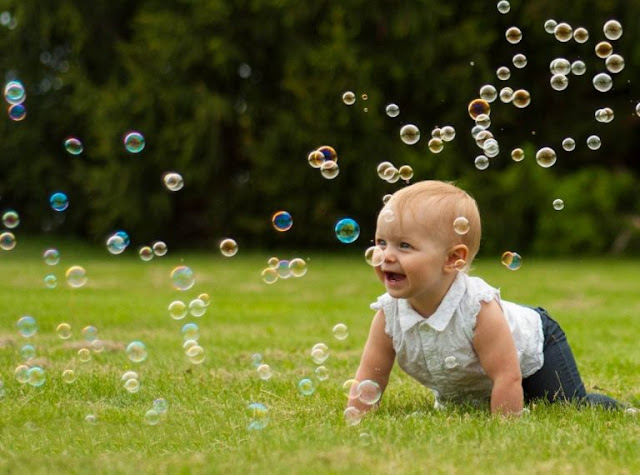
How to help children with social skills
6 Ways to Improve Your Child's Social Skills
Few things can be more frustrating than watching your child struggle to
make friends or having a difficult time fitting into certain social settings.
There are several steps parents can take to improve their child's social skills.
1. Follow Their Interests
Enjoying others will come more naturally when a child is doing something they are genuinely interested in. Whether it's participating in a favorite sport, playing an instrument they like or being part of a club they're interested in, this is the first step toward building social skills. It also places a child around like-minded individuals that the child will probably feel more at ease with. While it's important to be able to socialize with those of varying interests, starting out with other kids who like the same things is an excellent way to more easily build social skills.
2. Learn to Ask Questions
Sometimes when children get nervous or a conversation lags, they may become more introverted and ultimately struggle in future social situations. According to the Center for Development & Learning there are several ways children can initiate and carry on positive conversations with others. One important way is to ask questions. The best way to find out about others and form connections is to ask questions that specifically pertain to the person the child is talking with. Encourage your child to ask questions that can't be answered with just a yes or no.
3. Practice Role Playing
Pretend-play, with both younger and older children, is a great way for kids to actively practice their social skills. LD Online gives parents practical tips for effective role-playing. Have your child pretend to be the person they have difficulty talking to or getting along with. This will give you an idea of what this person is like, or at least how your child perceives this particular person. Then switch roles to see how your child does when pretending to interact with the person. Suggest ways your child can more effectively talk with the individual. Don't forget to include body language, such as smiling and making eye contact, when advising your child.
Don't forget to include body language, such as smiling and making eye contact, when advising your child.
4. Teach Empathy
If children have a better understanding of how others feel, they are much more likely to feel connected to other people and form positive bonds. Parents suggest teaching empathy by talking about different situations and scenarios with your child. Ask how other people might feel when each of these things happen. Part of teaching empathy is to help children learn how to actively listen to others. This involves focusing on what others are saying and then thinking about what the speaker has said once the conversation is over.
5. Know Your Child's Limits
Some children are simply more social than others. A child who is shy and introverted should not be expected to interact in the same way as a child who is naturally outgoing. Some children are comfortable in large settings, while others find it easier to relate to their peers when in smaller groups. It's also important to understand a child's time limits. Younger children and those with special needs may only feel comfortable socializing for an hour or two.
It's also important to understand a child's time limits. Younger children and those with special needs may only feel comfortable socializing for an hour or two.
6. Be a Good Role Model
It's important to be consciously aware of how you interact with others when your child is watching. Are you asking questions of others and then taking the time to actively listen? Do you show genuine empathy for friends and family in your life? The Center for Parenting Education states that being an effective role model requires conscious effort and forethought. Children are constantly watching the adults in their lives.
It's important to remember that it will take time for your child to develop good social skills. Social skills are something that are developed and improved upon over a lifetime.
Contact us today to schedule an assessment. You can also view the research and results of the program on the website.
8 Important Social Skills For Kids And How To Teach Them
Teaching social skills for kids is one of the most complex, confusing, but rewarding aspects of raising young children.
It’s no secret that preschoolers and kindergarteners are naturally egocentric. Even when playing or interacting with others, many children have difficulty sharing, empathizing, collaborating, and cooperating.
HOMER is here to help you learn eight of the most important social skills for kids, as well as how to incorporate them into your family life.
8 Important Social Skills For Kids
1) Sharing
Sharing is a part of daily life. That doesn’t mean it’s easy!
Sharing is a difficult concept for young children to get behind. Toddlers, preschoolers, and kindergarteners have a particularly difficult time, as they are more focused on their needs and desires than the needs and desires of others.
This is normal. The feeling that something “belongs” to them is typically much stronger than their desire to please others.
Even though it’s hard to share, doing so is critical to a child’s social skill development, as it helps them keep and advance friendships. It’s also a great way to bond and show appreciation.
It’s also a great way to bond and show appreciation.
2) Listening
Active listening is an important skill that even some adults struggle with. Properly deciphering and absorbing information requires significant focus.
We all know this can be challenging for young kids, but active listening can strengthen their receptive language skills (the ability to comprehend spoken language).
Receptive language skills help your child:
- Handle social interactions
- Answer questions
- Understand stories
- Comprehend what they’re reading
- Understand gestures
While developing their social skills, your child will come to see how important it is to actively listen when others are speaking.
Paying attention to what someone is saying and responding directly to their statements or questions is a big part of healthy communication.
3) Following Directions
The cousin of good listening skills would be executing the instructions your child heard — a. k.a., following directions!
k.a., following directions!
Following directions becomes particularly important once your child enters into their school years.
It’s one thing to follow directions at home with their parents where they’re innately comfortable; it’s another task entirely to follow directions from adult authority figures they may not know well.
Your child will learn how listening and following directions overlap with one another. If they listen well, it becomes easier for them to follow directions accurately. And when they follow directions accurately, they’ll often be rewarded for their hard work!
Keep in mind, however, that multi-step directions are challenging for young children. To help them develop the ability to follow directions, give them one direction at a time.
4) Collaborating And Cooperating
Similar to sharing, your child will learn how to move beyond sharing objects to sharing ideas, stories, and work.
With good collaboration and cooperation skills, children will learn that working in a group gives them a chance to express their ideas and listen to the ideas of others. It allows them to see that it can be fun to work on a shared project!
It allows them to see that it can be fun to work on a shared project!
This may sound simple, but for young children, cooperation can often require real effort. It will take time for them to learn to respect others’ opinions even when they’re different.
By working together toward a common goal, kids can advance their sharing skills to include both intellectual and physical (think: cleaning the dinner table with a sibling) feats.
5) Patience
How many times have you heard the cliche, “Patience is a virtue”? Well, we are here to say it one more time!
It’s normal for young children to be impatient. However, patience really is one of the most rewarding social skills for kids.
Patience is critical for many things, including maintaining friendships and relationships and achieving big goals that can only be completed over an extended period of time.
This is where the concept of delayed gratification comes into play. When you help your child understand that good things often take time (not everything in life is microwaveable!), you nurture them into a patient person.
Learning patience takes practice and, you guessed it, patience! Trust that it will come with time (as everything does).
6) Empathy
When we say “empathy,” we’re referring to the traditional definition — the ability to understand and share the feelings of another.
Your child will learn how to appreciate the similarities and differences between their lives and those of people they meet. They will also learn how to empathize with these people, no matter how different they are.
For young children, this can mean small gestures.
For example, if their friend or sibling cries because your child is playing with a specific toy, your child may pause and say, “I know you want to play, too. Don’t be sad. We can take turns!”
But this sense of empathy will likely not appear overnight! Empathy develops over time and across a variety of scenarios.
The easiest way to promote your child’s development of empathy is by showing it in action. When you extend grace to your child often, they will learn how to extend it back.
7) Respecting Boundaries
Some people require different emotional and physical boundaries than your child.
This can be a particularly difficult concept to learn, especially for very young children who receive most of their socialization from within the household.
Likely, if your child is extroverted, they may assume everyone is OK with hugs, questions, or lots of chit-chat. In some cases, they may be right! In others, they may accidentally cross boundaries in their efforts to be friendly.
Teaching your child how to ask permission and identify boundaries helps them establish a sense of respect between themselves and others. The same goes for helping them establish boundaries for themselves.
Let your child know that it’s OK to say no to hugs, kisses, or other displays of affection from someone — no matter who it may be — if they feel uncomfortable. Model this idea by asking questions yourself (“Would you like a hug?”).
When they make their boundaries clear and ask for others to do the same, it will make both parties feel much more at-home.
8) Positivity
Working on positivity can make it exponentially easier for your child to tackle many of the other social skills for kids we’ve mentioned, especially patience, boundaries, listening, and sharing.
With a positive attitude, your child will find it easier to make and keep friends, succeed in school, and achieve their goals.
The easiest way to demonstrate positivity is by modeling it. The more positive you are about your child’s social skill development (including their inevitable slip-ups), the more reassured and positive they will become themselves.
This doesn’t mean you have to be positive all the time. In fact, a healthy amount of honest criticism can be beneficial in helping your child learn to express their feelings.
To do this, start with your own emotions. Let them know how you’re feeling and how you’re managing it in real time if you can. Kids need to know it’s OK to be sad, angry, or mad sometimes and how to handle it.
How To Teach Social Skills To Kids
Now that you know what social skills for kids to include, how do you go about teaching them at home? Let’s take a look!
Normalize Mistakes
Your child should know that you do not expect perfection. There is no way to execute all of these social skills every time, everywhere, without mistakes.
There is no way to execute all of these social skills every time, everywhere, without mistakes.
That is OK! In fact, it’s encouraged. Mistakes are normal; they’re how we learn what went right or wrong.
Make sure you normalize this for your child. If they know all humans learn lessons this way, it’ll be easier for them to push through the sting of a mistake and try again.
Encourage Sharing (Without Violating Boundaries!)
Although sharing is great and should be encouraged, there may be some things that are special to your child that they don’t want to share. This can be especially true of stuffed animals, blankets, or special toys.
This is OK, too! It’s great for your child to set boundaries that you and other children respect. To encourage sharing, try not to force it.
Encouraging without forcing also demonstrates to kids how boundaries can be created, acknowledged, and respected between people.
This will motivate them to share with those around them by taking comfort in the fact that what is special to them has been kept sacred and separate. It will also encourage them to be direct about their and others’ boundaries when it comes to play, school, or emotional issues.
It will also encourage them to be direct about their and others’ boundaries when it comes to play, school, or emotional issues.
Check Their Listening
During social interactions within your own family or outside of it, pay attention to your child’s listening skills. You can observe them to see if they are listening carefully.
Do they seem engaged? Are the asking questions?
And remember it is just as important to listen to your child. This shows them that what they are saying is important and encourages them to listen to you in return.
Think About How You Give Directions
In teaching social skills for kids, the parent or authority figure is responsible for ensuring the directions they give are something a young child can execute successfully.
When giving instructions, be clear, firm, and gentle. As we mentioned earlier, children have a very difficult time executing tasks with many directions at once. Start with one direction at a time that your child can focus on.
When giving instructions, have your child repeat what you want them to do. Only give an additional instruction when the first has been completed. Repeat until the task is complete.
Your child can give you directions, too! That way they have a sense of what it takes to delegate, manage, and execute a task from start to finish.
Give Empathy To Get Empathy
Show your child that you think about other people’s emotions, too! This is less of a teaching moment and more of an authentic display of empathy.
If you see that your child is expressing an emotion, validate it for them. “Oh, I see that you’re excited. I love that you’re so eager and happy to do this!”
You can acknowledge negative emotions, too. For example, you might say, “I know that must make you angry. Do you know how I can tell? What can we do together to make you feel less unhappy?”
This not only helps them feel seen and heard in the moment, but it also gives them a direct example of how to tackle empathy with others in similar situations.
Social Skills For Kids Are Essential
The more your child experiences the benefits of social skills, the more intuitive these skills will become for them. However, all children learn at different rates. With practice (and patience!), we know they’ll get there.
The Learn with Sesame Street app is an effective tool that helps kids learn and develop their social and emotional skills. With the help of their Sesame Street friends, kids learn how to express their emotions, empathize with others, and create healthy relationships. Explore the Learn with Sesame Street app today!
Author
How to Develop Your Child's Social Skills - Child Development
Parents get upset when they see their children can't share a toy or can't make friends. If a child has developed social skills, he can cope with such difficult situations. Socially adapted children know how to make friends, play, start conversations with peers and adults.
Social skill: “The ability to ask”
It can be difficult for a child to approach other children and ask to play with them. In the end, children may answer, “No.” Fear of rejection can prevent a child from even trying, and then they will miss out on the fun of playing with peers, as well as the opportunity to learn something new in the process of playing.
The child is most successful when he first finds out what the peer group is doing, then finds out how he can be useful, and then invites him to join the game. For example, if the children are playing school, he might ask, "Can I be a student?"
How to help your child learn to ask
Watch other children play with your child. Ask him leading questions: “What do you think Sasha uses cubes for? Does he have enough dice to share with you? Maybe we need to look for more cubes so you can play with Sasha?” Invite your child to play with someone else. For him, it will be easier than joining a large group.
For him, it will be easier than joining a large group.
Social Skill: "Conversation Skill"
Children usually need some practice before they learn how to talk - to take turns talking, not interrupting and listening to the interlocutor. Introverted children require someone to start the conversation and keep it going. Extroverts, on the contrary, must learn not to interrupt the interlocutor and give him the opportunity to speak.
How to help a child learn to talk
A good way to develop this skill in a child is through parenting and role play. Show your child how to communicate properly by talking to him as often as possible.
Ask his opinion on various occasions and show genuine interest in what he has to say. If his speech is too long, carefully bring him back to the topic of conversation.
Play games in which everyone takes turns playing their turn. Make sure your child has opportunities for imaginative play. Scripted games: "Let's imagine that ..." will help him see different situations from a different point of view.
Scripted games: "Let's imagine that ..." will help him see different situations from a different point of view.
Social Skill: Understanding the Emotions of Others
To fully participate in social situations and develop relationships with others, children must read the emotions of the peers they play and interact with. Then they will be able to understand them and respond appropriately. This requires confidence from the child, because it is quite difficult to interpret the feelings of another person. If a confident child sees that two of his peers are arguing, he understands that now is not the right time to start the game. Moreover, he may try to defuse the situation. Or, if the child feels their friend is sad, they can offer support.
How to help a child understand people's emotions
First of all, teach your child to identify his own emotions: “You have a smile on your face! You must be feeling happy” or “I see tears on your face. Are you sad?" After that, you can suggest how to apply this skill to others: “Sasha seems angry. What do you think happened?" or “How do you think Anya felt when she fell off the swing? How can we help her?"
Are you sad?" After that, you can suggest how to apply this skill to others: “Sasha seems angry. What do you think happened?" or “How do you think Anya felt when she fell off the swing? How can we help her?"
Social skill: "Self-confidence"
When a child feels good in general, it also has a positive effect on his social skills. If he understands that making mistakes or failing is normal, it is easier for him to express his opinion, ask for help or communicate with each other. If a child is denied something, he does not take it personally and is ready to insist on his own, while not going beyond the bounds of politeness.
How to help your child gain self-confidence
It may seem paradoxical, but children must fail in order to succeed. They need to know that they have to try something over and over again - and in the end, they will succeed. The key to mastering new skills is self-confidence.
It is also necessary to properly praise the child. Instead of just saying, “Good job,” he needs to be as specific as possible: “I’m proud of how hard you worked to solve this difficult problem,” or “Thank you for bringing me the book. I really needed her."
Instead of just saying, “Good job,” he needs to be as specific as possible: “I’m proud of how hard you worked to solve this difficult problem,” or “Thank you for bringing me the book. I really needed her."
Social skills of preschoolers - the development of social skills in children
The development of social skills is a necessary point of education. A child with a high degree of socialization will quickly get used to kindergarten, school, any new team; in the future will easily find a job. Social skills have a positive effect on interpersonal relationships - friendship, the ability to cooperate.
Let's figure out what social skills are.
What are social skills and why develop them?
Social skills - a group of skills, abilities that are formed during the interaction of a person with society and affect the quality of communication with people.
Man is a social being: all our talents and aspirations are realized thanks to other members of the group. Others evaluate our actions, approve or condemn our behavior. It is difficult to reach the pinnacle of self-actualization alone.
Others evaluate our actions, approve or condemn our behavior. It is difficult to reach the pinnacle of self-actualization alone.
That is why social skills are important. They should be developed from early childhood and honed throughout life.
Social skills are a reflection of the child's emotional intelligence, to which educators and teachers assign an important role in the process of personality development. Without this group of skills, a smart child will not be able to apply the acquired knowledge in practice: it is not enough to create something outstanding, you need to be able to correctly convey thoughts to the public.
Sometimes people mistakenly believe that social skills relate exclusively to the topic of communication, communication. In fact, skills include many multidirectional aspects: an adequate perception of one's own individuality, the ability to empathize, work in a team, etc.
Why do we need social skills?
- Regulate the area of interpersonal relationships: the child easily makes new friends, finds like-minded people.

- Minimize psychological stress: children with developed social skills quickly adapt, do not feel sad due to changes in external circumstances.
- They form an adequate self-esteem from childhood, which positively affects life achievements and development in adulthood.
- Social skills cannot be separated from building a successful career: the best specialists must not only understand the profession, but also have high emotional intelligence.
Development of social skills in a child
Social skills need to be developed from preschool age, but older children and even teenagers may well learn to interact with the world.
It is recommended to pay attention to areas of life that bring discomfort to the child, significantly complicate everyday life.
- Friends, interesting interlocutors: the kid does not know how to join the team, he prefers to sit in the corner while the others are playing.
- Verbal difficulties.
 The child does not understand the rules of conversation, is poorly versed in the formulas of etiquette (when you need to say hello, say goodbye, offer help).
The child does not understand the rules of conversation, is poorly versed in the formulas of etiquette (when you need to say hello, say goodbye, offer help). - Problems with the non-verbal side of communication. Such a baby does not recognize the shades of emotions, it is difficult to understand how others relate to him. Cannot "read" faces and gestures.
- Does not know the measure in expressing a point of view: too passive or, conversely, aggressive.
- The child bullies classmates (participates in bullying) or is a victim.
In case of severe moral trauma, one should consult a psychologist: for example, school bullying is a complex problem that children are not able to cope with on their own. The involvement of parents and teachers is required.
In other cases, family members may well be able to help the child develop social skills.
What are the general recommendations?
1. Be patient
Don't push your child to get things done. Let them take the initiative: for example, do not rush to help during school gatherings, let the baby work on the problem on his own. The same goes for lessons and other activities.
Let them take the initiative: for example, do not rush to help during school gatherings, let the baby work on the problem on his own. The same goes for lessons and other activities.
2. Support undertakings
Children's dreams seem trifling to adults, but the initiative turns into a habit over the years and helps to discover new projects, meet people, and experiment.
3. Criticize the right way
When making negative comments, remember the golden rule of criticism: analyze the work, highlighting both positive and negative aspects in a polite way. Commenting on the specific actions of the child, and not his personality or appearance - this will lead to problems with self-esteem.
4. The right to choose
It is important for children to feel that their voice is taken into account and influences the course of events. Invite your child to personally choose clothes, books, cartoons. Ask about ideas, plans: “We are going to have a rest together at the weekend. What are your suggestions?
What are your suggestions?
5. Personal space
Make sure that the baby has a place where he can be alone and take a break from talking. Personal things should not be touched: rearrange without prior discussion, read correspondence with friends, check pockets, etc.
Children, noticing the respectful attitude of adults, quickly begin to pay in the same coin; the atmosphere in the family becomes warm and trusting.
What social skills should be developed in a child?
Let's dwell on the main qualities and skills, the development of which is worth paying attention to.
1. The ability to ask, accept and give help
Without the ability to ask for help, the child will deprive himself of valuable advice; the lack of the ability to accept help will lead to losses, and the inability to provide help will make the baby self-centered.
- Let the child help those in need: for example, a lagging classmate.
- Explain to your child that getting help from friends and teachers is not a shame.

- Show by personal example that mutual help enriches experience: tell how you exchange advice with colleagues, friends.
2. The ability to conduct a conversation and get the right information
Being a good conversationalist is difficult, but the skill is honed over time and brings a lot of benefits.
- Prompt the child for dialogue development options: for example, you can start a conversation with an appropriate question, a request for help.
- Do not leave the child in the role of a silent listener: discussing pressing issues at home, ask the opinion of the baby.
- Support children's public speaking: reports at school, performances, funny stories surrounded by loved ones will add confidence.
3. Empathy
Empathy is the ability to recognize the emotions of others, put yourself in the place of another person, empathize.
This ability will make the child humane, prudent. How can it be developed?
- Start by recognizing the child's feelings - it is useless to listen to people if the person does not feel personal feelings.
 Ask your baby: “How do you feel after a quarrel with friends?”, “Do you want to relax today?”
Ask your baby: “How do you feel after a quarrel with friends?”, “Do you want to relax today?” - After conflicts with classmates, ask your child how the children with whom the quarrel may feel now.
- While watching cartoons, reading books, pay your child's attention to the emotional state of the characters.
4. Ability to work in a team
Many children can easily cope with tasks alone, but this is not a reason to refuse to work in a team. It gives the opportunity to exchange ideas and experience, delegate tasks, achieve goals faster and more efficiently.
- If the child does not communicate with members of the team, try to introduce him to another social group: for example, the lack of communication with classmates can be compensated by a circle of interests, where the child will feel calmer.
- Make the family a friendly team in which the child has his own "duties": for example, do housework, remind parents of upcoming events.
 Any activity related to the well-being of other family members will do.
Any activity related to the well-being of other family members will do.
5. Respect for personal boundaries
The absence of an obsessive desire to interfere in other people's lives is a valuable skill that helps to win people's sympathy.
- Respect the child's personal boundaries: do not enter the nursery unannounced, do not rummage through personal belongings and correspondence, if the matter does not concern the life and safety of the baby.
- If the child violates other people's boundaries (takes toys without permission, asks uncomfortable questions), talk about it in private.
6. Ability to overcome conflict situations
It is difficult to imagine our life without conflicts. The task of the child is to learn how to culturally enter into a discussion, defend his point of view, and not be led by the provocations of his interlocutors.
- Talk about problems calmly, without raising your voice. Do not put pressure on the child with parental authority unnecessarily: the child is a separate person who has the right to an opinion.
- Do not judge people for views that differ from those of your family but do not affect your well-being. Show your child that the world is very different.
- You can demonstrate to children the basics of a civilized dispute, explain what arguments are, etc. It is advisable to teach this child in kindergarten.
7. Self-confidence
Stable and adequate self-esteem is a quality that not all adults possess.
It is formed under the influence of many factors: relationships between parents, the role of the child in the family circle, the characteristics of the environment that surrounded the child in early childhood.
It is important that the child does not grow up to be either a narcissistic narcissist with fragile self-esteem, or an overly shy person. How can you help your child find balance?
- Praise your child for personal progress: to receive a compliment from parents, it is not necessary to win prizes in school competitions.
Learn more