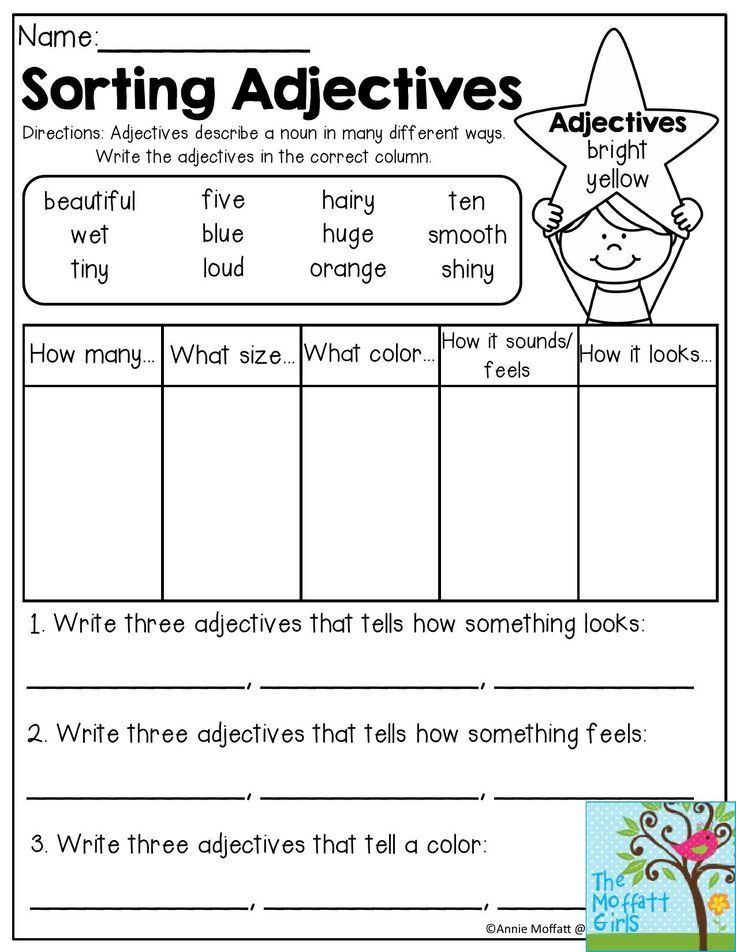
What is your reading level
How To Determine Your Child’s Reading Level And Choose The Best Books
When you sit down to read a book, you want to enjoy the story in front of you. The same is true for your child. That’s why uncovering your child’s reading level is an important step in fostering their love of words from a young age!
Consider the different factors that allow kids to enjoy the books they read. For example, does it tie into their interests, and is it slated as an appropriate option for their level? By answering these questions, you can make sure they’re reading books that are just right for them!
If your child is in school, you’re probably no stranger to jargon like “reading level.” But what exactly does Lexile Framework, Guided Reading Levels (GRL), or Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA) actually mean?
Additionally, if your child is just starting to read on their own (or already reading independently) and is learning from home, how can you figure out what reading level is right for them? If any of these thoughts have crossed your mind, you’ve come to the right place.
We’re here to answer your questions so you and your child can sit down and enjoy a good book together!
What Is A Reading Level?
A reading level is simply a measure of your child’s ability to read text. It reflects how well your little one can read independently. Importantly, reading levels help you choose books that are a good match for your child while still presenting a challenge.
Keep in mind these levels are meant to be helpful, not stressful. They don’t limit your child, but, rather, help them blossom into a fluent, excited reader.
When your child reads books that are appropriate for their current reading level, it boosts their confidence so they can truly enjoy reading! Also, knowing what level your child is at allows you to work with them to improve their skills.
That being said, it’s important to remember that children are unique and develop differently. Comparing your child to their peers isn’t necessarily the best approach when trying to assess their reading ability.
Why Is Determining Reading Level Important?
It’s helpful to determine your child’s reading level so you can find books that are appropriate for them to read on their own: not too difficult but challenging enough to encourage growth.
Reading level classification is a convenient tool you can use when searching online or at the library. And when you provide books that are on your child’s level, you create excitement and build their confidence, which can lead to a lifetime love of learning and reading!
If you’re looking for ways to help your little one read at the best level for them, Our new app HOMER Learn & Grow has a Stories section that gives age-appropriate story recommendations!
This is a great resource that takes your child’s specific interests and recommends stories just for them. What’s more, your child can choose to read along or read on their own.
How Is Your Child’s Reading Level Measured?
Your child’s reading level is usually measured at their school in first or second grade, and we’ll show you how that’s done.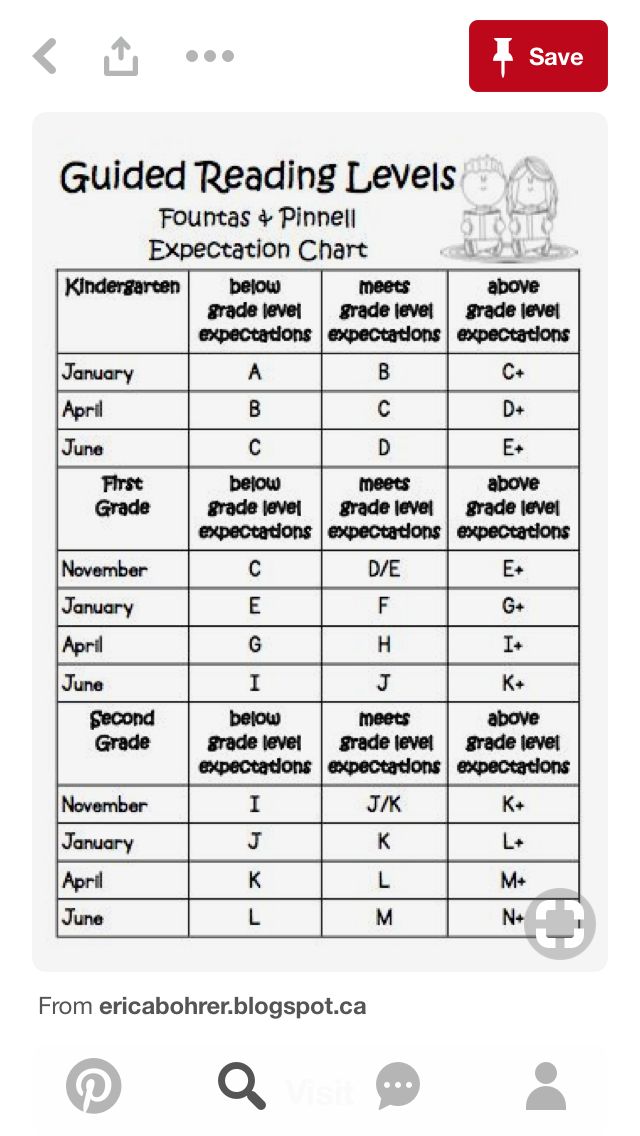 Here’s a tip: since your child’s teacher knows their reading level, consider asking the teacher (or the school librarian) for books your child can read at home.
Here’s a tip: since your child’s teacher knows their reading level, consider asking the teacher (or the school librarian) for books your child can read at home.
Don’t worry if your child isn’t in school yet or if they’re homeschooled. We’ll show you how you can measure their reading level at home, too!
Before we dive in, it’s important to note that we think of books for kids at three levels: independent reading, instructional reading, and frustrating to read.
As the names indicate, independent reading books are ones a child can read with ease and without support from an adult.
Instructional ones are the books just above independent that teachers might use to stretch a child’s reading as they offer support while the child makes that next step. Finally, frustrating books are too hard for a child to read even with adult guidance.
Now that you have an idea of how to think of the different books your child might encounter, let’s talk about the tools used for determining or describing reading levels.
Lexile Framework For Reading
Lexile Framework For Reading is an educational tool that ranks books by order of their difficulty using a scale called a Lexile. Usually, your child’s teacher will determine their Lexile reading level and then choose books that have a matching score.
The Lexile score, or measure, describes your child’s reading ability and matches them with books and other reading materials. This measure ranges anywhere from 0L to 2000L.
Kids are encouraged to read within their Lexile “range” — 50L above to 100L below their actual level. For instance, if your little one is reading with a Lexile measure of 500L, they would read books ranging anywhere from 400L to 550L.
Using standardized assessments, schools will often measure a child’s reading level several times a year to help them select books that are appropriate for independent reading.
Guided Reading Levels (GRL)
GRL is a guided reading system used in some schools.
To determine reading levels using GRL, children sit one-on-one with their teacher and read from a book that’s considered standard for their grade level — a “benchmark” book.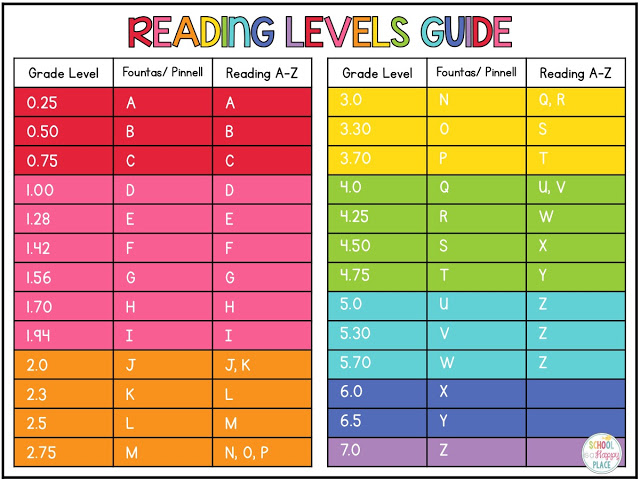 GRL books range from A to Z with A being the easiest.
GRL books range from A to Z with A being the easiest.
While reading these books, the teacher will take notes on any missed words and ask comprehension questions, such as, “When did the story take place?” or, “What was the problem in the story?”.
Through guided instruction, the teacher will gradually move children into more difficult books.
Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA)
DRA is a standardized reading test given by teachers or reading specialists. As with GRL, children sit individually with the test administrator and read a book.
Several factors are taken into consideration to determine reading level, including:
- Reading comprehension
- Phonemic awareness
- Fluency
DRA books are labeled with an A for the easiest books and then move into a numerical grading system. The levels range from 1 to 80 with 1-3 representing a kindergarten reading level and 80 representing an eighth-grade reading level.
Once a child has a DRA or a GRL level, a teacher or parent can search for the reading level of any particular book and can usually discover either the Lexile, DRA, or GRL of that particular text.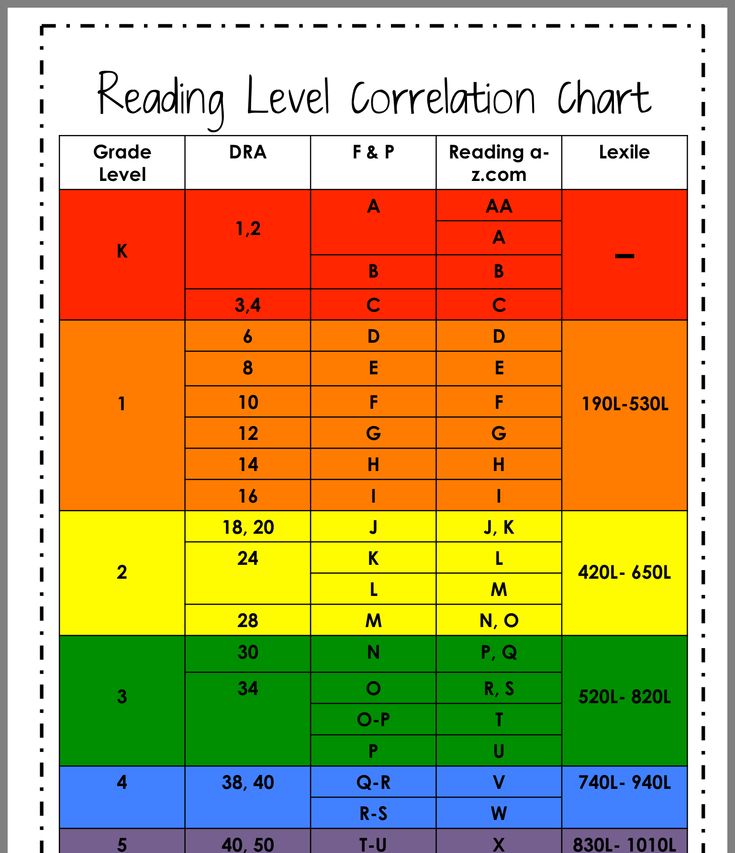 Here’s a chart for your reference.
Here’s a chart for your reference.
At-Home Reading Levels
If you’re looking for a way to find out your child’s reading level without using any of the methods listed above, you might try the five-finger rule.
For the five-finger rule, choose a book and flip to any page. If your child seems to have trouble reading more than five words on the page, it’s a good indicator that the book is too advanced for them.
To be sure, though, you can have your child try another page, especially if they seem eager to read a particular book.
This can be a helpful strategy, but it’s OK to let your child try a book and see how the reading goes. If a book is too hard, most kids will figure that out — and there is nothing wrong with reading books that are too easy!
Sometimes a child may be interested in a book that’s a little too hard for them. If this happens, we encourage you to read aloud to your child. You can also read together by alternating pages, paragraphs, or sentences.
It’s important not to completely avoid books that may be a little above your child’s reading level.
Even if your child struggles a bit to read them without assistance, these books can still be beneficial in helping build their vocabulary, improve comprehension, and increase general knowledge — not to mention, encourage their love of reading!
When your emerging reader seems overwhelmed by one book, you can always give the five-finger rule a try with other books until you find the right match. And if your child is particularly interested in a topic, you can always read the book to them and stop on words you know they can read.
Also remember that when a child is really enjoying a book and highly motivated to read it, they will read at a higher level than if the material is not as interesting to them.
Tip: Most libraries and bookstores have books arranged by reading level so you can easily choose the best one for your emerging reader!
Feel free to ask librarians and knowledgeable staff at bookstores to offer suggestions. You could even say something like, “My child happily read a Clifford book; can you suggest others at the same level?”
You could even say something like, “My child happily read a Clifford book; can you suggest others at the same level?”
How To Help Your Child Become A Stronger Reader
As we mentioned earlier, you can easily determine your child’s reading level at home so that you can help them choose books that are just right! We suggest incorporating some of the tips below to help your child become a stronger reader.
Start With Clues
- Is your child using “sounding out” techniques to figure out unknown words?
- When your child reads, are they getting tripped up by sight words — common words that are hard to sound out?
- Is your child using pictures to help them understand what is written on the page?
- Is your child using context clues to figure out what word makes sense to come next as they read sentences?
Check Vocabulary
- Play games with your child to see what words they know. For example, say a sentence and point out one word in the sentence.
 Then ask them if they can come up with a different word (synonym).
Then ask them if they can come up with a different word (synonym). - Play synonym games to see what words your child knows. For example, challenge yourselves to think of 10 or more ways to describe speaking (shout, whisper, mumble).
While you’re talking with your child, describe something specific from your day. Make sure to use interesting adjectives, and don’t hold back from using sophisticated vocabulary when talking with your child.
You can help your child’s vocabulary grow through day-to-day conversations and activities!
Ask Comprehension Questions
Understanding what they read is an important part of your child’s reading journey.
- To check for reading comprehension, we suggest pausing every other page to talk about what you’ve just read. Make this a natural reaction to the story, like you’re thinking aloud about the story or characters, so that it doesn’t feel like a test.
- Consider encouraging your child to act out and retell the story (for younger children).
- Try discussing themes/lessons with your child (for older children). Remember: this isn’t a test, but a conversation between book lovers!
Talk To Your Child
When most people implement strategies to help their children improve their reading skills, they often forget about the importance of verbal communication. It’s essential to talk to your child frequently in short and simple sentences.
This includes singing songs, telling them wonderful stories, reciting fun nursery rhymes, and describing the world around them. All of this exposes children to lots of different words. It also helps them learn that language is a powerful tool for communication.
Discover Your Child’s Favorite Books
- Children often choose books that are a little below their actual reading level. At home, this is a good thing. It keeps reading fun and exciting!
- We recommend choosing books that interest your child — with a certain character or activity they like — so they’re curious and excited about reading.
Reading books your child enjoys together can encourage their love of reading. And letting them read those same books to you can boost their confidence over time.
Together, these two activities increase your child’s fluency and reading enjoyment!
Create A Reading Corner
Establishing a reading corner in your house can benefit your child. The setup doesn’t need to be elaborate. This can be a simple, quiet, private area where your child can confidently read independently or with you.
It’s also great for the spot to be well-lit and filled with lots of books your child enjoys reading.
Is Reading The Same Book Over And Over OK?
Just like you might pick up an old favorite book to read, your child may do the same, and that’s OK! At least you know they’re enjoying a good book and the process of reading!
Rereading books can have many benefits for a child, including:
It allows children to get more from the text. Have you ever developed a deeper understanding of a story after rereading it? That’s because the more you engage with a story, the more you can take away from it.
You can pick up on new information, establish connections between yourself and some of the characters, and even improve your understanding of the overall story.
Similarly, allowing your child to read their favorite books for the second, third, fourth (or more) time will enable them to get more from the story.
It also allows for bonding. Did you know that rereading books can help bring your family closer together?
Many of us remember a couple of books that our family read together regularly. This can be a holiday book or a favorite story. Rereading is a great way to get the whole family involved, as everyone can take turns reading and connecting on the same story.
What’s more, reading familiar books can actually help develop a young reader’s fluency. It allows them to learn the words and helps them become familiar with narrative structure or storylines (i.e. beginning, middle, and end), which builds reading comprehension later on.
So feel free to let your child choose the same book over and over!
FAQs About Reading Levels
What Reading Level Should My Child Be In Each Grade?
It’s challenging to answer this question because each child is different and will naturally develop at their own pace. For example, just because your child’s friend has started reading fluently doesn’t mean your child will be able to do that yet.
For example, just because your child’s friend has started reading fluently doesn’t mean your child will be able to do that yet.
While no parent wants their own child to be a little behind compared to their peers, putting too much pressure on them to “catch up” might actually have an adverse effect. In fact, they might feel overwhelmed by the pressure and develop a negative attitude toward reading.
It’s also important to note that there’s no direct link between a certain Lexile measure and a specific grade level. When using any of the reading level measures we mentioned, remember that they are an estimate of a child’s performance and shouldn’t be interpreted literally.
Also, if you’re really concerned about your young learner’s development, you can always address those concerns with their teacher or another professional. They can offer tips and advice on how to best work with your child.
Finally, remember to be patient and positive no matter what. With lots of time and effort, your child will develop a lifetime love of reading!
Who Can Help Me Choose Books That Match My Child’s Reading Level?
The best place to start is to consult your child’s teacher. They will have the expertise to guide you in buying the right books for your child.
They will have the expertise to guide you in buying the right books for your child.
It’s also possible for you to look up most books online and find their reading levels. Furthermore, for beginner readers, there are publishers who label books in stages with age and/or grade suggestions attached.
If you’re homeschooling, you can also reach out to your local librarian or bookstores. As people who spend each day surrounded by books, they often have knowledge on this topic and may be able to recommend a few relevant books in your child’s reading level.
What If My Child Is Reading At A Lower Level?
The last thing a parent wants to hear is that their child’s reading level isn’t on par with their peers. But what can you do if, from the assessment used at your child’s school, you find out that your young learner is reading below the average grade level?
Firstly, it’s important not to panic. As mentioned earlier, kids develop reading skills at different stages of their development.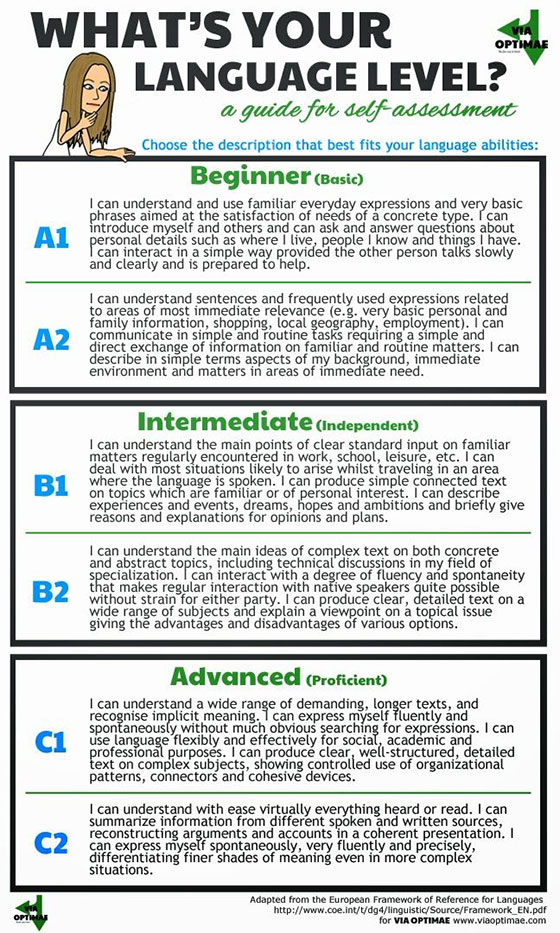 Some children might be early readers, while others may take time to get there.
Some children might be early readers, while others may take time to get there.
The most effective way to help your child improve their reading level is by continuing to encourage reading at home. While reading, remember to discuss the content to ensure comprehension.
Reading For Fun
From assessments to the five-finger rule, determining reading levels varies across the board. No matter which method you choose, remember these measurements are meant to be helpful and encouraging, not stressful and limiting.
Keep this in mind when assessing your young learner. You don’t want your child to sense any stress about their abilities, as this might overwhelm them and have an adverse effect on how they view reading.
While reading is an essential early learning (and lifelong) skill, you want your child to LOVE reading and not only view it as a test of their intelligence.
At the end of the day, the way reading makes your child feel is more important than their reading level. Each child learns in a way that’s special and unique to them.
Each child learns in a way that’s special and unique to them.
The HOMER Road To Reading
The road to discovering how to read can be a fun ride, but sometimes it’s bumpy. This is why we’re more than a learning program. We’re your learning partner.
If you’re looking for a resource to help develop your child’s love of reading and learning, consider taking a look at the HOMER Learn & Grow app. It’s full of stories curated based on your child’s interests!
When your child develops a love for reading, they’ll move up to the next level before you can say “Developmental Reading Assessment”!
Author
Reading Level: Determine Your Child's Reading Ability
Understanding the principles of reading level to your child’s age and grade is essential to a healthy developmental reading process. Leveled reading considers various factors.
What is a Reading Level?
Reading level is the measure of a child’s level of comprehension of text. This is a function of the child’s vocabulary and processing speed. The tool is used by instructors, librarians, and parents to better tailor instruction for children. So they don’t have to struggle through too much material before they are ready.
This is a function of the child’s vocabulary and processing speed. The tool is used by instructors, librarians, and parents to better tailor instruction for children. So they don’t have to struggle through too much material before they are ready.
Different students have different reading levels, and getting your child on the right track to learning can save a lot of time and frustration.
It should be noted that reading levels don’t determine your child’s intelligence or limit them. This is a tool to help your child grow into a more confident and fluent reader.
Is it Important for a Child?
Knowing your child’s reading level will help you choose the books appropriate for your little ones to make reading fun and progressive. As a result, children will enjoy reading the book and build confidence, leading to a lifetime love for reading.
The right books will challenge enough to encourage growth without overwhelming the child. Moreover, it will allow you to help them improve their reading skills to move to the next level.
Each child learns and develops differently. So, when it comes to measuring your child’s reading ability, it is best not to compare them with their peers.
Tools to Evaluate Reading Level
There are many different tools for determining the reading level, and depending on the situation, one might be more useful than the other. You should also keep in mind that reading level is just an estimate.
If a child reads beyond the level this tool estimates, it doesn’t mean they are smart or fast readers. It just means they’re reading more challenging text.
Photo by Josh Applegate on UnsplashFollowing are some of the prevalent tools to determine reading levels.
Guided Reading Level (GRL)
GRL is a reading level assessment tool designed specifically for teachers in a classroom. It is a set of consistent guidelines and objective criteria used to assign a reading level to a passage of text.
For the GRL test, children and the instructor sit one-to-one.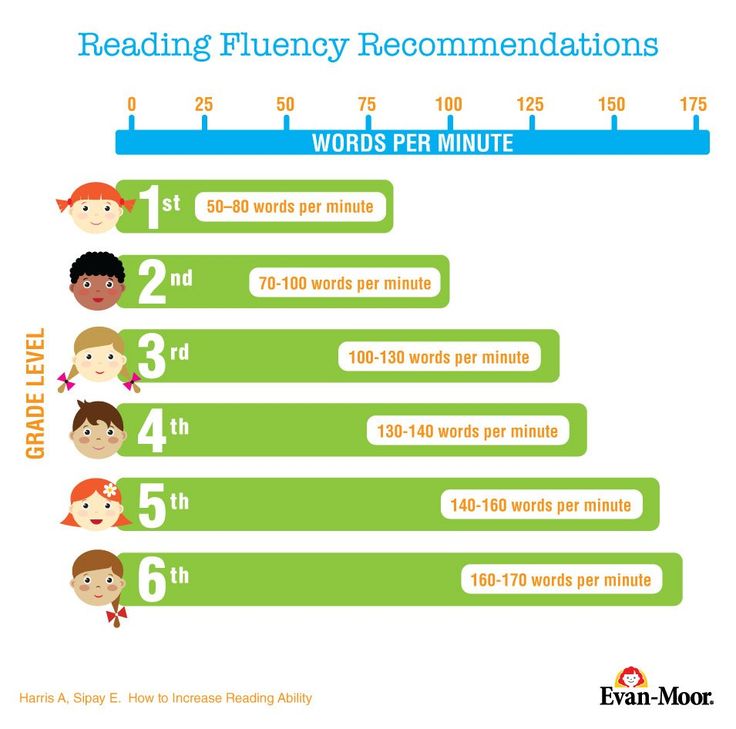 The child is asked to read a benchmark book standard to their grade level. The system assigns an alphabet to the books based on difficulty. Label A is for the easiest books and all the way through Z for the difficult ones.
The child is asked to read a benchmark book standard to their grade level. The system assigns an alphabet to the books based on difficulty. Label A is for the easiest books and all the way through Z for the difficult ones.
During the test, the teacher assesses the student’s reading comprehension through questions and takes notes of any missed words.
GRL may not be the best reading tool for parents because it is based on finely analyzing a text. However, it’s an excellent tool for teachers to use when evaluating the reading level of their students.
Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA)?
Developmental Reading Assessment is a standardized test to determine a child’s ability to understand and use words in meaningful ways. DRA is typically used to identify whether a child is on grade level and then provide feedback on the child’s current literacy skills.
Like GRL, children attend the DRA test by sitting individually with a reading specialist or instructor to read a book.
Several factors are considered to determine the level in this test, such as reading comprehension, phonemic awareness, and fluency.
The DRA books start with a label A as the easiest, then switch to a numeric system counting from 1 to 80.
Kindergarten reading level falls between 1-and 3, whereas level 80 stands for eighth-grade reading.
Lexile Framework?
The Lexile framework uses a Lexile scale to rank books in terms of increasing difficulty. Educational institutes use this tool to assess a child’s reading ability by taking a standardized test.
The test scores are converted to Lexile measures to choose appropriate books of matching scores. Lexile levels are indicated with a number and the letter L following it. The measure starts from as low as 0L to the maximum measurement being 2000L.
Children are motivated to read between 100L below to 50L above their Lexile range. For instance, If a child reads at a Lexile measure of 600L, he should be able to read books ranging from 500L to 650L.
Schools will measure a child’s reading level multiple times a year to graph their progress. They choose appropriate books to encourage the kids to do independent reading.
Conclusion
Kids are often told they need a specific reading level to perform well academically or even socially. So, how can a parent determine their child’s reading level?
This article covers the basics and provides you with the tools to identify your child’s reading needs to best support them. With this information, you may set your child up for success with the right texts to help them grow.
Frequently asked questions
What reading level should a 1st grader be at?
Reading levels for a first grader should range from 3 to 12. Reading levels indicate they are near the top of their class, but there is always room for growth. It is possible that your child falls below or above the range in some cases. Their reading will be enhanced by practice and proper tutoring.
What level should my 6 year old be reading at?
At this age, there is a wide range of reading levels for children.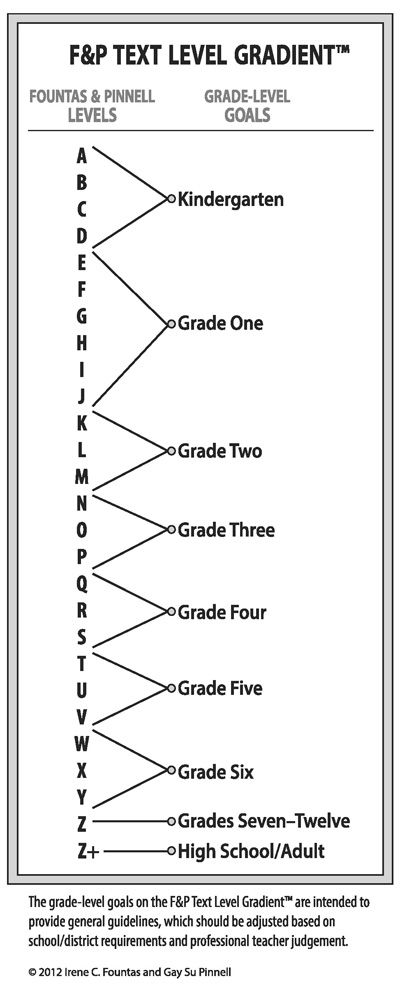 At the age of 6, though, most kids are learning to string letter sounds together to read short vowel words.
At the age of 6, though, most kids are learning to string letter sounds together to read short vowel words.
What a 6 year old should know academically?
- Make time
- The concept of numbers is understood.
- Day from night and left from right.
- Repetition of three numbers backwards is possible.
What level of reading should a 5 year old be on?
Also, 5 year olds should be able to read a few sight words. Children usually learn common words like the, come, some, many, from, where, were, etc. Before learning lesser common sight words like build, beautiful, group, thought, etc. Our shop offers kindergarten level books.
What is a good reading level?
Additionally, you can see what levels your child is enjoying and reading, as well as whether he is moving forward with his choices over time. Most students tend to read books at the appropriate reading level from 100L below to 50L above the Lexile® measure.
At what age should a child read fluently?
Children attain fluency when they have learned how to recognize words automatically, accurately, and quickly. 7 to 8 are most likely to develop this disease. If a child can read fluently, their brain is capable of performing multiple tasks at once.
7 to 8 are most likely to develop this disease. If a child can read fluently, their brain is capable of performing multiple tasks at once.
What reading level should a 2nd grader be on?
Your child should read 50-60 words per minute at the beginning of the school year and 90 words per month by the end of the year. To test this, give your child a story from her reading list that she hasn’t read but will pique her interest.
What reading stage should a 7 year old be on?
| Stage 1 | 3.5 to 4.5 years |
|---|---|
| Stage 6 | 6 to 6.5 years |
| Stage 7 | 6.5 to 7 years |
| Stage 8 | 7 to 7.5 years |
| Stage 9 | 7.5 to 8 years |
What age is a Level 3 reader?
7-9 (Level 3) More complex stories, challenging vocabulary, and engaging plots for the single reader. The paperback and hardcover editions are available.
Should my 7 year old be reading?
By age seven, most children have learned to read, but they are still building confidence in their fluency, vocabulary, and reading comprehension skills as they grow into strong readers.
What is the average reading level for an 8 year old?
| Grade Level and Age | Words-Per-Minute |
|---|---|
| 3rd Grade (Spring) 8-9 years old | 107 – 162 wpm |
| 4th Grade (Spring) 9-10 years old | 123 – 180 wpm |
| 5h Grade (Spring) 10-11 years old | 139 – 194 wpm |
| 6th-8th Grade (Spring) 11, 12, 13, 14 years old | 150 – 204 wpm |
How do you determine your reading level?
- Take a few paragraphs as your base.
- Write the average number of words per sentence. If you multiply the result by 0.39, you will get a result.
- Put the number of syllables in words by 11.8, then multiply by 12.8.
- We’ve combined the results of both studies.
- Subtract 1559
What level should a 7 year old be reading at?
Level 7. A recommended reading age range of 6 to 7. Reading complex sentences is fairly fluent for children, taking note of punctuation. In their opinion, they use expression and do not rely on illustrations.
In their opinion, they use expression and do not rely on illustrations.
Are reading levels important?
Reading levels are integral to a comprehensive reading assessment without a doubt. Reading levels are a good way to measure children’s comprehension and decoding skills.
What are the different reading levels for kids?
Reading level systems are guided reading level, accelerated reader, developmental reading assessment, and Lexile measurement level.
Read speed test. Online simulator for developing reading speed and awareness skills in 2021!
Reading speed is an important indicator not only for schoolchildren, who regularly check it. It is very important for an adult in the modern world to be able to navigate in huge flows of information. A reading speed test will help you determine your current level and see if you need to work on improving this skill or if you are reading fluently enough.
Content
1. How to check reading speed?
How to check reading speed?
2. How can I check my reading speed myself?
3. How to test a child's reading speed?
4. What reading speed is considered normal for adults and children?
5. How to choose the right text to test reading speed?
6. The book "Everything you wanted to know about speed reading, but were afraid to ask"
How to check reading speed?
The easiest way is to take a stopwatch (you can use the application on your phone), a text to check your reading speed and read it at a normal pace for one minute. It is important that the text is non-technical, does not contain highly specialized terms and concepts, and is not familiar to the reader. The text should not be too primitive. The testee must see the text for the first time so that the results are not artificially inflated.
But what do you care about speed, if you don't understand with what awareness you absorb the text? :)
A much better way to find out your reading speed is to take a free online test. To do this, sit back, enter your name in the form above, press the button and you will immediately see the text that you need to read, slowly, trying to understand everything that is written.
To do this, sit back, enter your name in the form above, press the button and you will immediately see the text that you need to read, slowly, trying to understand everything that is written.
When the entire text is read - click on the button at the very bottom. The program will automatically determine the reading speed and prompt you to answer a few questions to understand the degree of assimilation of the material. As a result of testing, you will receive not only the result of your reading speed and awareness, but also recommendations for improving your reading technique in the format of the book "Everything you wanted to know about speed reading, but were afraid to ask." Enter a name. Click the button and find out your real reading speed. Have a good day.
How can I test my reading speed myself?
We have prepared for you a tool with which you can independently check the speed of reading. Our tool include a certain amount of text that you need to read as quickly as possible. You will then have the opportunity to answer a series of questions about the text, allowing the program to determine your level of understanding. Based on the data received, a result and a certificate are issued. This certificate can be shared with your friends on social networks and challenge them to a battle to test the speed and awareness of reading :).
You will then have the opportunity to answer a series of questions about the text, allowing the program to determine your level of understanding. Based on the data received, a result and a certificate are issued. This certificate can be shared with your friends on social networks and challenge them to a battle to test the speed and awareness of reading :).
If you want to do it yourself, you can do it according to the following scenario. A text of medium complexity is taken, located on one sheet. You will need an assistant who will keep track of the time and will be able to test the level of your understanding of the information. Check algorithm:
Simultaneously with the start command and the start of the stopwatch, you begin to silently read the text.
When the text is finished, you say stop - time stops.
Then you need to answer a few questions regarding the content (reading speed implies a full reading comprehension).
The last step is to count the words in the text and determine the average number of words per minute (words in the text can be counted before reading).
This is the certificate you can get based on the results of passing the test
How to check the reading speed of a child?
A child's reading speed can be tested in a similar way. The child should read aloud, at least in elementary school. Then you can switch to the usual way of checking for adults.
Schools often test reading skills by counting the number of words read per minute. This gives a small error, since words come in different sizes, but a similar verification method can also be used.
What reading speed is considered normal for adults and children?
The average reading speed for an adult is 200-230 words per minute. Below average, but an acceptable rate is 150-200 words per minute. Adults who read more than 230 words per minute are considered fast readers. For the speed reading technique, the optimal speed is 350-400 words per minute.
In children, the indicators are dynamic and change depending on age. Approximate norms used in elementary school:
Approximate norms used in elementary school:
20-30 words per minute for first grade;
45-60 words per minute for second grade;
70-85 words per minute for third grade;
90-125 words per minute for fourth grade.
How to choose the right text to test reading speed?
The criteria for selecting text to test reading speed are identical for adults and children. The only difference is the volume and complexity of the information. The text must match the following parameters:
medium difficulty appropriate for age;
the absence of specific unfamiliar words or their minimum number;
no dialogs;
location on one page;
large, comfortable to read font;
lack of pictures and other distracting elements.
In our tool for testing reading speed and comprehension, we tried to take into account all these factors so that the resulting tool would be convenient for both adults and children. At the same time, he gave a fairly clear answer to the question about the real reading speed.
It should be remembered that reading speed is a variable parameter, which decreases if a person rarely sits down at a book, and increases with constant reading. There are many special techniques aimed at significantly increasing the speed of reading text information.
Everything you wanted to know about speed reading but were afraid to ask test. So don't waste a second,
go back to the very top of the page and go take the test!Reading speed test online is simple, convenient and fast
We have already written so much here about how to correctly measure your reading speed, achieve awareness and interpret the results, that every second of delay before you pass the online reading speed test and receive a personal certificate is just like death. Return to the very beginning of the page, enter your name in the field under the video and go to the enchanting world of unfamiliar texts and tricky questions :).
📖 Reading speed Q&A section
📕 What formula is used to calculate reading speed?
If it’s very short, then the formula for calculating the reading speed is as follows: V = (Q / T) x K.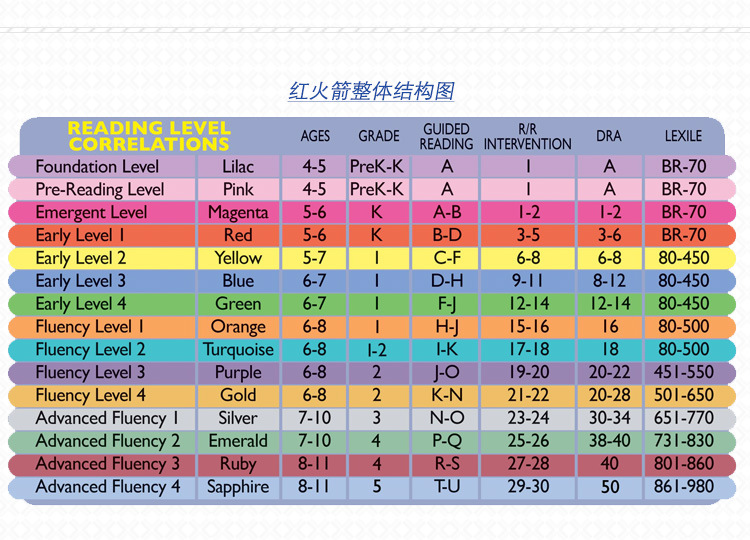 This formula allows you to get a real figure for reading speed with a correlation to the coefficient of meaningfulness. You can read more about the formula here in this article .
This formula allows you to get a real figure for reading speed with a correlation to the coefficient of meaningfulness. You can read more about the formula here in this article .
📗 What books do you recommend reading to develop speed reading?
We have compiled a list of the most useful books for the development of speed reading and posted it in a separate post on the blog. The list is constantly updated and gives an idea of the main books with which you can develop speed reading skills.
📘 What if I want to increase my reading speed?
You can start by learning the theory, or you can download our workbooks , which we have created especially for those who who wants to start learning speed reading. There are two of them: one notebook for adults, the second for children. Contains some theory and practical exercises designed for several weeks of regular classes.
📙 How to check a child's reading speed?
The reading speed test, which is located on our website, is suitable for both adults, as well as for children. We specifically tried to choose mostly literary texts that will be easy to read. to understand the child. Just go to the reading speed test page from the link above, enter child's name and start reading. Then the program will do everything for you.
📔 I want to check my reading speed online for free. How to do it?
Easier nowhere. The tool, which is located at https://bukva.info/rapid/ , was created just for this. You just enter your name, read the text and answer the questions. The program monitors the speed of your reading and its meaningfulness. After answering the questions, you will receive a certificate with your result. The certificate can be shared with friends in social networks :).
📓 What is the "Read Fast" project?
Read Fast is a project dedicated to the problem of fast and conscious reading. We believe that you can read 3-4 times faster. However, the quality of memory reading material will only increase. Let's try together :).
upper, pre intermediate and advanced
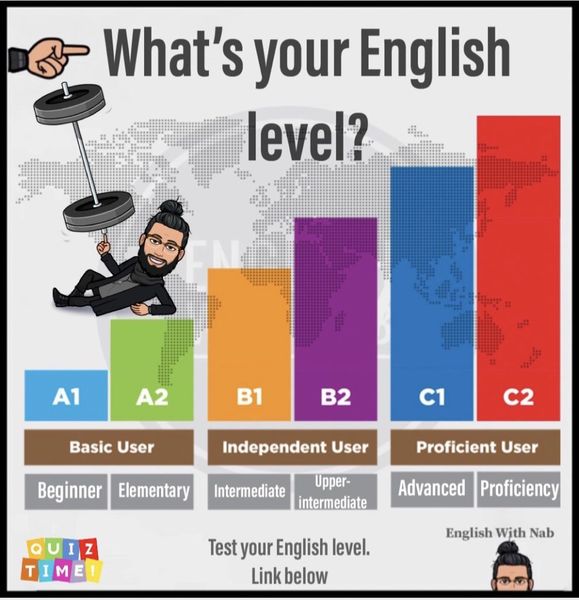
Gone are the days when the level of foreign language proficiency was determined subjectively, according to one's own understanding. In the era of globalization, the need for an objective assessment of this level has become vital, it is necessary to determine the levels of knowledge of the English language. Therefore, the formation of the Common European Framework (CEF) - the Common European System for Evaluating Knowledge of Foreign Languages - was a long-awaited response to the current requirement. Now it is the most popular measurement system in Europe, which determines how well people know a foreign language. It has established clear and precise standards of evaluation. The CEF system is accepted in all European countries and serves as a guideline for educational institutions where they study foreign languages, regardless of the teaching methodology. Since English is the most demanded language in our time, most of those who pass the test for their language proficiency deal primarily with English.
It has established clear and precise standards of evaluation. The CEF system is accepted in all European countries and serves as a guideline for educational institutions where they study foreign languages, regardless of the teaching methodology. Since English is the most demanded language in our time, most of those who pass the test for their language proficiency deal primarily with English.
CEF has divided the level of language proficiency into six gradations, which are in ascending order, from the most basic to the most advanced. At each level, the knowledge and skills that you need to have in order to correspond to it are determined.
Beginner level
This is the very initial stage in learning English, when a basic vocabulary is formed. It is important here to master the vocabulary that will help you communicate on a daily level. Beginner means that a person can talk about food, work, knows dates, dates, can talk about how he feels, about people and places, answer the question “what time is it?”, keep up a simple conversation about travel. At this level, knowledge of 500-700 words is sufficient.
At this level, knowledge of 500-700 words is sufficient.
Grammar rules, reading and writing skills are studied at the elementary level. At this level, there is a process of learning this and the skills to apply the acquired knowledge in different life situations.
Level Elementary
At this stage of mastering the language, a person can maintain a short conversation not only about himself. Pronunciation is also important here, it should be understandable to everyone present. This level of language proficiency implies that a person can use it in any English-speaking country in such a way as to be understood and understand what is said to him.
Listening is the most difficult part of learning a foreign language. Elementary assumes that the learner understands the key points of what is being said. Including he can talk on the phone. Mastering reading at this level involves capturing the main ideas of the text. As for writing, here the level allows you to write short messages, for example, a postcard, a request, a story about yourself.
Level Pre-Intermediate
As you continue to learn English, pre-intermediate is the next required level. This is a satisfactory level of mastery, allowing you to speak on personal and abstract topics with intelligible pronunciation. If something is not clear, the person can clearly explain what exactly is causing him difficulty. On everyday topics, the student can already communicate quite confidently, clearly expressing his thoughts and feelings.
When reading, he understands what is being said in this text. At the same time, he distinguishes intonation, understands where the stresses are. Mastery of writing reaches a level that allows you to build a sentence grammatically correctly, clearly formulate your thoughts, express your attitude to a variety of things. This means that a person is able to write even a formal letter, an apology or a petition, not to mention informal letters and messages and postcards.
Level
Intermediate - the level of English, which allows you to express your opinion in a simple form, understand someone else's, identify attitudes, context. If something is unclear, ask for clarification and understand it. The pronunciation is clear and understandable to others. At the Intermediate level, a person may already be using intonation and stress to express how they feel.
If something is unclear, ask for clarification and understand it. The pronunciation is clear and understandable to others. At the Intermediate level, a person may already be using intonation and stress to express how they feel.
By ear perceives the main ideas of what was said, its content and general meaning. A person already distinguishes between the pronunciation of a native speaker and a foreigner who has mastered the language in the learning process, hears an accent and can even distinguish how strong it is.
Reading English text, understands its meaning and some nuances. Can competently write any appeal, including filling out declarations, questionnaires, writing official letters, etc. The level of knowledge of the language allows you to even write stories, correctly state events, describe anything. Since the general meaning of what was said or written is already clear, a person can easily comment on this information both orally and in writing.
Upper-Intermediate Level
Upper intermediate - a level characterized by good command of the language. Depending on the situation, they may use a casual or formal style of conversation. They can carry on a conversation with two or more people without difficulty in understanding the general line of conversation. Having mastered the Upper Intermediate level, he understands that he has made some grammatical or lexical errors and is able to correct them during the conversation. Mistakes in pronunciation are also recognized.
Depending on the situation, they may use a casual or formal style of conversation. They can carry on a conversation with two or more people without difficulty in understanding the general line of conversation. Having mastered the Upper Intermediate level, he understands that he has made some grammatical or lexical errors and is able to correct them during the conversation. Mistakes in pronunciation are also recognized.
When listening, a person distinguishes regional accents of the language, easily speaks on the phone. He distinguishes between the styles of writing, reads the press and understands what it is about, can read any text and immediately understand its main idea. Mastering the letter allows you to write not only letters of various levels, but also simple instructions. Syntax is no longer a problem. A person can write brief analytical reviews.
Advanced level
Advanced - the level of English, which allows you to say that a person is fluent in English.