Hands on learning activities
13 Hands-On Activities for Kids That Will Make Learning Fun
* This post may contain affiliate links or sponsored content. *
Did you like this article? If so, please help by sharing it!
261 shares
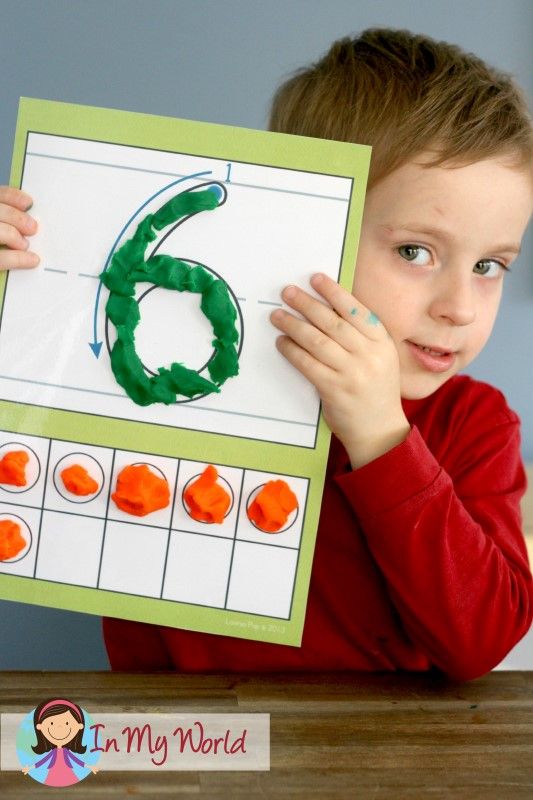
Hands-on activities for kids and teens make learning memorable and fun. Try these 13 hands-on learning activities that are versatile enough for any subject.
I still feel guilty. I carefully constructed my see-saw and placed the bucket of plastic army men on one end. Now, I was ready to jump on the other end and watch the bucket spin through the air, army men nestled safely inside, and land a few feet away just like the scenes in cartoons.
Except cartoons defy the laws of physics and gravity. Buckets of plastic army men in kindergarten classrooms do not.
I wish I could remember the name of the little boy I let take the fall for me. I’d apologize for high-tailing it in the other direction while our teacher scolded him for raining plastic army men all over the classroom.
Forever emblazed in my mind, that memory embodies hands-on learning at its finest. (Expect for my innocent classmate.) Activities that engage the body and mind enhance learning and retention. The best hands-on learning activities for kids are open-ended, versatile, and easily adaptable for all ages.
The following activities will work for any age and nearly any subject whether you’re looking for hands-on activities for middle school and high school students or ideas for your elementary kids.
Versatile Hands-on Activities for Kids
1. Build a Map
Increase understanding and help kids visualize history and geography with a 3-D map. Building maps helps kids understand things like why Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt appear mislabeled on a flat map.
Maps help them see the role that geography plays in wars, culture, and civilization. Try some of our favorite hands-on activities with maps such as:
- salt dough maps
- paper mâchè maps
- cookie maps
- crispy cereal maps
2.
 Make Costumes
Make CostumesKids love costumes, simple or elaborate. I’m no seamstress, so when my kids were little, we assembled store-bought costumes or simple, DIY options.
Sewing your own costumes provides hands-on learning for math skills as your child measures, figures out how much material she’ll need, and cuts out the pattern. Don’t forget to count this as home ec time!
3. Put on a Play or Puppet Show
From writing the script to building the set, kids practice a variety of skills as they prepare a puppet show or play. They learn dialogue, descriptive writing, oral communication, art, creativity, and more.
Performing the play and acting out the scenes they create, reinforces students’ understanding of the people, places, and events they’re studying.
4. Create a Presentation
Oral presentations make a fantastic alternative to written assessments. Preparing the presentation provides an opportunity for kids to
review.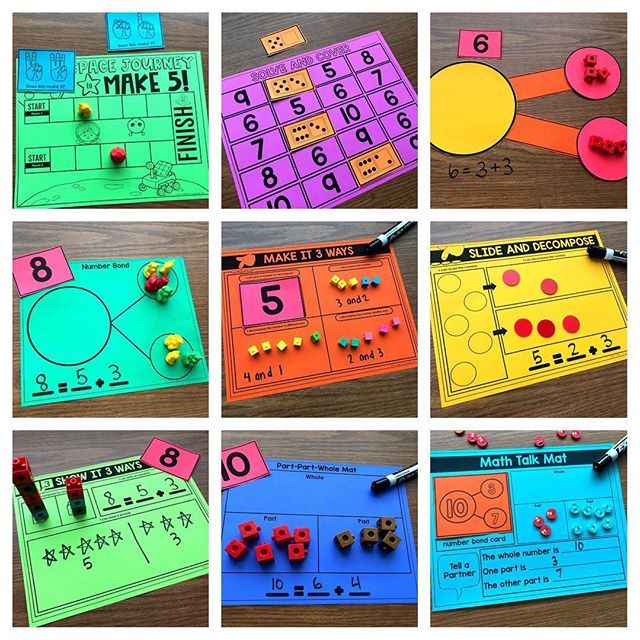 Presenting it showcases what they learned (and may highlight areas you need to go over again).
Presenting it showcases what they learned (and may highlight areas you need to go over again).
Students can assemble an oral presentation with or without a presentation board, or they can try their hand at PowerPoint, a slideshow, or photo journaling.
5. Make a Paper Mâchè Model
Easily add hands-on learning to subjects like history, science, or geography with paper mache models. Build a model of the earth or even the whole solar system.
Way back in the day, my oldest created a paper mache Leaning Tower of Pisa when we studied Italy. I remember my cousin making a model of the Liberty Bell when he was a kid. There are so many creative possibilities!
Think about science models, historic landmarks, or replicas of key elements from a novel for a literature course.
6. Prepare a Themed Dinner
You probably first think of history or geography when considering a themed dinner, but with a little creativity, meals could represent concepts from science, math and other subjects.
Fix pizza and a round cookie cake when studying circumference. Make a pie for Pi Day. Bake an apple pie when you study Issac Newton.
7. Do a Paper Bag Book Report
Toss boring written book reports and try a paper bag book report instead. Kids start with a paper bag and add items that represent some aspect of the book (or a person’s life, a time in history, or an invention). Then, they pull out the items, one by one, and recap the highlights of the book as they explain the significance of each.
8. Make a Lapbook or Notebook
One popular, hands-on method of showcasing what kids have learned is assembling a lapbook. You can make your own lapbooks or try a variety of ready-made lapbook sets.
If your kids aren’t fans of lapbooking (mine aren’t), let them make a story notebook or notebooking instead.
For those who want to give interactive lapbooks and notebooks a try, you might like this Landforms Interactive Notebooking Pack or some of these notebooking pages on topics from botany to art/artists to geography and more!
9.
 Build a Diorama or Model
Build a Diorama or ModelMy kids used to love building dioramas for different biomes (like the ocean or desert), but you can adapt these little shoebox models for many different purposes.
If dioramas aren’t your thing, try other model options like a construction paper representation of Earth’s layers, a shoebox lid Roman road replica, or an edible cell model. Just don’t drop it!
10. Create Art
Your kid doesn’t have to be an artist, and his projects don’t have to be elaborate. Encourage him to choose something that represents some aspect of the topic he’s studying. He might try a collage of vertebrates if studying mammals or a painting of sea creatures for marine biology.
Kids can make their own cave paintings on paper bags. Let them create a mixed media masterpiece depicting a historical event or famous person or try their hand at sculpting with clay.
11. Write an ABC BookDon’t skip this idea just because you have high school students! ABC books make a versatile tool for all ages. Use blank board books or homemade books to create an ABC story on any topic. The older your student, the more detail you can require for the book.
Use blank board books or homemade books to create an ABC story on any topic. The older your student, the more detail you can require for the book.
Your student can create a math ABC book – A is for angle, B is for base, and C is for circumference.
Try geography – A is for archipelago, B is for beach, and C is for canal.
The possibilities for ABC book topics are endless!
12. Play GamesGames make a fun, low-key way to learn new topics or review concepts. Bingo, matching, memory, or fishing are some of my favorite, easily adaptable, DIY games for almost any subject.
For fishing, tie a magnet to a dowel rod with a piece of twine. Then, put paper clips on index-card “fish” or cut fun fish shapes from construction paper. When kids catch the fish, they have to read or define the word, explain the concept, or answer a question based on what you wrote on the card.
You can also use your imagination, a pack of index cards, and the board from most board games to create your own homemade learning games. Jeopardy is a fantastic game for teens and tweens or try Periodic Table Battleship.
Jeopardy is a fantastic game for teens and tweens or try Periodic Table Battleship.
We’ve done everything from caves (for geology) to a replica of one of Columbus’ ships (history) to an emergency room (health and safety). We’ve even done an official (as opposed to a homeschool stereotype) field trip to a grocery store.
Heading out to see the things you’ve been studying in person is one of the best hands-on learning activities around. Simple, stress-free homeschool field trip planning tips make a group outing a breeze. Try my field trip ideas for middle school and high school students or get some fantastic field trip ideas for preschoolers.
Hands-on activities for kids and teens make learning fun and memorable – plastic army men and 5-year-old innocent bystanders not required.https://www.weirdunsocializedhomeschoolers.com/encounter-with-a-homeschooler/
What are some versatile hands-on activities that you and your kids enjoy?
You Might Also Like
Wendy Hilton
Weird, Unsocialized Homeschoolers | + posts
Wendy is one of the owners of Hip Homeschool Moms, Only Passionate Curiosity, Homeschool Road Trips, Love These Recipes, and Weird, Unsocialized Homeschoolers. She married her high school sweetheart, Scott, 31 years ago, and they live in the South. They have three adult children. Hannah, age 27, has autism and was the first homeschool graduate in the family. Noah, age 25, was the second homeschool graduate and the first to leave the nest. Mary Grace, age 19, was the last homeschool graduate. Wendy loves working out and teaching Training for Warriors classes at her local gym. She also enjoys learning along with her family, educational travel, reading, and writing, and she attempts to grow a garden every summer with limited success. (But she's learning!)
She married her high school sweetheart, Scott, 31 years ago, and they live in the South. They have three adult children. Hannah, age 27, has autism and was the first homeschool graduate in the family. Noah, age 25, was the second homeschool graduate and the first to leave the nest. Mary Grace, age 19, was the last homeschool graduate. Wendy loves working out and teaching Training for Warriors classes at her local gym. She also enjoys learning along with her family, educational travel, reading, and writing, and she attempts to grow a garden every summer with limited success. (But she's learning!)
Did you like this article? If so, please help by sharing it!
261 shares
The 20 Best Hands On Activities for Kids They Will Play for Hours
There are some hands on kids activities that are a ton of fun. Your kids will beg to play them, to do them over and over, and OVER again! These are the ones that would be on my kids short list. They love open-ended play ideas.
They love open-ended play ideas.
…And I love how these activities reach a wide range of ages. My tots and elementary aged kids have an activity they can do – together!
These hands on activities will keep your kids busy for hours!Hands On STEM Play Ideas
These hands on play ideas are not only fun, but many times educational in their own right. Many of them are actually STEM activities and ignites your child’s inquisitive side, as well as their creative side.
Whether you have young children or older kids these learning activities are a fun way to encourage sensory play and explore the natural world. Looking for a fun activity to practice fine motor skills? We have them!
These fun ideas are a perfect time to encourage messy play, enjoy craft supplies, and enjoy learning fun with these easy science experiments. These kids activities are the best ideas for little learners and even younger children.
Fun Hands On Educational Activities For Kids
1.
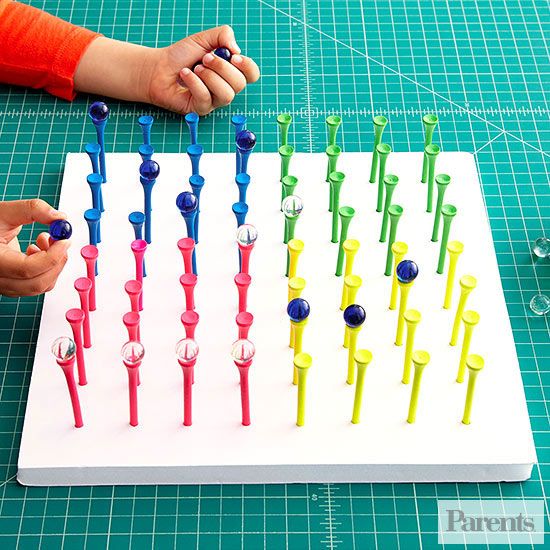 Straw and Stick Construction
Straw and Stick ConstructionWho knew that straws and sticks could entertain your kids so long! This is a great STEM activity as you are building engineering different things.
2. Kinetic Sand
I’m telling you, if your kids haven’t tried playing with kinetic sand yet they need to! The stuff is addicting. Promise! It is soft, damp, and sticks together like crazy!
3. Building Paper Blocks
Paper blocks are so much fun to make AND build with. All you need is scraps of paper and tape. This is another great STEM activity as it focuses on both science and engineering.
4. Silly Faces
Make silly faces! It’s fun in the mirror, fun to mimic each other and even fun to recreate on paper!
5. Paper Boxes
These Paper Boxes are harder to make than they look. Perfect for a puzzling kiddo. Preschoolers can just glue bits of paper together. Next: Build with our blocks!
This gives a literal meaning to hands on activities.Hands On Science Kids Activities
6.
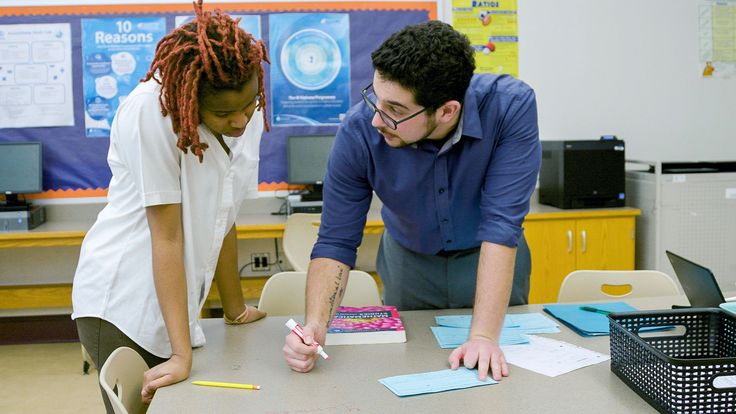 Brain Building Activity
Brain Building ActivityWho knew building brain neurons could be so fun! My son LOVED this “activity.” This really explains the brain to children and how it works. It’s a cool experiment.
7. Marshmallow Sculptures
Add some marshmallows and toothpicks to your kiddos play and not only will they have a blast building, they will also love the sugar rush… it’ll wear off.
8. Make The Best Paper Airplane
Paper Airplanes is a classic activity that’s been a favorite for years. The cost for an afternoon of play is just a ream of paper. Make paper airplanes – try this design, BEST ever!
These hands on activities are great for kids of all ages including toddlers, preschoolers, and kindergarten kids.STEM Activities for Kids
9. Portable Tinkering Kit
Tinker away! Create a kit of random bits for your kids to build and create with! Plus, it is portable, take it anywhere!
10. Reasons To Build A Court
Build a fort! It doesn’t matter if you make it out of PVC piping, old bed sheets or chairs. Your kids will have a blast!
Your kids will have a blast!
11. Pool Noodle Structures
Old pool noodles are not trash!! Your kids can build massive structures with them, all you need are toothpicks.
12. Pom Pom Maze
Make a maze for your kids to navigate a pom-pom through. All you need is a stack of post-it notes!
That string obstacle course looks like so much fun. That could easily be turned into a ‘Mission Impossible’ type pretend play.What To Do When Kids Are Bored
12. Super Mario Dollhouse
Make a Mario World, or whatever your kids favorite screen game is, bring it to the real world.
13. Upcycled Cardboard Mazes
Mazes are mesmerizing. Make one with supplies you have on hand.
13. Giant Web
Never ending fun! That is what a skien of yarn will give you. Give your kids the task to make a giant web – and then they can crawl through it.
14. Engineering Challenges
Plastic disposable cups and craft sticks! Just sit back and watch your kiddos will build and create.
Fun Hands On Activities
Half the fun in this activity is the creation, plus this is yet another amazing STEM activity. Make a maze!!
15. Tiny Dancers
This dancing battery gal is easy to make, try giving the instructions to your elementary aged kiddos along with the supplies.
16. Air Fort
All you need is a box fan, a big sheet and an empty room. Hours. Your kids will be shrieking and crawling as a snake for hours.
17. Cardboard Castle
Got a big box? If not, check with your local appliance store! You can make an accordian castle!
Look at all the beautiful colors on the cd’s.18. DIY Cardboard Construction
You don’t need to spend money to make toys that will help build your kids brains. Raid the rubbish bin for some cardboard!
19. Button Spinner
Spin away! Decorate CDs to become colorful orbs of color. This is one of our many fun hands on activities.
20. Basic Toothbrush Robotics
Who knew that a toothbrush could be and do so much more than just brush teeth. Transform it into a robot.
Transform it into a robot.
21. DIY Guess Who
Learn about historical figures – create a game of Guess Who. This is a great game for elementary kids.
More Science and Educational Activities From Kids Activities Blog:
- If you are looking for science projects for 4 year olds, we got ya covered!
- Science Activity: Pillow Stacking <–it is fun!
- Create your own LEGO instruction books with this fun STEM idea for kids.
- Build this solar system model for kids
- You already have the red cups from this STEM project, so here is another one in a red cup challenge which is a cup building project.
- Follow along the simple steps to how to fold a paper airplane and then host your own paper airplane challenge!
- Build this straw tower STEM challenge!
- Got a lot of building bricks at home? This LEGO STEM activity can put those bricks to good learning use.
- Here are a bunch more STEM activities for kids!
Which hands on activities for kids did you try? Which ones are your favorite? Let us know in the comments, we’d love to hear from you.
Diagnosis of left-handedness as a condition for the development of cognitive abilities of younger students in educational activities
The article gives a brief idea of left-handedness, diagnostic complexes for its detection to take into account the organization of educational activities in order to develop cognitive abilities in left-handed younger schoolchildren.
Keywords: left-handedness, abilities, educational activity, diagnostics.
.
Today, in almost every class there are children who work with their left hand - left-handed, that is, they actively prefer the left hand to the right when writing, drawing and performing other activities. Left-handed children (as well as right-handed ones) are different in their psychological and physiological characteristics, in their abilities, interests and problems.
In our time, it is hard to even believe that left-handed people were once treated as cripples, sinners, or degenerates, that they were burned on inquisitorial fires and placed in asylums for the mentally ill.
Until recently, left-handedness was a serious pedagogical problem. It was considered necessary to systematically retrain left-handed children, who had no alternative in choosing a hand for writing - everyone had to write with the right.
There is still no clear and unambiguous answer to the question: what is the cause of left-handedness and how does a left-handed person differ from a right-handed person? But experts agree that left-handedness is the result of a special organization of the brain, one of the options for the normal development of a child. And of course, left-handedness cannot be considered a disease, and even more so a prerequisite for a decrease in mental abilities.
On July 8, 1980, the Pravda newspaper published an article “If you are left-handed?”. For the first time, it was publicly announced that the forced retraining of left-handed children causes them irreparable psychological trauma.
For the first time, it was publicly announced that the forced retraining of left-handed children causes them irreparable psychological trauma.
Symposiums and conferences were held, lectures were given for teachers, at which experts convincingly argued that it was impossible to forcibly retrain left-handed people at preschool age, and especially in the elementary grades of the school. This can cause a negative attitude towards learning, failure and even cause mental illness in a child. “Double” retraining after the first or second quarter of the first grade is strictly contraindicated.
Since 1985, schools have gradually abandoned the retraining of left-handed children, as a result of which they began to appear en masse. Now left-handers are retrained only by the most dense or unscrupulous teachers.
Thus, the problem of left-handedness for the school is not removed, since children with “hidden left-handedness” remain.
A fairly weighty methodological base of works on the problems of left-handedness belongs to such scientists as A.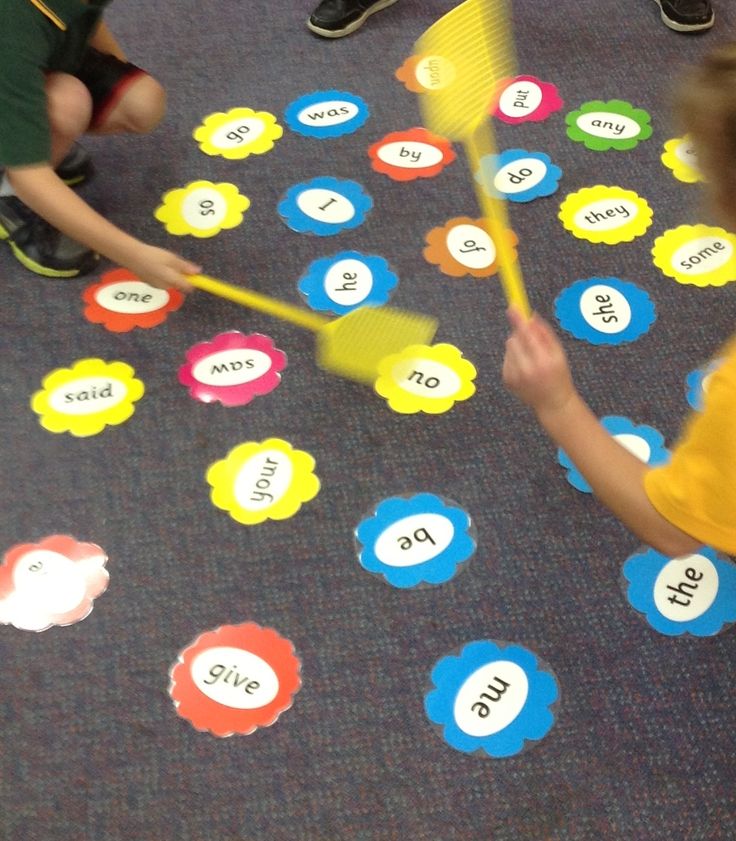 P. Chuprikov, A. R. Luria, V. A. Moskvin, T. A. Dobrokhotova, N. N. Bragina, M. M. Bezrukikh.
P. Chuprikov, A. R. Luria, V. A. Moskvin, T. A. Dobrokhotova, N. N. Bragina, M. M. Bezrukikh.
In connection with the foregoing, the topic is relevant at the present stage of development of correctional pedagogy.
If the leading hand was not identified before school, then this must be done in the first year of study. This process is complicated by the fact that relearning could occur in the early period of the child’s development, as a result of which later he already draws and writes with his right hand, but performs everyday activities with his left [1].
When mastering everyday skills, the hidden left-handedness of the child, as a rule, does not affect the success of performing actions, however, when starting systematic schooling, especially when mastering writing and reading, such children may encounter unexpected difficulties.
Therefore, it is important to determine the direction of the child's "handedness" before the start of training: in kindergarten or when entering school.
The developed methods of foreign and domestic scientists make it possible to diagnose children in identifying the leading hand in order not to encounter problems associated with educational activities in the future.
To diagnose the dominant hand, questionnaires are used, as well as functional tests, among which the most popular are: “Napoleon’s Pose”, “Clutch of fingers”, “Applause”, “Shoulder test”, “Drawing geometric shapes”, “Hand taking objects. A hand that better recognizes an object”, “A hand that performs habitual actions” [2].
Having a variety of different methods for determining the dominant hand, a comparative analysis of two diagnostic complexes for the identification and study of left-handedness was carried out:
‒ a set of tests developed on the basis of the classical methods of such scientists as A. R. Luria and A. P. Chuprikov (“Poses of Napoleon”, “Clutch of fingers”, “Applause”, “Shoulder test”, “Drawing of geometric shapes”, “ Hand that picks up objects, “Hand that better recognizes an object”, “Hand that performs habitual actions”).
‒ a set of tests developed by M. G. Knyazeva and V. L. Vildavsky (“Drawing”, “Opening a matchbox”, “Folding a well from sticks”, “Playing a ball”, Cutting with scissors along the contour of a picture”, “Stringing beads ”, “Performing rotational movements”, “Untying knots”, “Building from cubes according to the model”) [5].
As a result of an empirical study conducted in the secondary school No. 4 of the city of Fryazino, Moscow region among students in grades 1–4 in the amount of 12 people, after receiving the results, the hypothesis was proved using two methods: Rosenbaum's Q criterion; The Mann-Whitney U criterion, about the most informative and reliable diagnostic procedure for detecting and studying left-handedness in children, complex 1 proved to be more informative and reliable compared to complex 2.
What should be taken into account when organizing educational activities for left-handed people:
- Spatial organization of the working field (part of the board): objects on the right side of the board and on the right side of the notebook, sheet are perceived better;
‒ Color organization (blackboard and chalk color): optimal perception of notes made with dark chalk on a light board;
‒ Conditions for successful activity: the presence of figurative visualization, context, connection of information with reality, with practice, preference for creative tasks, experiments, background music and speech rhythm have a beneficial effect;
‒Formation of motivation: gaining authority, the prestige of a position in a team, the desire to establish new contacts, understanding the social significance of activity are significant;
- Perception of material: integrity of perception, priority of visual perception of information, good understanding and orientation to intonation in speech;
‒ Information processing: fast, instant material processing;
- Activity: preference for practical activities in the lesson;
- Memory: involuntary, visual-figurative;
- Thinking: visual-figurative, spontaneous, emotional, intuitive, three-dimensional;
- Self-control: do not control the correctness of speech, allow semantic omissions;
‒ Characteristic errors: stressed vowels, dictionary words, omissions of letters, misspellings, proper names are written with a lowercase letter;
‒ Test methods: oral survey with open-ended questions (own detailed answer) is preferred.
So, a left-handed child can have a lot of problems at school. But it should be noted that left-handedness is a risk factor not in itself, but in connection with certain disorders and developmental disabilities that may occur in a particular child [3]. Not all left-handed children, especially if attention was paid to their full-fledged mental development in preschool childhood, will have serious complications in mastering educational activities.
The most successful in all aspects of life are children with hereditary left-handedness, who have genetic left-handedness, which is not associated with impaired brain activity. When studying, they, as a rule, do not have acute problems, show good results in writing, reading, mathematics and other subjects.
A left-handed child requires special attention and a special approach, not because he is left-handed, but because, like any child, he is unique and individual.
Literature:
- Emelyanova EN Levshata at school and at home: how to define leftism; help you study well.
 — M.: Eksmo, 2010. — 160 p. — (Learning? Easy! Neuropsychologist's advice).
— M.: Eksmo, 2010. — 160 p. — (Learning? Easy! Neuropsychologist's advice). - Nikolaeva E. I. Left-handed child: diagnosis, training, correction. - St. Petersburg: "CHILDHOOD-PRESS", 2009. - 128 p.
- Practical Psychology of Education: Textbook 4th ed. / Edited by I. V. Dubrovina - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2007. - 592 p.: ill.
- Semenovich A.V. Introduction to neuropsychology of childhood: Textbook. — M.: Genesis, 2005. — 319 p.: ill.
- Shelopukho O. A. Left-handed and right-handed. - M .: CJSC "OLMA Media Group", 2011. - 320 p. - (Series "Mom's school").
Basic terms (automatically generated) : child, learning activity, dominant hand, set of tests, left hand, object, problem, hand, school.
Main page
All news and announcements
News
10.10.2022
Talk about something important: "The role of the father in shaping the personality of the child"
10. 10.2022
10.2022
Teachers of the CHCI RUK visited the Pervomaiskaya secondary school of the Batyrevsky district
10.10.2022
Information for applicants
Announcements
10/07/2022
Attention! Career Guidance Week at CHKI RUK!
07.10.2022
Russian Drama Theater invites
06.10.2022
We invite you to professional retraining courses!
Training programs
Take control of the future
Economics
Economics and management of the national economy (regional economy)
Law
Civil law; business law; family law;
private international law
Jurisprudence
Legal support of entrepreneurial activity
State and municipal administration
Public-private partnership
Management
Project management
Management
Human Resources
Economics
Finance and credit
Economics
Banking and financial management
Economics
Accounting, analysis and audit
Service
Organization and management of events
Advertising and public relations
Advertising and public relations
Jurisprudence
Criminal law profile
Merchandising
Quality management
and assortment of goods
Trade
Commerce
State and municipal administration
Territory development management
Management
Logistics and supply chain management
Economics
Economics of small and medium business
Psychology
Management psychology
Product technology and catering
Production and service organization in the catering industry
Information systems and technologies
Electronic business information systems
Anti-corruption organization in institutions and organizations
Entrepreneurship and innovative business development
Development of personal and business qualities as a tool for a successful career
Fundamentals of litigation in the Russian Federation
Introduction to the practice of law
School of Healthy Nutrition "Health Management or Youth Navigator"
Cooperative business
Creative management in consumer cooperation
Career and time management
Modern methods of managing organizations and developing the thinking of leaders
Modern approaches to teaching a foreign language in a non-linguistic university
Topical aspects of psychodiagnostics for managers of the system of organizations and enterprises
Culture of business communication in the "seller-buyer" system
Basics of work in the program 1C: Enterprise 8. Trade management
Trade management
System Administration
Fundamentals of work in the program 1C: Enterprise 8. Salary and personnel management
1C operator
Management
Cooperative business model
Economy
Digital economy
Economics
Accounting, analysis and audit
Finance and credit
Financial management of commercial organizations
Commodity research
Commodity research and expertise in foreign trade activities
Management
Business Marketing
Economics
Accounting and taxation
State and municipal administration
Project and program management
Customs
Customs logistics
Customs
International customs cooperation
Customs
Customs payments
Economic security
Economic and legal support of economic security
Our graduates work here
Photo stories I Photo gallery
Student life
With the help of photographs, we try to preserve the whole life of the university, all significant events, all holidays here.