth Goodman and Peter Kolers (70s). (slide 14) The most general definition of J. Bruner became fundamental for all subsequent works: “A strategy is a certain way of acquiring, storing and using information that serves to achieve certain goals in the sense that it should lead to certain results. ”
”
In case of success, the student remembers the ways of his actions, operations, resources used, transfers the strategy to other situations, makes it universal. The number of strategies and the frequency of their use are individual.
Strategy No. 1. Directed reading
Purpose: to form the ability to purposefully read the educational text. Ask questions and lead group discussions.
1. Update. Reception "Associative Bush": the teacher writes a keyword or title of the text, students express their associations one by one, the teacher writes down. The use of this technique allows you to update knowledge, motivate subsequent activities, activate the cognitive activity of students, set them up for work.
2. Pupils silently read a short text or part of a text, stopping at the indicated places.
3. The teacher asks a problematic question on what has been read.
4. The answers of several students are discussed in class.
5. The students make an assumption about the further development of the event.
Strategy #2. Reading in pairs - generalization in pairs
Purpose: to form the ability to highlight the main thing, summarize what was read in the form of a thesis, ask problematic questions.
1. The students silently read the text or part of the text chosen by the teacher.
2. The teacher puts the students in pairs and gives clear instruction. Each student alternately performs two roles: speaker - reads and summarizes the content in the form of one thesis; the respondent listens to the speaker and asks him two substantive questions. Next comes the role reversal.
3. The teacher invites all students to the discussion.
Strategy No. 3. Reading and asking
Purpose: to form the ability to work independently with printed information, formulate questions, work in pairs.
1. Students silently read the proposed text or part of the text chosen by the teacher.
Students silently read the proposed text or part of the text chosen by the teacher.
2. The students work in pairs and discuss which key words should be highlighted in the reading. (Which words appear most often in the text? How many times? Which words are in bold? Why?
If you read the text aloud, how would you make it clear that this sentence is the main one? It is about highlighting the phrase voice, which hides an unobtrusive but reliable memorization.)
3. One of the students formulates a question using key words, the other answers it.
4. Discuss key words, questions and answers in class. Correction.
Strategy No. 4. Double entry diary
Goal: to form the ability to ask questions while reading, critically evaluate information, compare what is read with one's own experience.
1. The teacher instructs the students to divide the notebook into two parts.
2. In the process of reading, students should write down on the left side the moments that struck, surprised, reminded of some facts, caused any associations; on the right - write a concise commentary: why this particular moment surprised you, what associations it caused, what thoughts it prompted.
Strategy No. 5. Reading with notes
Purpose: to form the ability to read thoughtfully, evaluate information, formulate the author's thoughts in your own words.
The teacher gives the students the task to write information in the margins with icons according to the following algorithm:
- V Familiar information
- + New information
- - I thought (thought) otherwise
- ? This interested me (surprised), I want to know more
The essence of semantic reading strategies is that the strategy is related to choice, functions automatically at the unconscious level and is formed in the course of the development of cognitive activity. Teaching reading strategies includes the acquisition of skills:
- Distinguishing types of message content - facts, opinions, judgments, evaluations;
- recognition of the hierarchy of meanings within the text - the main idea, theme and its components;
- own understanding - the process of reflective perception of the cultural meaning of information.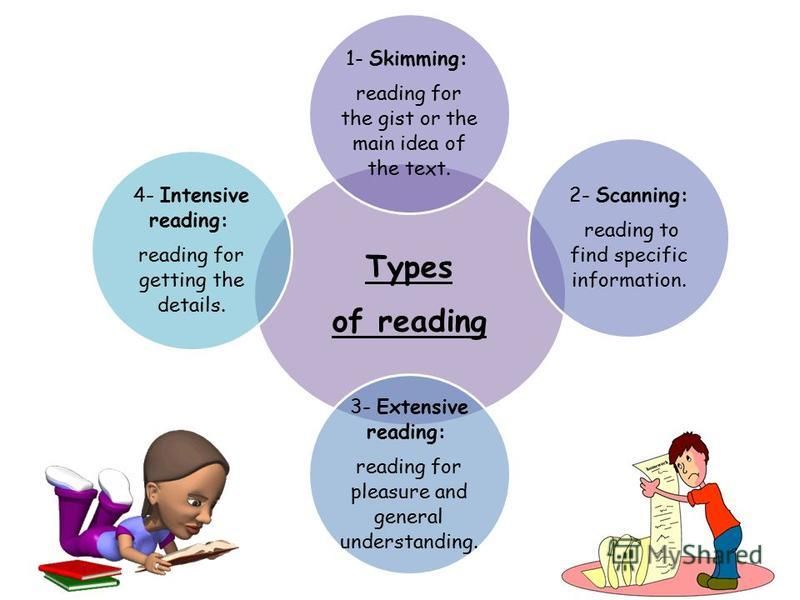
Mastering strategies occurs mainly in groups or pairs, which allows students to develop not only speech, but also communicative competence.
4. Techniques for teaching the strategy of semantic reading and working with text
The strategy of semantic reading provides understanding of the text by mastering the techniques of mastering it at the stages before reading, during reading and after reading. Working with any text involves three stages: pre-text activity, text and post-text activity
Stage 1. Work with text before reading.
1. Anticipation (anticipation, anticipation of the upcoming reading). Determining the semantic, thematic, emotional orientation of the text, highlighting its heroes by the title of the work, the name of the author, key words, illustrations preceding the text based on the reader's experience.
2. Setting the objectives of the lesson, taking into account the general (educational, motivational, emotional, psychological) readiness of students for work.
Purpose of stage 1: development of the most important reading skill, anticipation, that is, the ability to guess, predict the content of the text by title, author's name, illustration.
Techniques of pre-text activity:
If earlier, according to the traditional method, only one task “Read the text” was given at the stage of pre-reading the text, and the main attention was paid to control of reading comprehension, now we know that the better organized the stage of pre-reading, the easier it is for the student to read the text and the higher the result achieved by him.
Pre-text orienting techniques are aimed at staging reading and, consequently, at choosing the type of reading, updating previous knowledge and experience, concepts and vocabulary of the text, as well as creating motivation for reading.
Most common techniques:
- Brainstorming
- Glossary
- "Landmarks of anticipation"
- Preliminary Questions
- "Dissection questions".
Brainstorming, headline prediction.
The goal is to update previous knowledge and experience related to the topic of the text.
The question is asked: what associations do you have about the stated topic?
Associations are written on the board.
The teacher can add various information.
Reading text. Comparison of information with that learned from the text.
"Glossary"
The purpose of is to update and repeat the vocabulary related to the topic of the text.
The teacher says the name of the text, gives a list of words and suggests marking those that may be related to the text.
Having finished reading the text, they return to these words (this will be a post-text strategy) and look at the meaning and use of the words used in the text.
"Landmarks of anticipation"
The purpose of is to update previous knowledge and experience related to the topic of the text. Students are given judgments. They should mark the ones they agree with. After reading, they mark them again. If the answer has changed, then the students explain why this happened (post-text strategy)
Students are given judgments. They should mark the ones they agree with. After reading, they mark them again. If the answer has changed, then the students explain why this happened (post-text strategy)
“Dissections of the Question”
The goal of is a semantic guess about the possible content of the text based on the analysis of its title. It is proposed to read the title of the text and divide it into semantic groups. What do you think the text will be about?
"Preparatory questions"
The purpose of is to update existing knowledge on the topic of the text.
Detailed reception algorithm:
1. Scan the text quickly. (Review reading.)
2. Answer the question asked in the title of the text.
Stage 2. Working with text while reading.
Purpose of stage 2: understanding of the text and creation of its reader's interpretation (interpretation, evaluation).
1. Primary reading of the text. Independent reading in the classroom or reading-listening, or combined reading (at the choice of the teacher) in accordance with the characteristics of the text, age and individual abilities of students. Identification of primary perception (with the help of a conversation, fixing primary impressions, related arts - at the teacher's choice).
2. Rereading the text. Slow "thoughtful" repeated reading (of the entire text or its individual fragments). Text analysis. Statement of a clarifying question for each semantic part.
3. Conversation on the content of the text. Summary of what has been read. Identification of the hidden meaning of the work, if any. Statement of generalizing questions to the text, both by the teacher and by the children. Appeal (if necessary) to individual fragments of the text.
Text activities include:
- Read aloud
- "Reading to yourself with questions"
- Stop Reading
- "Reading to yourself with a mark"
"Reading aloud"
The goal is to check the understanding of the text read aloud .
1. Reading text paragraph by paragraph. The task is to read with understanding, the task of the listeners is to ask the reader questions to check whether he understands the text being read.
2. Listeners ask questions about the content of the text, the reader answers. If his answer is incorrect or inaccurate, the listeners correct him.
“Reading to yourself with questions”
The goal is to teach you to read the text thoughtfully by asking yourself increasingly difficult questions .
1. Reading the first paragraph. Questions are being asked.
2. Reading the second paragraph to yourself. Work in pairs. One student asks questions, the other answers.
3. Reading the third paragraph. They change roles. They ask questions and answer.
Stop Reading
Goals - managing the process of understanding the text while reading it.
Reading the text with stops during which questions are asked.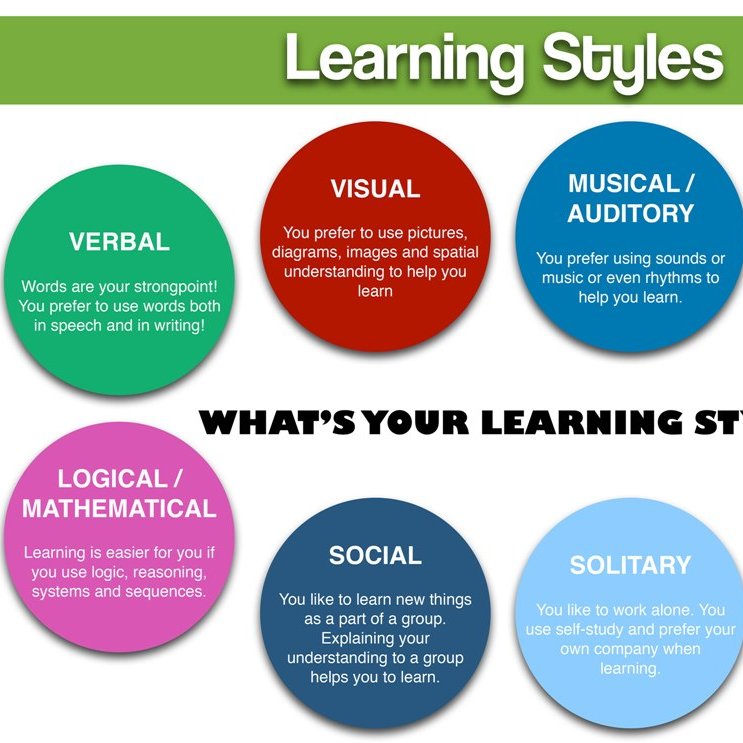 Some of them are aimed at testing understanding, others - at predicting the content of the following passage.
Some of them are aimed at testing understanding, others - at predicting the content of the following passage.
“Reading to yourself with notes” (“Insert”)
The goal is to monitor the understanding of the text being read and its critical analysis . This strategy is most often used to work with complex scientific texts. It is used to stimulate more careful reading. Reading becomes an exciting journey.
1. Individual reading.
While reading, the student makes notes in the text:
- V – already knew;
- + - new;
- - thought differently;
- ? - I do not understand, there are questions.
2. Reading, the second time, fill in the table, systematizing the material.
| Already knew (V) | Learned something new (+) | Thought otherwise (–) | Questions (?) |
Records - keywords, phrases. After completing the table, students will have a mini-outline. After the students fill in the table, we summarize the results of the work in the conversation mode. If the students have any questions, then I answer them, having previously found out if one of the students can answer the question that has arisen. This technique contributes to the development of the ability to classify, systematize incoming information, highlight the new.
After completing the table, students will have a mini-outline. After the students fill in the table, we summarize the results of the work in the conversation mode. If the students have any questions, then I answer them, having previously found out if one of the students can answer the question that has arisen. This technique contributes to the development of the ability to classify, systematize incoming information, highlight the new.
“Creating a question plan”.
The student carries out a semantic grouping of the text, highlights the strong points, divides the text into semantic parts and titles each part with a key question
Stage 3. Working with text after reading .
Purpose: correction of the reader's interpretation in accordance with the author's intention
1. Conceptual (semantic) conversation on the text. Collective discussion of the read, discussion. Correlation of readers' interpretations (interpretations, evaluations) of the work with the author's position.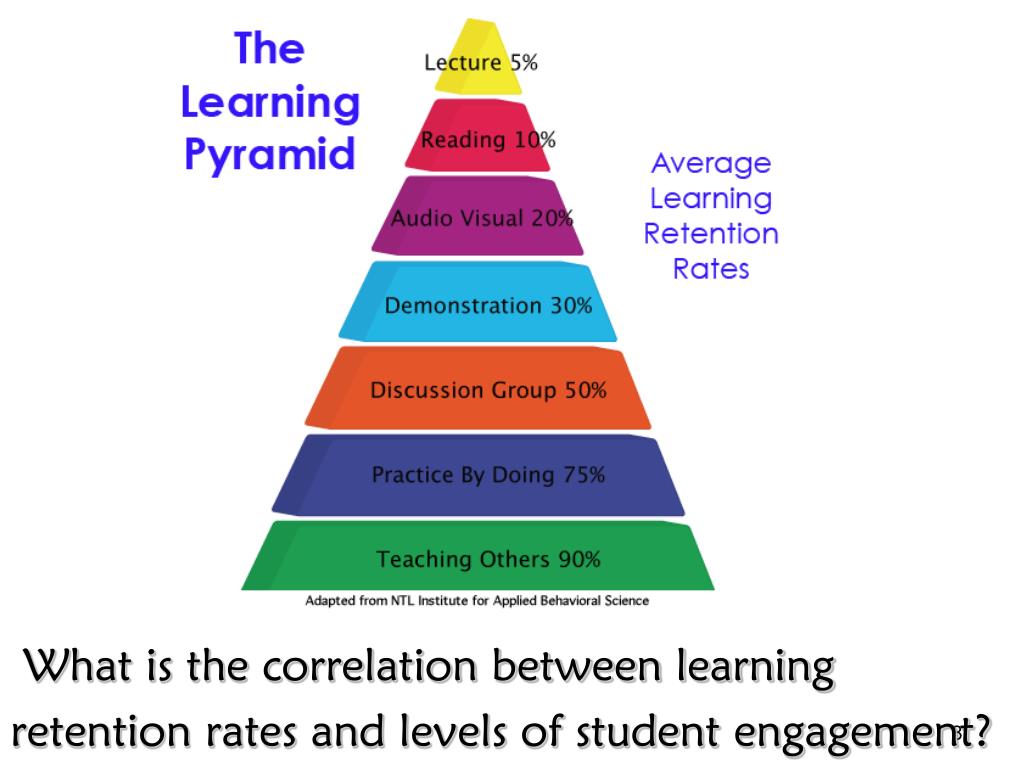 Identification and formulation of the main idea of the text or the totality of its main meanings.
Identification and formulation of the main idea of the text or the totality of its main meanings.
2. Acquaintance with the writer. Story about a writer. Talk about the personality of the writer. Working with textbook materials, additional sources.
3. Work with the title, illustrations. Discussing the meaning of the title. Referring students to ready-made illustrations. Correlation of the artist's vision with the reader's idea.
4. Creative tasks based on any area of students' reading activity (emotions, imagination, comprehension of content, artistic
Techniques for post-text activities.
- "Relationship between question and answer"
- "Time out"
- "Checklist"
- "Questions after the text"
"Relationship between question and answer"
The goal is to teach understanding of the text . One of the most effective post-text techniques. It differs from the rest in that it teaches the process of understanding the text, and does not control the result (understood - did not understand), shows the need to search for the location of the answer.
The answer to the question can be in the text or in the reader's word. If the answer is in the text, it can be in one sentence of the text or in several of its parts. To answer the question, you need to find the exact answer in one sentence of the text. If it is contained in several parts of the text, such an answer must be formulated by connecting them.
If the answer is in the reader's head, then in one case the reader constructs it by connecting what the author says between the lines or indirectly and how the reader interprets the author's words. In another case, the answer is outside the text and the reader is looking for it in his knowledge.
"Time out"
Objectives - self-test and assessment of understanding of the text by discussing it in pairs and in a group.
Reception implementation algorithm:
1. Reading the first part of the text. Work in pairs.
2. Ask each other clarifying questions. They answer them. If there is no confidence in the correctness of the answer, questions are submitted for discussion by the whole group after the completion of the work with the text.
They answer them. If there is no confidence in the correctness of the answer, questions are submitted for discussion by the whole group after the completion of the work with the text.
Checklist
This strategy is quite flexible. It lays down the conditions for the qualitative performance of any task. The “checklist” is compiled by the teacher for students at the first stages of applying the strategy.
Checklist "Brief retelling":
1. The main idea of the text is named. (Yes / No.)
2. The main thoughts of the text and the main details are named. (Yes/No.)
3. There is a logical and semantic structure of the text. (Yes/No.)
4. There are necessary means of communication that unite the main ideas of the text. (Yes/No.)
5. The content is presented in one's own words (language means) while preserving the lexical units of the author's text. (Yes/No.)
“Questions after the text”
The classification of questions, known as the “Taxonomy of questions”, involves a balance between groups of questions to:
- the factual information of the text, presented verbally;
- subtext information hidden between lines, in subtext;
- conceptual information, often outside the text.
These three groups of questions are now being supplemented by a fourth one - a group of evaluative, reflective questions related to the critical analysis of the text.
"Thin" and "thick" questions
After studying the topic, students are asked to formulate three "thin" and three "thick" questions related to the material covered. They then quiz each other using tables of "thick" and "thin" questions.
| Thick questions | Subtle questions |
| Explain why….? | Who..? What…? When…? |
- Read the text.

- What words occur most often in the text? How many times?
- Which words are in bold? Why?
- If you were to read the text aloud, how would you make it clear that this sentence is the main one?
- Noun (subject).
- Two adjectives (description)
- Three verbs (action).

- Four-word phrase (description).
- Noun (paraphrasing of the topic).
- How many paragraphs of the text?
- Pay attention to the words in thinned and bold type.
- Write out keywords.
- Coordinating conjunctions
- Intonation
- general minor member
- Explanatory words
- Comma
- Semicolon
- Dash
- No comma
- Reading 1 paragraph.
- We ask questions to the reader, he answers them.
- Reading in pairs to yourself 2 paragraphs, one student asks a question - the other answers.
- Reading 3, 4 paragraphs - students change roles.
- Give an example of a compound sentence, give a description according to the plan, draw up a diagram;
- make a mind map.

Question Tree
Crown - what? where? when? Barrel - why? How? Could you? Roots - how to relate the text to life? With current events? What is the author trying to show?
"Bloom's Cube" (Benjamin Bloom is a famous American teacher, author of many pedagogical strategies = technician).
The beginnings of the questions are written on the sides of the cube: “Why?”, “Explain”, “Name”, “Suggest”, “Think up”, “Share”. The teacher or student rolls the die.
It is necessary to formulate a question to the educational material on the side on which the cube fell.
The “Name” question is aimed at the level of reproduction, that is, at the simple reproduction of knowledge.
The question "Why" - the student in this case must find cause-and-effect relationships, describe the processes that occur with a particular object or phenomenon.
"Explain" question - the student uses concepts and principles in new situations.
Question Tree
Options for working with text.
"Questions to the text of the textbook"
The strategy allows you to form the ability to work independently with printed information, formulate questions, work in pairs.
We are talking about highlighting a phrase with your voice. Here lies an unobtrusive but reliable memorization.
Cluster
I use clusters for structuring and systematizing material. A cluster is a way of graphic organization of educational material, the essence of which is that in the middle of the sheet the main word (idea, topic) is written or sketched, and ideas (words, pictures) associated with it are fixed on the sides of it.
"Keywords"
These are words that can be used to compose a story or definitions of some concept.
"True and False Statements"
has a universal device, which contributes to the actualization of students' knowledge and the activation of mental activity. This technique makes it possible to quickly include children in mental activity and it is logical to proceed to the study of the topic of the lesson. Reception forms the ability to assess the situation or facts, the ability to analyze information, the ability to reflect one's opinion. Children are invited to express their attitude to a number of statements according to the rule: true - "+", not true - "-".
This technique makes it possible to quickly include children in mental activity and it is logical to proceed to the study of the topic of the lesson. Reception forms the ability to assess the situation or facts, the ability to analyze information, the ability to reflect one's opinion. Children are invited to express their attitude to a number of statements according to the rule: true - "+", not true - "-".
"Do you believe..."
It is carried out in order to arouse interest in the study of the topic and create a positive motivation for independent study of the text on this topic.
Conducted at the beginning of the lesson, after the announcement of the topic.
Sincwine
Develops the ability of students to highlight key concepts in the reading, the main ideas, synthesize the knowledge gained and show creativity.
Sinkwine structure:
"Mental maps" (graphic technique for organizing text),
Mind Mapping is a mind visualization technique. The applications of mental maps are very diverse - for example, they can be used to fix, understand and remember the content of a book or text, generate and write down ideas, understand a new topic for yourself, prepare for making a decision.
In the center of a landscape sheet, one word indicates the subject, which is enclosed in a closed outline. Branches are drawn from it, on which keywords are located. Sub-branches are added to branches until the topic is exhausted.
Mind maps activate memory. Lists, solid text, trees, and diagrams are the same. Mind maps, on the other hand, use every possible means to activate perception through diversity: different line weights, different colors of branches, precisely chosen keywords that are personally meaningful to you, the use of images and symbols. The technique of mental maps helps not only to organize and organize information, but also to better perceive, understand, remember and associate it.
The technique of mental maps helps not only to organize and organize information, but also to better perceive, understand, remember and associate it.
5. Diagnosis of educational outcomes using semantic reading techniques
The network project "Techniques of Semantic Reading" [1] describes the model of V.V. Pikan, in which all cognitive levels are illustrated by exemplary examples of key questions and tasks that make it possible to diagnose the quality of mastering knowledge and ways of students' activities. Each of the cognitive levels (knowledge, understanding, application, generalization and systematization, value attitude) is assigned the number of points received for completing the tasks of the mastered level. The table below shows examples of questions and tasks, assessment criteria.
| Cognitive levels and assessment criteria | Examples of key questions and tasks (beginning of formulations) |
| Knowledge - 1 point | Name. |
| Comprehension - 2 points | As you understand... Explain the relationship. Why ... Connect in semantic pairs .... Show on the graph... |
| Application - according to sample 3 b. | Make an offer…. Identify Traits character…. Apply the appropriate rule.... Compare…. Draw conclusions.... Present your point of view... |
| Generalization and systematization | Make a summary…. Make a table. |
| Value attitude - 2-10 b. | What does it matter…. What do you think…. Do you like…. |
6. Implementation of semantic reading technology techniques
1. Work with text before reading. Reception dissection question.
It is proposed to read the title of the paragraph "Compound sentence", the title of the scientific style text, and divide it into semantic groups; answer the question: what do you think the text will be about?
2. Working with text while reading.
Primary reading . Review reading or introductory reading:
1. Compound
2. Communication
3. Additional communications
Additional communications
4. Punctuation marks
Learning reading . Rereading text
3. Work with the text after reading.
Work in groups: 1 group, using keywords, makes up a story about a compound sentence; Group 2, based on the plan for syntactic analysis of a simple sentence, draws up a plan for characterizing a complex sentence.
General job:
Fig.1. Mind map "Compound sentence" of a 9th grade student Samara D.
7. Conclusion
Semantic reading forms cognitive interest, the ability to compare facts and draw conclusions, activates the imagination, develops speech, thinking, and also teaches how to work with information. The active implementation of semantic reading strategies, technologies by all teachers of various academic disciplines will make our graduates full members of the new information society.
References and references
- Project "Techniques of semantic reading" Auth. Dozmorova E.V., Director of the Center for Innovations in Education, FPC and PC TSPU, Ph.D. - https://www.planeta.tspu.ru/files/file/doc/1464065663.pdf
- Federal State Educational Standard for Primary General Education // http://standart.edu.ru/catalog.aspx?CatalogId=959.
- Variable learning technology / under.
 ed. Pikan V.V. / Teaching aid.: UTs Perspektiva, 2008
ed. Pikan V.V. / Teaching aid.: UTs Perspektiva, 2008 - Dozmorova E.V. Development of creative thinking of students in mathematics lessons. Methodological guide for teachers of mathematics - Tomsk 2008.
- Rozhdestvenskaya L., Logvina I. Formation of functional reading skills. A guide for the teacher. – https://slovesnic.ru/attachments/article/303/frrozhdest.pdf
- Fisenko T.I. Development of semantic reading skills when working with various texts in classes in grades 5–11 - https://www.kreativ-didaktika.ru/bailainer-obuchenie/didakticheskii-tramplin/razvitie-navykov-smyslovogo-chtenija.html
- Sapa A.V. Formation of the foundations of semantic reading within the framework of the implementation of the Federal State Educational Standard of basic general education.
strategies for reading and understanding texts
Content
- What are the strategies for reading and understanding texts?
- How do parents of children with dyslexia find support?
- Are there reading programs in kindergartens?
- At what age should a child learn to read?
- How does reading affect the worldview?
- Is the so-called “SMS language” a danger or an alternative?
Alexander Nikolayevich Kornev, Doctor of Psychology, Candidate of Medical Sciences, answers questions. A person who has been studying the meaning of texts for many years.
A person who has been studying the meaning of texts for many years.
What are the strategies for reading and understanding texts?
Alexander Nikolaevich: Despite the fact that reading is an important and significant area in our lives, one cannot fail to say that this is a serious work that requires considerable effort. An adult becomes able to read, loves to read after he, while a child, has been learning this for quite a few years. We can say that reading is the art of penetrating the text. What we understand by reading is a synthesis of the information contained in the text and our knowledge. Each of us has accumulated our own life experience and, reading the text, we give rise to individual associations. These associations and depth of immersion in the text vary greatly from reader to reader. It is a mistake to think, as they often say in school, that the author laid down some content, and the task of the student is to learn how to extract it. In fact, everything is more complicated: in the process of reading, a kind of dialogue between the reader and the text takes place, which gives rise to the result .
In order to penetrate into the process of reading and understand it, a number of studies were carried out using the eye-tracking procedure - tracking eye movements during reading. Research has shown that adults have different strategies for scanning text.
Continuous fast reading
Continuous fast reading strategy, when the eye goes through all the lines, one by one. This strategy is not the most efficient, and it is also quite time consuming. The study was conducted on a sample of students and it was determined that 10-15% of them have only this strategy. And, accordingly, even when it is not needed, they still spend a lot of effort and time using it. The school has different priorities, so the use of a variety of reading strategies is not taught there.
Selective reading
Another strategy is selective reading, where the reader selectively reads what interests him and skips the rest. It is more economical than the previous one. It is often used by competent readers.
Diagonal reading
The extreme expression of selective reading is called "diagonal reading". Skimming through the text, the reader chooses the key points of the content of the text and synthesizes the whole. This strategy is the most economical, but requires special training. Although some master it on their own.
A person with functional reading literacy has a range of strategies and can use them flexibly. This is the ultimate goal of what the school should teach. So far, unfortunately, this has not happened.
It is also impossible not to say that there are children who, having quite sufficient mental abilities, intellect, spending many years at school cannot learn the full skill of reading. For some children, this concerns mainly reading technique, for others, understanding also complements the problem.
Many of these children are invisible, and their difficulties are invisible not only to teachers, but also to parents. This was shown by recent mass surveys, which were initiated by the Association of Parents of Children with Dyslexia. These children experience enormous hardships, but often do not receive help. Studying them is just one of our tasks. In Russia, this problem, unfortunately, has not been actively studied for many years. And now the Laboratory of Neurocognitive Technologies of the National Research Center and the Department of Logopathology of the St. Petersburg Pediatric Medical University in Russia are perhaps the most active in such studies.
These children experience enormous hardships, but often do not receive help. Studying them is just one of our tasks. In Russia, this problem, unfortunately, has not been actively studied for many years. And now the Laboratory of Neurocognitive Technologies of the National Research Center and the Department of Logopathology of the St. Petersburg Pediatric Medical University in Russia are perhaps the most active in such studies.
Representatives of different sciences participate in these studies, because reading requires the use of resources of a very different nature: cognitive, physiological, linguistic. And psychologists, linguists, psychophysiologists and doctors are participating in the study of this issue. Interdisciplinarity for the development of this problematic is very important.
How do parents of dyslexic children find support?
Alexander Nikolaevich: This question is very topical and difficult. I would divide parents into 2 categories: the first, not very numerous, those who try to find help, do their best, literally devote themselves to helping the child. And, most importantly, they treat him sympathetically, condescendingly, psychologically support him.
And, most importantly, they treat him sympathetically, condescendingly, psychologically support him.
And another category is parents, who, alas, underestimate the seriousness of this deficiency and the severity of the child's experiences. Often, they see the reason for the child's lagging behind in negligence, bully the child, forcibly force him to read a lot. As a result, they exacerbate the child's feelings, but do not help.
It turns out that actually far fewer parents seek help than needy children, and also because at the moment there is no network of centers where dyslexics would be helped effectively.
That's why we go forward ourselves. We go to schools, because often such children remain unidentified. And we are starting to move towards providing assistance, including with the help of a specially developed digital methodology hosted on the SLOGY.RU online platform. The creation of a digital methodology has made it possible to make a breakthrough in the provision of effective and affordable assistance. Because anywhere in Russia, anyone who has access to the Internet can get help, even if there is no speech therapist nearby.
Because anywhere in Russia, anyone who has access to the Internet can get help, even if there is no speech therapist nearby.
Are there reading programs in kindergartens?
Alexander Nikolaevich: Of course, there is. There are several such recommended lists in preschool education programs. They contain works that are read to children. And they are sorted by age. But the fact is that reading aloud to children is an art. Being a reader does not mean just reading. And when it comes to children, this is especially important.
First, the reading must be expressive and artistic. Secondly, it should not be formal.
For example, this is what is called reading-dialogue, when the reading of a fairy tale is interspersed with a conversation, a dialogue with children. When they are invited to give their opinion. Not the one that is imposed on them, but their own impression that arose when listening to a fairy tale. Unfortunately, many institutions do not pay serious attention to this. This kind of reading, fairy tales, narratives allows, if it is done correctly, to infect the child with an interest in stories. First, an adult reads them, and then the child wants to do it himself. Of course, the family plays a huge role here.
This kind of reading, fairy tales, narratives allows, if it is done correctly, to infect the child with an interest in stories. First, an adult reads them, and then the child wants to do it himself. Of course, the family plays a huge role here.
Studies have shown that the more parents are interested in reading, the more often they read, the more likely that the child will develop an interest in reading. And it helps a lot if the child has difficulties. That is, a lot depends on the attitude of adults to the book, on the value position of reading.
Unfortunately, in our society, this is not as good as we would like. And adults began to read less often, and children are much less likely to reach for a book. In other words, this is a social problem, and not just a methodological one.
At what age should a child learn to read?
Alexander Nikolaevich: if we talk about the average figures that are known, then this age coincides with the beginning of schooling - 6. 5-7 years. It takes about three years to master the technique of reading. And then the child feels more free in the space of the text and begins to enjoy, he develops interest. He reads of his own free will, and not because he was told at school. But there are many exceptions: there are children who, at the age of three or four, learned to read on their own. However, it is difficult to predict the likelihood of such an early reading acquisition. It is partly genetically determined, but the contribution of the environment is also great: at the end of 19- At the beginning of the 20th century there was a tradition of family reading, when adults read aloud to each other. The kids got into it too. Alas, this tradition has died out and is very rare now, and this infects the child - children have well-developed imitation, and if they see that adults are interested, they become interested too. And they are trying to get into this world. Therefore, the value position of reading, in my opinion, is very important.
5-7 years. It takes about three years to master the technique of reading. And then the child feels more free in the space of the text and begins to enjoy, he develops interest. He reads of his own free will, and not because he was told at school. But there are many exceptions: there are children who, at the age of three or four, learned to read on their own. However, it is difficult to predict the likelihood of such an early reading acquisition. It is partly genetically determined, but the contribution of the environment is also great: at the end of 19- At the beginning of the 20th century there was a tradition of family reading, when adults read aloud to each other. The kids got into it too. Alas, this tradition has died out and is very rare now, and this infects the child - children have well-developed imitation, and if they see that adults are interested, they become interested too. And they are trying to get into this world. Therefore, the value position of reading, in my opinion, is very important.
How does reading affect the worldview?
Alexander Nikolaevich: When a person reads a book, he creates an imaginary world, forms his own "text image", reflects and draws his own conclusions. By thinking, he develops his brain. Figuratively speaking, it builds a kind of processor in the brain that can process texts and extract meanings. On the other hand, literary texts enrich the child's personality. Because in fiction we are given a colossal layer of experience that we are deprived of in real life. And it helps personal growth. This contribution is, of course, invaluable. I'm not talking about the benefits for the development of speech and the enrichment of vocabulary.
Is the so-called “SMS language” a danger or an alternative?
Alexander Nikolayevich: Regarding the language of communication on the Internet and embedding it in our everyday communication, speech, there are different points of view, but they can rather be called opinions - this topic has not yet been seriously studied not only in Russia, but also in the world . In my opinion, cause and effect are often confused here. That is, it's not about the Internet, not about SMS, but about the language poverty of a considerable proportion of the population.
In my opinion, cause and effect are often confused here. That is, it's not about the Internet, not about SMS, but about the language poverty of a considerable proportion of the population.
If a child or an adult has a need to communicate with a book, he will not replace it by flipping through pictures or something like that. But if there is no gravity, then the void can be filled with anything.
It is impossible not to say about the change in culture and oral language, which, alas, is not growing in our country, but rather falling. Thus, a vicious circle is created - the poverty of the dictionary makes it difficult to understand the text, and little reading experience limits the growth of vocabulary. And we see this clearly and concretely. Children, reading texts of literature, especially classical ones, sometimes do not understand up to a third, or even half of the full meaning of words. A colleague will add to my words.
Ingrida Balciuniene: I am Associate Professor of the Department of Logopathology at the Pediatric Medical University and Vytautas Magnus University (Kaunas, Lithuania). I study reading problems both there and here. I would like to draw attention to the frequent complaints from parents and teachers that the child does not want to read and does not like the book. He is happy to “sit in a laptop or phone”, but does not want to take up reading. Often in response to this complaint, advice is given: give him an e-book, download it to the tablet, and let the child read and develop. I don't think this is an option. Digitizing a book when the child is presented with the same material on a tablet screen will not help. Book speech is complex, it is characterized by long complex sentences, low-frequency and therefore unfamiliar words to the child. In order for the e-book to really help and the child to read with pleasure, additional technological solutions must be taken. For example, interactivity, intertextuality - so that the child can click on any word that he did not understand, and with this click he would open a definition, an explanation. Such active meaningful and meaningful reading can partially help solve this problem.
I study reading problems both there and here. I would like to draw attention to the frequent complaints from parents and teachers that the child does not want to read and does not like the book. He is happy to “sit in a laptop or phone”, but does not want to take up reading. Often in response to this complaint, advice is given: give him an e-book, download it to the tablet, and let the child read and develop. I don't think this is an option. Digitizing a book when the child is presented with the same material on a tablet screen will not help. Book speech is complex, it is characterized by long complex sentences, low-frequency and therefore unfamiliar words to the child. In order for the e-book to really help and the child to read with pleasure, additional technological solutions must be taken. For example, interactivity, intertextuality - so that the child can click on any word that he did not understand, and with this click he would open a definition, an explanation. Such active meaningful and meaningful reading can partially help solve this problem.
Alexander Nikolaevich: And I would add that the contribution of parents can be very large. Alas, in my experience, this happens quite rarely. Reading aloud to children usually ends at the age of 2-3 years and rarely, rarely reaches the beginning of schooling. And when a child has learned to read, parents for some reason think that since he can do it himself, now he no longer needs to read aloud. In fact, it is only after three or four years that the child will begin to understand in any depth what he is reading. This emphasizes the fact that reading aloud by an adult is also necessary for a child at school age. And in many countries this is cultivated: there is even an international society of narratologists, which specifically shares its experience and develops appropriate methods for reading and telling stories to children. You need to make time and spend it reading aloud to your child. Of course, every adult has his own life and his own troubles, but this contribution can hardly be overestimated, because it is a contribution to the formation of the child's personality.

 .., Define..., Formulate... . Retell ... List .... Choose the correct answer…. Complete the word…. Show…, Find out...etc.
.., Define..., Formulate... . Retell ... List .... Choose the correct answer…. Complete the word…. Show…, Find out...etc.